| 69c. From Jesus to Christ (single)
04 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 69c. From Jesus to Christ (single)
04 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
As our subject is arousing the very widest interest everywhere, it seems justifiable to approach it from an anthroposophical standpoint. The manner in which it is being discussed and brought to public notice is, of course, very far removed from this point of view. If it is true that Anthroposophy is little understood and liked to-day, it may be said at once that the treating of this theme in an anthroposophical manner presents peculiar difficulties.1 It is unusual in our age for the feelings to be so attuned as to appreciate anthroposophical truths bearing on the more obvious matters of spiritual life, and it is directly repugnant to our present-day consciousness when a topic has to be discussed which calls for the application of Anthroposophy or Spiritual Science to the most difficult and holiest subjects. It may be safely affirmed at the outset that the Being around Whom our thoughts are about to centre has been for many centuries the turning point of all thought and feeling, and moreover that He has called forth widely differing judgments, emotions and opinions. Countless as are those who for centuries have held firmly as a rock to all that is connected with the Name of Christ and of Jesus, beyond number also are pictures of Him which have moved souls and occupied thoughtful men ever since the Event in Palestine. Always the picture has been modified according to the general views of the times, to what was felt and considered true at any given period. Thus, when the way had been prepared by the intellectual currents of thought of the eighteenth century, it came about in the course of the following century that what could be intellectually grasped as “Christ” withdrew into the background as compared with what was called later the “Historical Jesus.” It is around the “Historical Jesus” that the widely extended controversy has arisen, and which has here in Carlsruhe its most important protagonists and its most vigorous combatants. For this reason it is as well to give a short indication of the actual position of the controversy before entering on the subject of “Christ Jesus.” We might say that the Historical Jesus of nineteenth century thought originated under the influence of the intellectual current that takes a merely external view of spiritual life and judges it by means of external documents: that there is evidence of His having lived at the beginning of our era in Palestine, that He was crucified and, according to the faithful, rose again. It is quite in line with the character and nature of the present era, now approaching its termination, that in the case of theological research, faith limited itself to what it was thought could be confirmed by historical documents in the same way as any ordinary event is confirmed by independent writings. It may be said that all the historical written traditions elsewhere than in the New Testament could, in the opinion of one of the most important judges, be “easily contained in a quarto page.” All the other references to the historical Jesus in any documents whatever, such for example as in Josephus or Tacitus, may be put out of court, for they can never be used from the standpoint of that historical science which holds good to-day. Beyond these there are only the Gospels and the Pauline Epistles. How did the historical research of the nineteenth century examine the Gospels? Regarded purely externally how do they appear? If taken like other records, such as those of military engagements and so forth, they seem to be very contradictory documents of the physical plane, the fourfold presentation of which cannot be brought into harmony. In face of what we call historical criticism these records fall to pieces. For it must be allowed that everything which the earnest and diligent research of the nineteenth century collected out of the Gospels themselves, in order to gain a true picture of Jesus of Nazareth, has crumbled away through the presentation of the kind of research brought forward by Professor Drews. As to all that can be said against the Gospels as facts of history, it is evident that nothing can come to light about the Person of Jesus of Nazareth if we apply the methods whereby accurate science and strict criticism ratify other historical facts. We can only be considered very dilettante scientists if we do not make this concession to the science of the day. Is it not the case that those who in the nineteenth century presented the teaching of Jesus of Nazareth, and wanted to arrive at an historical portrait of Him, had an entirely false conception of the Gospels? Were the Gospels really intended to be historical records in the sense understood in that century? Whatever was to be said on this subject I endeavoured to state many years ago in my work, Christianity as Mystical Fact, and our present question, as to what was the real object of the Gospels, was intended to receive its answer not merely through the contents of that book but through the tide itself. For the title was not ‘The Mysticism of Christianity,’ nor ‘The Mystical Contents of Christianity:’ its object was rather to show that Christianity in its origin and its whole being is not an external fact but a Fact of the Spiritual world, and one that can only be comprehended by an insight into a realm lying behind the world of sense and behind what can be corroborated by historical records. It was shown that the forces and causes which brought about the Event of Palestine were not to be found in that region wherein external historical events take place, and thus that possibly not only may Christianity have a mystical content but that Mysticism—the actual gazing into the spiritual—is necessary to disentangle the threads that were woven behind the Event in Palestine and made it possible. In order to realize what Christianity is, and what it can and must be in the soul of man to-day if he is to understand it aright, let us see how deeply grounded in the spiritual facts of human development were the words of St. Augustine: “That which we now call the Christian Religion already existed among the ancients and was never absent from the beginning of the human race up to the time when Christ appeared in the flesh, from which time forward the true religion which was already there received the name of the Christian Religion.” Thus does a standard authority point to the fact that it was not something new which came into humanity with the events of Palestine, but that in a certain sense a transformation had taken place in that which from time immemorial the souls of men had sought and striven for as knowledge. Something was given to humanity which had always been in existence, though hitherto along other lines than the Christian. If we wish to test the other way in which the preceding ages could come to the truths and wisdom of Christianity, we are referred by the historical development of humanity to the Mysteries of Antiquity or the Ancient Mysteries. What is meant by these expressions is little understood to-day, but it will become clearer the more men grasp the conception of the cosmos as presented by Spiritual Science. Not merely upon the external religions of the people of antiquity must attention be focused, but upon what was practised in pre-Christian times in those mystic abodes designated by the name of the Mysteries. In the book Occult Science is to be found an explanation from the aspect of Spiritual Science, and there are also numbers of secular writers who have declared publicly what was the secret of mankind in antiquity. We read that only a few were admitted to the schools which were designated “The Mysteries,” and that these schools were the homes of the cults. Also there was a small circle of men admitted to the Mysteries by the priestly sages, and for them this meant a kind of retirement from the outer world: they realized that if they were to reach what was to be attained they must lead a different life than they had so far lived openly, and above all that they must accustom themselves to another way of thinking. These Mysteries existed all over the world, among the Greeks and Romans and other peoples, as may be confirmed by referring to extensive literature which still exists. The pupils admitted to the Mysteries were taught something comparable with what is now called science or knowledge, but they did not receive it in the same way, for by what they experienced they became quite other beings. To them came the conviction that in every man there lives, deeply hidden and slumbering so that the ordinary consciousness knows it not, a higher man. As the ordinary man looks through his eyes upon the world and with his thought-power thinks over what he experiences, so can this other man—at first unknown to external consciousness, but capable of being awakened in the depths of his nature recognize another world unattainable by external sight and thought. This was called “The birth of the inner man.” The expression is still used, though in these days it is dry and abstract in character and regarded lightly, but when the disciple of the Mysteries applied it to himself it stood for a tremendous event to be compared in some measure with being born in the physical sense. As man in the physical world is born out of a dark substratum (be it one of nature according to the materialistic idea, or a spiritual sub-stratum in the view of Spiritual Science) so, physically speaking, there was really born through the processes of the Mysteries a higher man who previously had been as little present as was the human being before birth or conception. The disciple was a new-born being. The present view of knowledge, as given everywhere in answer to a deeply philosophic question, is exactly the opposite of that which formed the central point of the whole idea and outlook of the Mysteries. It is now asked in the sense of Kant and Schopenhauer, “Where lie the limits of knowledge? What is it in the power of man to know?” We need only take up a newspaper to meet the answer that here or there lie the limits and that beyond them it is impossible to go. Certainly it was admitted in the Mysteries that there were problems which man could not solve, but it would never have been held in the sense of Kant or in Schopenhauer's Theory of Cognition that “Man cannot know” this or that! What would have been appealed to was man's capability of development, to the powers lying dormant within him which must be evoked so that he might rise to higher capacities of knowledge. The question in those times resolved itself into what was to be done in order to get beyond that which in normal life is the boundary of knowledge; how to develop deeper powers in human nature. Something more is needed if we are to feel the whole magic charm of the Mysteries that, like a breath, pervades the works of the exoteric writers, Plato, Aristides, Plutarch and Cicero. Here we must be clear that the kind of mental comprehension present in the forming of the disciples of the Mysteries was quite different from that of the men of to-day when they confront scientific truths. What we now call science is open to anybody and everybody in any condition of receptivity whatever. It is just here that we recognize the characteristic of Truth, that it is independent of mood and feeling. For the pupil of the Mysteries the most necessary thing was that, before he was brought to the great Truths, he should go through something whereby his soul was transformed in his feelings and impressions. What to-day appears as a simple scientific truth would not have been put to him so that he could grasp it externally with his understanding, but his natural temperament would have been prepared beforehand so that he could draw near with reverential awe to what could approach him. Consequently his preparation was not one of learning; it was a gradual and radical transformation and education of his soul. The question was how the soul approached the great Truths and Wisdom and how it reacted to them, and hence arose the conviction that through the Mysteries man was bound up and united with the very foundations of the Cosmos and with what flowed from the springs of all cosmic beginnings. Thus was the disciple prepared for the experiencing of something which is described by Aristides. He who, according to what is to be found in my Knowledge of the Higher Worlds and its Attainment has lived through what these disciples experienced can himself bear witness. He knows that the words of Aristides correspond with the truth when he writes, “I seemed to be approaching God, I seemed to feel His Presence, and I was in a state between waking and sleeping; my spirit was quite light—so light that no one who was uninitiated could describe or understand it.” There was a way, therefore, to the divine foundations of the Universe which was neither Science nor one-sided Religion, but consisted in a thorough preparation of the soul for the realization of the ideas about the Evolution of the Universe so that it might draw near to God and those spiritual foundations. As we take in the external air with our breath and make it a part of our body, so did the disciple of the Mysteries receive into his soul that which pulsates spiritually through the Universe until he was united with it and so became a new man permeated by the Divinity. Now, however, Anthroposophy or Spiritual Science shows that what was then possible was only an historical phenomenon in human evolution, and when the question arises as to whether the Ancient Mysteries of pre-Christian times are still possible in the same way it can only be said that historical research verily proves that what has just been described did really exist but that it exists no longer in the same form. The pre-Christian method of Initiation is not now possible. A man must indeed be short-sighted if he believes that the human soul is the same in all epochs, or that the spiritual path of the olden times holds good for the present. The path to the divine and primal sources of the world has now become another, and intellectual historical research shows that it did so in its very essence at the time ascribed by tradition to the Events of Palestine. These Events made a deep incision in the evolution of man. Something entered into human nature in the post-Christian period which entirely differed from what was there before. Such a method of thinking as is possible nowadays—the method of drawing nearer to the Universe through scientific thought—did not exist in pre-Christian ages. The Mysteries did not conduct man in the manner described to the very highest treasures of Wisdom in order that he might do something in secret, or acquire something special for himself as a member of a small circle, but because our modern way of combining thoughts through logic was not possible at that time. A glance at the history of humanity will show that in the course of two centuries, during the time of the Greek philosophers, the present mode of thinking was gradually prepared, and that only now has it reached the point of embracing external nature so wonderfully. Thus the entire form our consciousness takes and the way we create our conceptions of the Universe differ entirely from pre-Christian times. For the moment we are only concerned with this fact as showing that human nature has changed. A careful review of human evolution makes it clear that the entire consciousness has altered in the course of evolution (the results arising from research are to be found in my Occult Science. The men of old did not regard things and think about them as we do with our senses and understanding; they had a kind of clairvoyance, but this was of a dim and dreamlike nature (not such as is described in my The Way of Initiation). Herein lies the import of evolution, that an old clairvoyance which in primitive times was spread over all humanity gave way to that form of thought which we possess to-day. The ordinary inhabitants of every country had this kind of clairvoyant power, and a path leading from that to higher stages was provided in the Mysteries. Thereby development was given to the normal soul-faculties of man. Observation of the world by what we call reasoning and logic having displaced the old clairvoyance, the latter is no longer a natural faculty, but it lasted right through the historical period and reached its culmination in the Greco-Roman era during which the Appearance of Christ occurred. At that point of time collective humanity everywhere had come so far in its evolution that the old clairvoyance had passed away and the old Mysteries were no longer possible. What then took the place of the old Mysteries and what did man acquire through the Mysteries? These were of two kinds: the one proceeded from that centre of civilization which was afterwards occupied by the ancient Persians, and the other was to be met with in its purest form in Egypt and Greece. They were entirely different throughout those times. It was the endeavour of all the Mysteries to produce in man an extension of his soul-powers, but this was achieved in a different way in Greece and Egypt, than in Persia. In the two former, which agreed essentially, the object was to effect in the disciples a transformation of their soul-powers. This transformation took place under a certain supposition which must be understood before anything else. It was that in the depths of the soul there slumbers another, a divine man; that from the same sources whence the rock forms into crystal and the plants break forth in the Spring the hidden man originated. Plants, however, had already utilized all that was contained within them, whereas man, in so far as he had understood himself and worked with his own powers, had remained an imperfect being, and that which was within him had only come to the fore after much endeavour. Appeal, therefore, in the Egyptian and Greek Mysteries was made to a spiritual, a divine inner man, and when this was referred to, allusion was made also to the powers within the Earth. For according to the views held the Earth was not regarded as the lifeless cosmic body of modern astronomy, but as a spiritual planetary being. In Egypt reference was made to the wonderful spirit-forces and nature-forces, called by the names of Isis and Osiris, when it was desired to contemplate the origin and source of what could be experienced as manifestation in the inner man. In Greece this primal source was referred to under the name of Dionysos. As a consequence of this, profane writers asserted that the nature and being of things were the objects sought for, and in the Greek Mysteries they called what was found of the forces of human nature the “sub-earthly” portion of man, not the “super-earthly.” The Nature of the great “Daemons” was spoken of, and under this tide was represented all that worked on the Earth of the nature of spiritual forces. The nature of these daemons (in a good sense) was sought for through that which man was to bring forth from himself. Then the disciple had to go through all the feelings and perceptions that were possible for him in the course of evolution. He had to experience what was meant by “going down into the depths of his soul;” to learn that a fundamental feeling so dominated all soul-being that in ordinary life no conception of it could be formed, and that that feeling was a deep egoism—the almost unconquerable selfishness lying within the inner recesses of a human being. By means of struggling against and conquering all selfishness and egoism the disciple had to go through something for which we have to-day only an abstract expression, i.e., the feeling of all inclusive love and sympathy for men and beings. Sympathy, in so far as the human soul was capable of it, was to take the place of selfishness. It was clearly understood that if the disciple evoked this sympathy, which belonged in the first place to the hidden forces of the world of feeling, it could draw out from the depths of his soul the divine powers slumbering therein. It was held moreover that as he looked out upon the world with his ordinary understanding he must soon become aware of his powerlessness as a man with reference to the Cosmos, and that the further he projected his conceptions and ideas the stronger this feeling grew until in the end he was led to doubt what indeed could be called knowledge, i.e., Gnosis. Arrived at that point he must then overcome this feeling of emptiness in his soul whenever he desired to encompass the Cosmos with his ideas. This consciousness of a void was accompanied by fear and anxiety, and consequently the Greek disciple of Mysticism first filled himself with a dread of the unknown and then by coupling this with sympathy drew forth the divine powers lying within him. So did he learn to transform fear into awe and reverence, and to realize how the highest kind of awe and reverential devotion for all the phenomena of the Universe was able to penetrate every substance and conception that lay beyond the scope of ordinary knowledge. Thus the Greek Mysteries, as also those of Isis and Osiris in the Egyptian Mysteries, worked outwards from the inmost nature of man and sought to lead him into the spiritual worlds. It was a living apprehension of the “God in Man.” A real acquaintance was formed between man and God, and immortality ranked not as mere abstract theory and philosophy but as something known, something as firmly grounded as the knowledge of external colours, and this was experienced as an intimate connection with external things. With no less certainty was this experienced also in the Persian or Mithraic Mysteries. Whereas man was led in the Greek and Egyptian Mysteries through the unfettering of his soul-powers, he was confronted at once with the Universe itself in the Mithraic Mysteries; not only did the Universe work upon him through the great and mighty Nature which is overlooked by those who regard the world in its external aspect, but by gaining a deep intimacy with Nature, he could gaze upon phenomena that lay outside the limits of the human understanding. By the methods then used the most terrible and magnificent powers were brought before the pupil from Universal Space. Whereas the Greek disciple was affected by a deep feeling of reverence, to the Mithraic disciple alone was given the knowledge of the terrible and awe-inspiring powers in Nature so that he felt himself infinitesimally small in comparison. So powerful was this impression, consequent upon his alienation from the primal source of being, that he felt that in its vastness the Universe could at any moment overwhelm and annihilate him. The first impulse came from his being led through a comprehensive astronomy and science away from external things to the greatness of the phenomena of the Universe, and what he further developed in the Mysteries was then more a consequence of the Truth in all its ramifications when Nature in her details (science in the old sense of the word) worked upon his soul. The Greek disciple became fearless through the setting free of his powers. The Mithraic disciple was brought so far that he drank in the greatness of Cosmic Thought, and thereby his soul also became strong and courageous. A knowledge of the dignity and value of a human being was gained, and with it a feeling for truth and fidelity; the disciple learned to recognize that man must always hold himself under control during his earthly existence. Such were the benefits obtained especially through the Mithraic Mysteries, and whereas the Greek and Egyptian Mysteries are to be found spread over Greece and Egypt, the Mithraic are diffused from Persia as far as the Caspian Sea, along the Danube into Germany, and even to the South of France, to Spain and to England. Europe was indeed permeated by the Mithraic Mysteries, and everywhere it was seen clearly that something streamed into man from the Universe if only he could learn to understand it, and this that could be received was Mithra, the God that streams through the world in all worlds. It was through this power of action that courage was aroused: the warriors, the Roman legionaries, were filled with the Mithraic service or cult of Mithra. Both leaders and men were initiated into the Mysteries. Thus was God sought on the one hand by the freeing of the individual soul-powers, and it was quite evident that through this process something streamed out from the depths of the soul. On the other hand, however, it was equally evident that when man sought God by devoting himself to the great cosmic phenomena, something streamed into his soul as the essence, the finest life-sap contained in the world. There were found the primordial forces of the Universe. God came as it were into human souls through this development which was attained in the Mystery schools. A veritable process is to be seen here: each soul became a door for the entrance of the Godhead into human evolution on earth. Few were able to undergo such a development, and a special preparation for it was necessary. The teaching consisted in showing that what was hidden in external nature (Mithra) as also in the inner man of the Greek, poured through the world as a stream of divine consecration. The evolution of man has now changed, and the entire method of Initiation is different. Here we touch upon what must be called the Mystical Fact of the Christ Event. To penetrate deeply into history is to see that the early Christians were more or less dimly conscious that the same force which entered the soul only through devotion to the Mysteries, to the Divine Principle of the Universe (streaming forth from Cosmos as the Mithra or out of the depths of the soul as the Dionysos), was as the deed of a unique Cosmic Divinity in one single Fact in the evolution of the Earth. That which was sought for beyond this, and was not to be found except by those who alienated themselves from outer life in the Mysteries, was at a given time incorporated into the Earth by the Divinity. No human effort was needed, for the Divinity once and for all permeated the Being of the Earth, and henceforth even those who had lost the power to penetrate to the Divine Principle of the Cosmos could meet Him in another way. The God Who could now penetrate into the human soul (neither as Mithra from without nor Dionysos from within) was Himself a fusion of Mithra and Dionysos, and also was related to human nature in its depths. He was embraced and encompassed by the Name of CHRIST. Mithra and Dionysos were united in the Being Who entered humanity in the Event of Palestine, and Christianity was the confluence of both Cults. The Hebrews, who were chosen that they might provide the necessary body through which this Event might take place, had become acquainted with the Mithraic and Dionysian Cults, but they remained far removed from either. The Greek thought of himself as a weak man who must develop deeper powers before he could penetrate into the depths of his soul, while the follower of Mithra felt that by letting the whole surrounding sphere of the air work upon him he might become united with the divine qualities of the Universe. The Hebrew, on the other hand, held that the deeper human nature, with all that was hidden within it, was already there in the first Man, and the ancient Hebrews called this Primal man Adam. According to old Hebraic ideas that which man could seek, and which joined him with the divine, was present originally in Adam, but in course of evolution the descendants of each generation became further and further removed from the Source of Existence. Being “subject to original sin,” as they put it, meant that man had not remained as he was and had been ejected from the sphere of the Divine; regarding himself as standing below Adam he sought the reason in original sin. But though less than that which lived in the depths of human nature, he could unite himself with the deeper powers and thereby be raised again. This point of view, that once man had stood higher and that through the qualities connected with the blood-ties he had lost something, was an historical one. What the adherent of the Mithraic Mysteries saw in humanity as One Whole the Hebrew saw in his own nation and was conscious that its original source had been lost. So that while among the Persians there was a kind of training of the consciousness, there was among the ancient Hebrews a consciousness of a historical development; Adam, by falling into sin, had fallen from the heights where he once stood. Consequently the Hebrews were the best prepared for the thought that that which had happened at the initial point of evolution (and which had brought about a deterioration in humanity) could only be raised again through an historical Event, i.e., by something actually taking place in the spiritual sub-strata of the Earth's being. The ancient Hebrew who rightly understood evolution felt that the Mithra God, equally with the God Who is evoked from the depths of the human soul, could come down without man going through a development in the Mysteries. Thus in these people, and above all in the case of John the Baptist, there arose a consciousness of the fact that the same which the Mysteries had handed down in the form of Dionysos and Mithra was born at one and the same time in One Man. Those of them who felt this in a deeper sense held that even as through Adam the descent of man into the world was brought about (all men having descended from one forefather and inherited from him all the deeper forces that lead to sin and error) so, through One Being Who descends from the spiritual worlds as the union of Mithra and Dionysos, must the initial point be formed to which men can look when they have to rise again. As in the Mysteries human nature was developed through the setting free of the deeper soul forces or through a view of the Cosmos, the Hebrews now saw in the God Who came down into physical being Him on Whom the soul must look and believe, for Whom it must develop the deepest love, and Who as the Great Example could lead them back to their divine origin. He who had the profoundest knowledge of this fact of Christianity was Paul. The Apostle recognized that as men looked to Adam as their physical progenitor they could, through the Christ Impulse, look to the Christ as the Great Example, and so attain to what was striven for in the Mysteries and must be born again if they were to know their own original nature. The knowledge that was kept within the recesses of the Temples, and could only be attained after ascetic training, was set forth neither in mundane document nor as some external fact but as having been accomplished as a mystical fact, the God Who pervaded the world having actually appeared in one single Form. What the disciples of the Mithraic Mysteries acquired through looking upon the Greatest Model had now been attained through Christ. The courage, self control and energy acquired by those disciples had also to be acquired by those who could no longer be initiated in the old Mithraic sense; through the Model of the historical Christ and the gazing upon Him the impulse towards this fortitude was now to pour itself out upon the soul. In the Mithraic Mysteries, as has been shown, the whole Universe was in a certain sense born in the soul of the disciple, and the courageous soul was fired with all the inner forces of initiative. In the Baptism of John something was poured down from above of which human nature could be the vehicle; when a man was permeated with the thought that his nature was capable of assimilating the profoundest harmony of the Universe, the view of the Baptism aroused within him the understanding that Mithra could be born in human nature. Those, therefore, who grasped the original meaning of Christianity, acknowledged that the end of the Mysteries had come: the God Who formerly had poured Himself into the Mysteries had now flowed directly into the being of the Earth through the Personality Who stood at the beginning of a new era (our present one). The connection with the Greek or Dionysian Mysteries has now to be considered. Through the fact that the human gaze was guided to Jesus of Nazareth in Whom Mithra lived and Who then passed through death, an indication was given that Mithra (the bestower of courage, self control and energy) had Himself died with the death of Jesus. It was further seen that because Mithra had so vanished that which man found in his deepest nature, and had attained earlier through the Dionysian Mysteries, had now become in Jesus of Nazareth the immortal conqueror over death. Herein lies the true Christian meaning of the Resurrection if it is grasped in its spiritually scientific sense. The Baptism by John in [the] Jordan demonstrated that the old Mithra had entered into man, that thereby human nature had won the victory over death, and that by the example so created the soul could unite itself in the deepest love in order to come to that which lived in its own depths. In the Risen Christ was seen the fact that man, by living according to the event that had taken place in history, could rise above the level of ordinary humanity. Thus in the centre of the history of the world was set an historical event in the place of that which had been sought in the Mysteries times without number. The great revelation that came to St. Paul was that human nature had thereby become different, and this was concealed within what is known as “The Event of Damascus.” Writing of what he experienced before Damascus, the Apostle relates how he learned to understand, not from external documents but through a purely spiritual clairvoyant experience, that the moment when the Incarnation itself should take place in an historical personage had already passed. The existence of Christ as a real man could never be experienced by Paul through an external fact, and what he could learn in Palestine did not convince him that the Union of Mithra and Dionysos had lived in Jesus of Nazareth. But when, before Damascus, his spiritual sight was opened, it became clear that a God Who could be called by the Name of Christ not only worked through the world as a super-sensible Being but had actually come to earth and conquered death. Henceforth he preached that what for the Initiates had previously been a streaming substance was now to be found as continuous historical fact. This lies at the basis of his words, “If Christ be not risen then is our preaching vain, and your faith is also vain.” Such was the path by which Paul came to Jesus by the indirect way of Christ, it being clear to him that something had taken place in Palestine which previously could only be experienced in the Mysteries. And this still applies to-day. Because Christ is the focus of all human development and the highest example for the inmost powers of the soul the bond established with Him must be of the most intimate kind. To become a disciple it is required of a man that he set little value upon his own life, and so it must be regarded as of small importance to lay aside all documentary evidence and historical traditions in order to come to Christ. Indeed there is cause for thankfulness that the fact that there ever was an historical Christ Jesus cannot be established, for no document could prove that He was the most significant of all that has passed into humanity. The connection between Christ and the ancient Mysteries is therefore quite clear. The disciples of the latter had to go through what may be called intimate soul experiences in order to come to God; their inner feelings and sensations were more lively and intense than those of the ordinary man, and so they became aware that they were set fast in a lower nature which hindered them from arriving at the Sources of Being. This lower nature was indeed a seducer leading them away from the upward path, and that which so allured them had also become their own lower nature, and herein lay the “Temptation” that came to every disciple of the Mysteries. At the moment when God awoke within them they became aware also of their lower or sensual natures. It was as though some strange unknown being were urging them not to follow the unsubstantial and airy heights of the spiritual world, but to seize the coarse and material things that lay close at hand. Each disciple had to pass through a time when everything spiritual seemed unreal in comparison with the ordinary way of looking at things, and all that was connected with the senses appeared alluring as against the stress of spiritual effort. At another stage in mystic development these lower forces were overcome, a higher outlook being attained with the growth of invigorated powers of courage and so forth. All this teaching was clothed in certain instructions that may be verified from the writings of exoteric authors, as also in the methods of Initiation given by Spiritual Science and set forth in Occult Science. There were various methods both in the Greek and the Mithraic Mysteries. Finally the disciples experienced the “at-one-ment” with Him Who was the Divine Man, but here the methods were different and varied widely in the many countries where Initiation existed. In my Christianity as Mystical Fact the purpose is to show that in the Gospels nothing is to be met with but a rebirth of old Initiation instructions. What took place externally had already taken place similarly in the course of the Mysteries, and therefore the Divine Being Who was in Jesus of Nazareth after the descent of the Mithra Being had to experience the “Temptation.” As the Tempter came on a small scale to the pupil of the Mysteries so did he also confront the God become man. All that was true in the Mysteries is to be found repeated in the Gospel records which were new versions of the old inscriptions and instructions given in the Initiations. The writers of the Gospels saw that once that which hitherto had lain only in the Mysteries had been enacted on the plane of Cosmic History, it was permissible to describe it in the same words as those in which their directions for Initiation were recorded. It is for this very reason that the Gospels were not intended to be biographies of Him Who was the vehicle for the Christ. This is just the mistake of all modern criticisms of the Gospels. At the time they were written the sole object was to lead the human soul to a real love for the Great Soul, the Source of the world's existence. Strangely enough a clear consciousness of this prevailed almost to the end of the eighteenth century. It is pointed out in isolated writings of remarkable interest that through the Gospels the soul can be so transformed as to find the Christ. Old Meister Eckhardt writes, “Some people want to look at God with their eyes as they look at a cow, and want to love God as they love a cow. They love God as an outward possession and an inward comfort, but these people do not love Him aright ... Simple folk imagine they ought to see God as if He stood there and they here; it is not so; God and I are One in recognition.” In another passage he writes, “A Master says, ‘God has become man, and thereby the whole human race is raised in dignity. We may rejoice that Christ our Brother has through His own power passed beyond the choir of angels, and sits at the right hand of the Father.’ This Master has spoken rightly, but verily I do not pay much attention to it. What help would it be to me if I had a brother who was a rich man, and I was at the same time a poor one? How would it help me if I had a brother who was a wise man, and I myself a fool? ... The heavenly Father begat His only Son in Himself and in me. Why in Himself and in me? I am one with Him, and it is not possible for Him to exclude me. In the same work the Holy Ghost received His Being, and is from me as from God. Why? I am in God, and if the Holy Ghost does not receive His Being from me neither does he receive it from God. I am in no way excluded.” That is the point: that man through mystic development, without external mysteries but through the simple evolution of the soul, will in later times be able to experience that which was once experienced in the Mysteries. This, however, will only be possible because the Christ Event took place. Even if there were no Gospels, no records and no traditions, he who experiences the Christ in himself along with the being filled with Christ has the certainty, as St. Paul had it, that at the beginning of our era Christ was incarnated in a physical body. An historical biography of Jesus of Nazareth can never be gathered out of the Gospels, but through the right unfolding of his soul powers man can and must raise himself up to the Christ, and through the Christ to Jesus. Thus only can be understood what was the aim of the Gospels and what was lacking in the whole of the nineteenth century researches on the subject of Jesus. The picture of the Christ was allowed to recede into the background in order to present a tangible Jesus quite externally from the historical records. The Gospels were misunderstood, and consequently the methods of investigation crumbled to pieces. Herewith the way is at the same time made clear to Spiritual Science. Its object is to show what are the deeper powers that have lain in man since the coming of Christ, and which he can develop. Not in the depths of externally appointed Mysteries, but in the stillness of his room, man can attain by devoting himself to what happened in Palestine that which was attained by the disciples of the Mysteries. By experiencing the Christ within himself he gains in courage and energy and in a consciousness of his dignity as man, and comes to the knowledge of how he has to take his place in humanity in the right sense. And at the same time he experiences, as could the adherent of the Greek Mysteries, the Universal Love which lives in Christ and embraces all external creatures. He learns never to be afraid or to despair in face of the world, and in full freedom and at the same time humility is sensible of devotion to the secrets of the Universe. All this comes to the man who permeates himself with the Mystical Fact of Christianity, the successor of the old Mysteries. Simply through a cognitional development of these fundamental thoughts the Historical Jesus becomes a fact for those who have a deep knowledge of Christ. In Western philosophy it was said that without eyes none could see colour nor hear without ears; the Universe would be without light and sound. True as this is with regard to seeing and hearing, it is equally true that without light no eye could have come into existence nor could man have had any perceptions connected with it. As Goethe says, “If the eye were not born of like nature to the sun it could never look upon the sun,” and “The eye is a creation of the light.” The Mystical Christ, spoken of by those whose spiritual sight is opened and who behold Him as Paul did, was not always in man. In pre-Christian times He was unattainable in any development through the Mysteries in the way in which He was to be found after the Mystery of Golgotha. That there might be an inner Christ and that the higher man could be born an historical Christ was needed, the Incarnation of the Christ in the Jesus. As the eye can originate only through the effect of light, so in order that there could be a Mystical Christ the historical Christ must have been there. Had there been no documents containing a biography of Jesus of Nazareth this could still be said and felt, for Jesus is not to be recognized through external writings. This fact was long known in the evolution of the West and will again be known. Spiritual Science will so formulate that it can draw together from out its various spheres what will lead to a real understanding of the Christ, and thereby to an understanding of Jesus. It has come about that Jesus has been actually alienated from the world and the methods of the Jesus investigations have melted away, but the deepening of ourselves in the Christ Being (in the Christ as a Being) will lead to a recognition of the greatness of Jesus of Nazareth. This path, by which the Christ is first recognized through inward soul experience, leads through what really has developed out of the soul to the understanding of the Mystical Fact of Christianity, and of the gradual development of humanity, as being such that the Christ Event must take place within it as the most significant point in the evolution of man. The way leads through the Christ to Jesus. The Christ Idea bears fruitful seed that will bring humanity not merely to the apprehension of a general pantheistic Cosmic Spirit, but the individual man to the understanding of his own history; as he feels his Earth to be bound up with all cosmic existence so will he recognize that his past is bound up with a super-sensible and super-historical Event. This Event is that the Christ Being stands as a super-sensible Mystical Fact at the middle point of human evolution, and that so will He be recognized by the humanity of the future apart from all external historical research and documents. Christ will remain the strong cornerstone of mankind's evolution. Man will bring the forces out of himself to renew his own history, and therewith also the history of the evolution of the world.
|
| 68d. The Nature of Man in the Light of Spiritual Science: The Course of Human Development from the Standpoint of Occult Science
06 Feb 1908, Karlsruhe Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 68d. The Nature of Man in the Light of Spiritual Science: The Course of Human Development from the Standpoint of Occult Science
06 Feb 1908, Karlsruhe Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
When the subject of theosophy or the theosophical worldview comes up, people often think: Oh, we are dealing with something that leads to remote realms of thought, something that takes us to nebulous, fantastic regions. In any case, many people have the idea that Theosophy or, as we can also say in the true sense of the word, spiritual science, that Theosophy or spiritual science is not for practical people, for people who are fully immersed in life, that it is not for them! Now, my esteemed audience, but the one who delves deeper into what Theosophy or spiritual science has to give, and then is able to see life, our immediate existence, in the light of this spiritual science, will soon be able to notice how this Theosophy is something that leads to the right, true life practice, as it is not just some theoretical knowledge, some speculation, but something that makes people capable, able to work in life, hopeful, confident, yes, healthy, because it makes our everyday life immediately understandable to us - if we start from the right points of view - makes it transparent. This everyday life truly offers us enough puzzles. We can only solve these puzzles if we are able to grasp what lies behind the sensual phenomena, if we are able to rise to the world of supersensible facts. The few times that I have been permitted to speak to you here in this city about Theosophical matters have already familiarized the audience with what underlies the Theosophical worldview. Therefore, only a brief reference will be made here. The Theosophical worldview rests on two pillars, on two pillars of knowledge. The first is that it shows people that there is a supersensible, a superphysical world above our sensual, our physical world. Secondly, it familiarizes people with the fact that they can penetrate these supersensible realms themselves — if they only want to — and that they can draw their powers and abilities from within. In this way, however, Theosophy is confronted with widespread prejudices in the present day, but even if it does not change overnight, over time more and more of these prejudices, which today affect wide circles of our present-day people, will fade. Many people today say: To speak of supersensible worlds, of a spiritual background to existence, is unseemly in our enlightened times, in our time of great scientific achievements... In the childhood cultures of humanity, where imagination still held sway, it was said that people dreamt of supersensible facts, of supersensible phenomena behind our sensory world. But now we are at the point where science, with its tools and methods, is revealing to us the world as one would think, in its natural, lawful context and does not make it necessary to assume anything behind what can be seen and what can be grasped by the mind. Many of our contemporaries think they are quite enlightened when they deny everything that lies behind the phenomena! This brings us to the question: in what sense does Theosophy speak of supersensible worlds? Not in the sense that these supersensible worlds lie somewhere in a cloud cuckoo land, but in a completely natural sense, in a completely logical sense, Theosophy speaks of higher worlds than the one that is accessible to our are accessible to our senses, in the same sense that a German philosopher, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, spoke of these worlds when he was at the height of his thinking: in 1809, for example, in front of his audience in Berlin. At that time he said: “I have something to tell you about worlds that lie beyond the ordinary sensual world and therefore cannot be perceived with the ordinary physical senses.” Therefore, anyone who is only willing to acknowledge a world that can be perceived by the physical senses can easily consider everything that can be said about supersensible worlds to be fantasy. But — it was not I who said this, but Fichte. Imagine going through a world of blind people as the only one who can see and telling these blind people about the world of colors and the world of light. If they want, they can also say: All that you are telling me about color and light is empty dreaming, mere fantasy... ... and we can now tie in with Johann Gottlieb Fichte's thoughts and say: Let us assume that a person born blind is led into this room of ours and that we are able to operate on him here, to give him sight. What was around him before, what you can all see with your physical eyes, light and color, was not there for him; for him, the world was only what was given to his sense of touch and the other senses. But now that he has had the operation, light and color and radiance are emerging bit by bit from the bleak darkness and gloom. They were around him, but for him they have become a world only after he had the organs for them. Not every physically blind person can be operated on, but it is possible for everyone to awaken the abilities and powers slumbering within them – what Goethe calls “spiritual eyes” – to open them up, to opens up by itself through appropriate behavior, and he becomes aware of an awakening of a higher, more brilliant kind than that through which the blind person sees a new world entering him when he is operated on. Who can logically deny that there are worlds around us that the senses cannot perceive? Logically, no one can! Logically, a person can only make a statement about what he sees and perceives, never about what he does not perceive. But there have always been people in the world, and there are people today, who awaken these abilities and powers slumbering within us and who know from their own experience that spiritual worlds exist around us, know of worlds that are active and whose forces have an effect in our world. And it is of these worlds that spiritual science, theosophy, speaks – we only call it secret science because in order to gain access to it, man must first awaken the forces slumbering in him, and until he has done so all this remains hidden from him. But when he becomes a citizen of these worlds, when the spiritual lights around us dawn on him, then entities reach into this life for him that he can only now recognize, that... and in this way he attains knowledge that makes him fully able and willing to work. This will now become clear to us when we look at our own human life from the standpoint of this supersensible knowledge, not at something remote but at the most everyday things there are for us. Then we will see how we can apply this spiritual science. As far as I am concerned, someone can come and say: There are such twisted minds, oddballs, who call themselves Theosophists and bring all sorts of confused stuff, they may keep it to themselves, it is not for a reasonable person! Good, he may act on it! But now there is another point of view that says: Well, since things don't look so unreasonable after all, let's try to live life and work in life as if these assumptions were correct, and if they prove themselves in life, then we can talk to them. This is a thoroughly healthy point of view, and today's question in particular will enable us to find such a kind of truth, such proof of the theosophical premise, if we try to apply what the lecture contains to life. First, however, we must take a brief look at the human being in the theosophical or esoteric sense. If we look at the human being from this point of view, then what the senses can see, what eyes can see and hands can grasp, appears to us as only a part, a single limb of the entire human being. In the spiritual sense, we call this part of the human being the physical body. This physical body is shared by the human being with all the seemingly inanimate beings around him; the same substances and forces that are found outside in the inanimate minerals are also found in the physical human body. However, in this physical human body – and in fact in the body of every living being are so intricately combined and interwoven that the physical body of a living being, if it is left to the physical substances and forces alone, then it disintegrates into itself. No matter what a merely materialistically thinking wisdom may say – the theosophist knows very well what it can say – and no matter what it may say, there is a principle embedded in the physical body of every living being that can be logically , who is able to consider these things only philosophically, perceptible for him who has developed the higher abilities, the spiritual eyes, as Goethe says. For the materialistically-minded, it is of course a nothing, one can well understand that. ... For the person who sees through things, this etheric or life body is a fighter against the disintegration of the physical body in every moment. In all of you, this life body is a fighter that prevents physical substances and forces from following their own laws. At the moment of death, the physical body separates from the etheric body, and then the physical body follows its own substances and forces, then it is a corpse, then it decays. So we have this second link, the etheric body, in every living being, which the human being has in common with all plants and animals. The third link is the so-called astral body... This too is a fact for the spiritual seer. But you can get a logical idea of it if you consider the following: when you look at the person standing in front of you, you have not only what you can perceive as a physical body with your physical senses, not only what as an etheric and life body constantly protects this physical body from decay... but there is something else in this space in front of you: something is in it that is much closer to many people than the physical body and the etheric body. The details of the physical body, what do many people know about that... but there is something that is infinitely close to the simplest human being, much closer than his physical body, and that is the sum of pleasure and suffering, of joy and pain, of urges, desires and passions. The sum of all sensations that rise and fall in the soul, that which we call the inner life or human inner life. And the carrier of this human inner life, in spiritual science we call this the astral body, the human being no longer shares this with plants and minerals, but only with the animal world. As long as we hold the view that this astral body, or if we want to speak in everyday terms: that drives, desires and passions, feelings and instincts and the surging and surging sensations, that these are only evoked by the physical body... Only at that moment do we have the right to speak of it... where we see the original not in the physical and not in the etheric body, but precisely in this astral body the original... It would take us too far today to show fully – we have a different goal today – that the physical body and the etheric body relate to this astral body as ice, for example, relates to water. If a child comes and shows you a piece of ice and you tell him that this is water in solid form, the child may not immediately see it, and you will have to make it clear to him in some way that the ice is water in a different form. Just as the child may not know that ice is just water in a different form, so someone who is accustomed to looking at things from a materialistic point of view does not yet know that the physical body and etheric body is only, basically speaking, let us say, condensed, condensed, crystallized out of this spiritual carrier of joy and sorrow, pleasure and pain, urges, desires and passions and perceptions. Everything that is physical is generated out of the spiritual, let us say condensed, crystallized out of the spiritual. ... You get an idea of this... if you take this as a small theoretical down payment for what spiritual science is gradually showing you comprehensively. Take the very simple two phenomena that a person experiences within himself: the feeling of shame or the feeling that arises when something near us puts people into fear and terror. Fear and terror make him pale, his blood takes on very specific movements, it changes in the body, it goes, if we may say so, from the outer surface to the center. The opposite happens with shame... So we have an external physical process under the influence of mental agitation. This is a small example of how one can see material effects arising from the spiritual. Imagine these effects increasing until the process of building the external physical... the material itself, is built out of the spiritual. Then you have something to which you cannot, admittedly, arrive in an instant, but which you can arrive at through patient study... to which spiritual science can lead you more and more. But now there is one thing by which man stands out above all the visible earthly creatures around him. We come to this when we study a very simple fact of human experience, which is only usually not properly interpreted and paid attention to; you will come to it when you go through a very simple contemplation with me, which is indeed somewhat subtle. Anyone can say “table” to the table, “clock” to the clock, and anyone can pronounce the name given to the external object in the language; but there is only one name, one little name, in the German language that not everyone can pronounce to the one that this name denotes. This is the name that lies in the little word “I”. Only one person can pronounce “I” if this “I” is to mean what it is. If the “I” is to mean you yourself, then no one can ever say “I” to you. You are a you to everyone else, everyone else is a you to you! If the little word “I” is to mean you yourself, then it must resound from the innermost part of the soul itself. That is why all religions and world views... that were based on spiritual science... called this short little word 'I' the unspeakable name of God... so that the power within can pronounce this name, which cannot access the soul through external senses and organs... that was called the divine power, the spark of God that is in us... Yes, you make a god out of man, many say. ... Anyone who makes this accusation can see from another example]... I have taken a drop of water out of the great, all-encompassing sea and I now claim that this drop is the same substance and essence as the sea, but it is not the whole sea... In the same way, the theosophist does not make a god out of the human ego when he declares: This “I” is a drop, a spark of divine substance. ... This “I” and the sum total of powers and principles that enable a person to let this divine, this God, speak within them, we call the fourth link of human essence, that makes man the crown of earthly creation. ... This is what distinguishes him from all other beings on earth. ... Thus, the human being stands before us as a four-part entity... Today, we will not discuss the further, higher aspects of human nature. ... This classification suffices for us today. ... When we consider these aspects of the human being and look at the human being, then in his development from birth to death, then spiritual science shows us that these individual aspects by no means develop in the same way or in the same times. ... When we have a person before us at any age, we do not have them before us in such a way that these four elements are always present in the same way. We only understand the human being when we know that the development of the human being takes place in different ways at different ages... After all, a person's life is preceded by a prenatal life... We know that when a person is born, they have a life behind them in their mother's womb, where their physical body was enclosed on all sides by the physical womb, where all organs have gradually developed to such an extent that when the person sees the light of day, their physical body was previously protected by an outer physical shell... which they now shed... We speak of the external physical birth of a person when the person sheds this physical shell around him, and his physical body is exposed to the external physical elements. Before that, the rays of light could not penetrate the eyes. Had these rays of light penetrated his eyes immediately, these eyes would not have been able to develop into today's human eyes.... And so it is with all organs of the human being.... Only then can he be directly exposed to external impressions and influences when these organs, protected by this cover, have matured for such influences... Now spiritual science also speaks of other births of man. ... When the spiritual seer now looks at man as he is born after his physical birth, he sees how the physical body is handed over to the external physical elements... but the second link of the human being is not yet handed over to the external powers, which act on the etheric body. What we have described as the etheric body is still surrounded by an - albeit ethereal - shell... and we speak of a second birth, through which it also sheds this etheric shell. When a person is born physically, his etheric body still has an etheric mother around it, which protects him, and it protects him until the change of teeth, until the time when the person loses the so-called milk teeth and gradually gets his own teeth, around the seventh year, then the human being is born of his second link; he sheds the protective etheric cover, as with the physical birth the physical mother shell. We will soon learn the full implications of these spiritual facts. But there is still another birth; this occurs because, even though the human being has freed his etheric body from external influences when his teeth change, for example, he is still surrounded by a protective astral mother-shell, as it were, around the third limb of his being, and this continues until sexual maturity. With this sexual maturity, around the age of 14 to 15, this further spiritual birth is also slowly taking place, that is, the astral mother shell is being shed, and thus the astral body of the person becomes free and can be directly exposed to the astral influences... that are working around him. Only later is there a time when, in a similar way, what we call the “ego” is born. ... One can only understand the course of a person's life, and one can only educate a person reasonably, if one knows and applies all of this to the fullest extent. ... Let us now first look at the ascending life. ... This brings us to an important field of human activity, that of education and teaching. Let us consider this and see how it presents itself to us when we consider the human being in terms of his or her entire nature and being. We know that from the time of his physical birth until he changes his teeth, the human being is enveloped in an etheric covering, which he then sheds. If we observe this, we will say to ourselves: We must keep away everything that has a direct effect on the etheric body or life body until this second birth has taken place. For the spiritual seer, it is just as nonsensical to allow direct effects on the etheric body with its etheric mother shell before the birth of the etheric body, as it would be for the ordinary consciousness of a person to allow direct effects on the physical body of the child before its physical birth. The first thing that happens is that the physical body, which was previously under the protective cover, is exposed to direct external physical influences. The time from birth to the seventh year is especially the time when we have to monitor the direct influence of physical elements on the physical human being. The detailed development of this results in many, many rules that spiritual science can provide for a healthy pedagogy. Above all, it is a matter of knowing what is happening during these developmental years until the change of teeth. Spiritual science tells us that up to this point of the change of teeth, the forms, the physical forms of the physical body, are established. ... The forms continue to increase in size only, but the plasticity of the forms, including the finer plasticity of the form, the balance of power in which they will develop, are determined up to the seventh year. And whatever has been neglected in the development of the human being up to that point can never be made up for later; it has been neglected for the whole of life... Because from the seventh year onwards, it becomes possible to influence the etheric body. ... The physical body is then under the influence of the etheric body, which then further regulates growth... It follows that the physical environment must be carefully arranged in the way it is designed until the teeth change. Not only the coarse, but also the finer structural and formative conditions of the physical body are formed under the influence of this physical environment.... A rough comparison:... If you strain any muscle, that is, expose it to what it belongs to, it becomes strong, powerful and expands... this is how it is with all the internal forms of the physical body... SO it is with our visual abilities, our vision... The forces that are in our physical body are tools that serve the soul to perceive the physical world... For example, it is not irrelevant what kind of color environment a person experiences in their physical environment between birth and the age of seven. Depending on the colors we choose for the child's environment, the inner formative forces will develop in opposition to this world of colors. Let us assume, for example, that we have a fidgety child, a nervous child, and in the other case an overly calm, “dead” child, who is “dead” in his behavior, his mannerisms. ... Both types, in order to develop in the appropriate way, must be placed in the right physical environment. ... Someone who only sees the world with their physical eye will probably place a fidgety child in an environment of so-called calming colors, of blue or green, while believing that a calm child should be placed in an environment of red or yellow... Countless mistakes are made here. ... Because the exact opposite is correct. If you want to proceed in the right way, you should, if possible, place a fidgety child in a red or reddish-yellow environment and a calm child in a blue or blue-green one. If you know how the internal structure of the organs is formed, you will be able to see this through pure logic. You stare at a red spot on a white surface and then, after staring at it for some time, you suddenly look at a different spot on the white surface, so you see the green counteraction on the empty white surface... What does this mean? While you are looking at the red color on the outside, the inside of the body tends to develop the opposite color. If you look at the red, the body adjusts itself internally so that it forms the green, and this is important for the internal formation of the plastic organs. ... If you have a restless, nervous child and you give him a red environment, then a countervailing force towards green, blue-green, is formed internally, and this has a calming effect on the plastic forces of the internal organs... Here things are much deeper than an external sensory observation usually shows... Sometimes I have been told: But that is really quite strange. When I work with any lamp that has a red shade, it makes me feel agitated; so why should it have a favorable effect on the child? - ... I have not claimed that a red glow has a favorable effect on a man of 56 years; I have only said that it stimulates the internal organs, the plastic of the internal organs of the child in a calming sense. ... Similarly, something extraordinarily important arises when we consider children's toys from this point of view. You will have often observed that a child with a healthy mind rejects dolls with beautifully painted faces and natural hair, or at least puts them aside soon. Let's take a closer look at this doll and admit to ourselves: it is, of course, hideous... But if you ever make a doll for your child out of an old napkin, you will have a completely different experience. The child will enjoy the so-called beautiful doll for a while. But then the child will soon throw it away and always return to the homemade napkin doll. This is a very correct, healthy instinct. ... For a power is constantly at work in the child to shape the organs plastically. If the child now has this self-made doll in front of them, the following occurs: the child must make an effort to first turn it into a human being through inner imagination; they must first apply forces to the imperfect doll in order to create the human image. This is beneficial for them internally and shapes the internal organs in a more perfect way. These inner plastic forces are not activated when you present the child with such a “beautiful” doll; these forces remain inert, and what should be active internally, the forces of the organs to form, cannot happen. The tools in our physical body, which should be active forces, are formed when we give the child something to do that requires it to be active through its imagination. The child must imagine something that the external object does not give it, it merely stimulates. And people have no idea how much harm they do to children if they do not give them the opportunity to develop this inner counterforce in the appropriate way. ... Oh, the one who looks deeper into human nature also knows something else. He knows that there is a huge difference between keeping a child busy putting together figures out of individual stones and keeping him busy with a toy that gives the impression of being alive, inwardly animated. ... Something completely different happens inside... and vividly brings the body to life... when you give the child a toy that creates the illusion of life through the way it moves when the child plays with it... There used to be old picture books in which whole scenes were presented in moving pictures, whole stories, and which thereby evoked the inner sculpture. They were wonderfully suited to developing the organs in a plastic way during the time when they had to be developed. Those who look more deeply into this want to... when they often and often have to watch with a bleeding soul as everything, absolutely everything, is neglected due to instinctive materialism.... Those who can see into our time with spiritual eyes can trace materialistic thinking back and see how it has been brought about that children have been given construction kits instead of living toys, with which they build something out of individual parts. This is what creates the materialistic mind, much more than materialistic literature... Materialistic theories are the least dangerous aspect of materialism. But if, instead of observing the inner life, a child who is putting together his body, this instrument of the human being, at the time when it should be developing its forms plastically, is concerned with putting the individual parts together, then he comes to imagine that the world is made up of individual clusters of atoms. ... So you see how spiritual science works in practice. But it goes even further. ... Right down to the instincts of eating, you can understand the course of human life and influence its shaping from the perspective of spiritual science. Spiritual science can draw attention to the fact that something that needs to be developed in the child's soul is being held back by certain foods... In the child's soul, the tools for healthy instincts and desires must develop. We do not have a certain desire for nothing. ... That is why they are there, so that when the instinct arises and is satisfied, life is steered in healthy directions. ... See how animals walk across the pasture and carefully choose the foods that are beneficial to them, leaving the others standing... What is the upward development into a human being? It gives man higher gifts, but it exposes him to the possibility of error, which the animal with its instinctive certainty is not exposed to. What matters is that man, with his higher gifts, nevertheless retains this security. And we can preserve this security of healthy instinct for the child if we do not stuff him full of an excess of such substances that kill such an instinct. Overfeeding children with protein-rich food is, many people believe today, the greatest care in the care of young children. But this is not true at all. The moment the child receives too much protein, the moment it is overfed with protein, it loses its sure instincts for nourishment, while another child sometimes rejects what is harmful to it, even down to a glass of water, and desires what is good for it, what is healthy. This is extremely important. It is an example of the practical knowledge of life that can flow from spiritual science. ... We could do a lot if we only wanted to pay attention to the principles of the matter... We can raise the question: What is the law of the human life cycle up to this change of teeth? ... This is described in a word that resonates like a magic [word] for everything that is influenced by these years. Imitation is the magic of education in these years, when the physical body has become accessible to the immediate influence of the outside world. The child strives to emulate what it sees. Therefore, education must, above all, be based on the child's intention to imitate; it should not demand or admonish, as this is not the main thing in these years. The main thing is that the child can follow what it sees during these years, and that nothing happens that the child is not allowed to imitate. ... However, there are a number of points to be considered. Imagine a couple... — I always tell such cases as examples that have really happened — they have a child who is very well-behaved, nothing to complain about, suddenly one day the child has stolen, as they say, from his parents' cash box. The child is so good that it did not use this money for itself, but gave it to others whom it believed needed it. ... You can perhaps imagine that the parents would be outraged if they did not know that during this time, until the permanent teeth have come in – and these things do not abruptly follow one another – during this time, everything is characterized by imitation, the child has always seen that the parents themselves take money out... and what it sees its parents doing is right for the child; it imitates it. To apply moral concepts here, such as stealing or the like, is in no way appropriate. The child only imitates what its parents demonstrate to it. Therefore, we know that in terms of everything we want to cultivate in the child, a plastic molding must be called forth from within through imitation. Therefore, we must build everything on imitation in the child during this first period, that is, the adults around him must not do or say anything that the child should not also do in exactly the same way. ... This is of profound significance. ... If imitation is the magic word for education until the seventh year of a child's development, then from the time when the teeth change and the etheric or life body is freed for direct external influence ... the word 'authority' applies, and succession. What can be understood by these words must be the guiding principle of education for these years. ... Just as children must be able to imitate what is going on around them until their teeth change... so now, in the second phase of life, there must be someone alongside them who can be called an authority. ... In detail, we can say something like this: only after sexual maturity does the time come when a person, through the powers of their mind, understands what is good or bad, clever or stupid.... We do young people an injustice if we place too much emphasis on intellectual insight and education before this time, prematurely. During this time, until sexual maturity is reached, it is necessary for a personality of some kind to stand beside the child and determine what is true or false, good or bad, beautiful or ugly. These concepts must have an authoritative effect on the child at this age, not through mental judgments but through the power of the personality.... And it is the greatest joy for a child to have such personalities in their lives during these years, to whom they can look up as natural authorities who are truly worthy of emulation. A person becomes mature enough to judge when, during these years of their life, they have been influenced by an authoritative personality whom they looked up to and followed in awe. This is a beneficial power that affects a person throughout their life. Oh, if only people could know what it means for a person's whole life when something like this happens to them, such as hearing about a much-admired personality in the family whom they have not yet seen. Timid reverence already sits in his soul, the heart pounds until he is allowed to see the personality for the first time.... These are the most beautiful, wonderful feelings in his soul for the rest of his life, the moments of celebration that ignite forces that are as important as hardly anything else for the whole life of a person until death. Everything that one carries within the etheric body, the body that carries all growth, but also temperament, habits, and character, is decisively influenced in this way during this time between the change of teeth and sexual maturity. And it is important, for example, that this etheric or life body is also the carrier of memory. Therefore, it is essential that conscious care is taken during this time, above all, in the development of memory. In this respect, there is confusion has arisen. Precisely in our time, as a result of materialistic basic views, many educational efforts work towards having children do mental work as early as possible, so that they calculate and do similar things based on their own judgment. That looks quite progressive, but it is nevertheless extremely harmful for the development of the growing human being. First you have to have a store of knowledge and insights in your memory; only then can you form judgments about them. The time for judgment comes with sexual maturity. Until then, it is a time for purely memorized learning. The memory must be formed in the time until then. It is not important – as one would like to say today – that the child is already able to judge, for example, what he or she has to learn in history. It is precisely this that is so damaging, to want to evoke judgment at this time. In this time, the events must be presented to the soul in a purely factual and objective way, in large images, through an authority that is taken for granted. These events must first live in the soul of the child; only then has the time for judgment come. And what is very important at this time is that, because the etheric body now receives the direct influence of the forces that express themselves in memory and in other spiritual faculties, we will particularly develop these forces during this time, the qualities that are anchored in the etheric body. Above all, what is anchored there is what is called the pictorial power of human vision. ... Many people today look at the world so unimaginatively and soberly because the world has not been presented to them in vital images during this time. ... Man should first get to know this world in images. If you want to give people a healthy foundation for the higher supernatural truths, then you have to teach them the corresponding images at this age. During this time, the truths must first be brought to people in images and symbols if they are to be truly grasped later on. If in later life a person is to be able to say to himself: The human soul is immortal, when the human being passes through the gate of death, then the soul rises to higher regions, only the body remains behind and decays, then this is properly prepared in this age, when one tells the child, for example, “Watch the caterpillar as it transforms into a chrysalis and thus falls into deathly rigidity, and then how the chrysalis breaks something and the butterfly rises from the breaking shell into an airy, light existence." But it would be a mistake for teachers to use these images today. They no longer have an effect because those who use these images no longer believe in what they are supposed to express. Only when the image is a reality for them, then something in it takes effect, which naturally passes over into the soul of the child and works as a force that later awakens the right knowledge. For the spiritual scientist, the given is an image of immortality in reality, in truth. For him, it is not something that he laboriously devises with his mind, but rather, for him, life passes through a series of stages... and on the lower stage, the butterfly's emergence from the chrysalis is truly what, on the higher stage, is the soul's emergence from the dying body. If this is the case for you, then you will naturally be able to bring about an emotional understanding in the child first, in the magical touch of imagery, before you cultivate the sober judgments of the mind, which is only made possible by the correct understanding of the whole personality at a later stage. Here we see reason in something that is often viewed as unreasonable today. I know what misunderstandings we are exposed to in this matter, but it must be said not out of a reactionary sense, but out of a sense of truth. How clever we have become, many think today, how they look back on our forefathers, who told their children all kinds of tall tales. ... Today we must no longer tell such lies to children. Our forefathers taught their children things that are not true at all, such as the story of the stork. But, again, it must be said that, although not out of reactionary sentiment, their way of doing so was much more correct than the modern approach. For once you have seen through things, there is nothing more childish and naive you can say to a child than that nothing more is needed for a human being to come into the world than the purely physical process. ... That is fundamentally wrong from a deeper perspective. The reality is: the human being comes from a spiritual world... from a spiritual existence before birth, and the physical process is only the mediator of the spiritual person's entry into this sensual world, and what our enlightened people want to teach children today is much, much more untrue and unreal than the old stork tale. ... Everything that has been said in the image of the flying was the image of the spiritual for our ancestors. ... The image of something flying always appears when the spiritual is to be pointed out in a fairy tale. For example, in the children's song “Fly, little bird, fly... your mother is in Pommerland”... Pommerland is not Pommern... Pommerland is Kinderland... “fly, little beetle, fly”... the same image is everywhere, and it is the basis of the stork fairy tale. ... Man from a different developmental period before the time when he should have soberly understood it in everyday life, believed in the stork fairy tale himself, because at the time the magic touch of imagery had been breathed over what is in the world around us. ... And it is quite different when I have first had a mysterious natural process in front of me in the picture... first carried this image around with me for a long time and only then was faced with the task of understanding it intellectually. Only then did I mature and then I absorb what came later in a completely different way. This shows us, in turn, how we must know those forces that develop at a certain age. ... And so we can specify for each age what it is in detail. ... So then, around the 14th or 15th year, the time of sexual maturity is an important stage. For it is at this time that the growing human being's astral mother-shell is cast off and the astral body, to which, for example, judgment and many other things adhere, is released to the direct influence of the outer world. Therefore, it is only during this time that the human being is mature enough to be exposed to external judgment and to acquire independent judgment. If we bring this judgment forward, we arrive at these things that force their way into today's life as formidable dark sides... where people grow into them without consideration... Only when puberty has occurred should independent judgment be formed on the basis of what has developed in terms of imagery, of noble feelings... under the influence of authority.... otherwise we see that the youngest people, who have not even been born yet, people who should first learn to mature their judgment, are already making their appearance with their own judgment at the time when they should only be developing it.... But this is also the time when the astral body emerges with the instincts and drives for life that are inherent in it. ... These forces arise in the form that we call “youthful ideals”, “springtime hopes”, hopes for life. A dry, sober person can easily look down on what he has experienced in his youthful soul as a mere infatuation. Even if none of this materializes, even if these are hopes that are left out in the cold in life, the fact remains that they were hopes, ideals, and that is during the time when the astral body gradually emerges. What matters is not that hopes are fulfilled, that ideals are realized, but that they are there. For they are forces in the soul and as forces they are formative, they give life inwardness, they give life strength, even if they have been there as hopes that were later destroyed. Therefore, we must do everything to ensure that these spring hopes of life are developed during this time, that they are there. Then the time gradually comes for the human being to give birth to his or her full self, which now approaches the world around in a completely free way. ... And just as there is an ascending life, there is also a descending life in the second half. Just a few words about this: the birth and gradual development of the ego comes to an end with normal life around the age of 35. At this point, the human being is at the zenith of life. Everything that was laid down in him at birth has emerged in him by this time. But now something else begins; now begins the time when, just as before, things have been shaped out of life, just as before, the abilities have been developed, so now begins the time when they are processed and consumed in pieces, from the age of 35 onwards, when in normal life, first of all, the forces of the astral body are gradually consumed inwardly. We see all astral things gradually receding again. The person becomes sober, develops more sense of reality... he becomes what, in our times, is fashion, what one can call a Philistine. While until then the person had more to do with himself, from the age of 35 begins the time when he acquires value for his environment. Before that, he had to use his time to mature his judgment and enter into a firm, definite relationship between his ego and the world around him. Now, what he is begins to have value for his fellow human beings. Now his judgment has weight, now people start to listen to him, now he radiates valuable things that he himself has to consume. Now he shows, even to an intimate observer, whether the ascending path was the right one. Now it becomes clear how barren and empty are the judgments of someone who has not grown under the influence of ideals in the period from 14 to 21 years... In order to radiate, one must first have acquired the right kind of thing at the right time. All esoteric development is subject to strict laws... those who have become teachers in this spiritual science strictly observe the rules... and today things are such that, precisely because of our culture, no one is let loose on the world by the appointed authorities before this mid-life... The true secret teachers do not allow their students to present themselves to the world with what they are supposed to give before they are ready. Everyone's tongue is only loosened at this midpoint in life. And if personalities appear before this time, you can be sure that they are doing so without a mandate, without the authorization of the individuals behind our movement. On average, no one is let loose on people before this time... Only the nonsense of our time makes it... that in these areas... the nonsense that young people, who are far from being finished with themselves, also appear in these areas... And then we see further how, roughly from the 1940s onwards, a new epoch is reached with the descending life, even if no such great regularity can be observed here as in the ascending life. ... Now that the astral body has been consumed, the time comes when the human being also begins to consume his etheric body, which he built up in the period from the change of teeth to sexual maturity. This is then depleted again around the fiftieth year... You can see this in certain signs that occur at this age. Try to look at life in its truth, and you will see how, in this period, the memory is just what cannot receive new impressions, new forces. On the other hand, just what was in this etheric body, that comes out just now, that which this etheric body has taken in, that occurs in the sharpest, strongest memory at this age. ... Observe life from this point of view and you will experience time and again how people of this age come back again and again and have a good memory of what was incorporated into them at those ages. See the sense of well-being that old people experience at this time when they can tell their memories of their youth over and over again... and consider what good you can do them by enabling them to tell such stories... And then, in the last stage of life, see how little by little the physical body is consumed too... see how the bones become more and more calcified, how they become more physical. The cartilages ossify... this last stage of life also consumes the physical body... Once the ascending life is properly regulated, another thing will show up, which is often ignored today. From the age of 35 onwards, a person radiates such judgments, which are decisive and have value for his environment... Then he comes to not only radiate judgments for his environment, but also to the fact that what he radiates as authority may also be considered authoritative for his environment... First the judgments become decisive, then in the penultimate epoch of life the life radiations themselves become decisive and a value for the environment... and last of all... man gains such judgment, such inner fullness, that what he then gives of himself has something mature not only for his time, but for all times. Those who see into things therefore also see in a completely different way... why certain people speak of this time in a very special way... With Dante, for example, you can see this in the very first lines of his “Divina Commedia”. There you can see how he says: “In the midst of life I saw all this...” And so you can look at all the great minds in this way... And if you look at a person like Goethe... you have to take into account the difference between what he created when he was in ascending development and what he created after the middle of his life. That by which he has become for humanity what he is to it, that falls after the middle of life... But if we look at the second half of life, we see that nothing external is developed for the temporal human being, for the outer limbs, physical body, etheric and astral body. This is consumed. But the moment the outer shell begins to disintegrate, that is when enrichment and the development of the essential begins. The forces of the inner being, the forces of the actual self, become ever more powerful and powerful in that which lives in these shells, for which the outer being begins the descending development. In the second half of life, the eternal, the lasting, the immortal in man develops, and when death occurs, we see how the outer shell falls away and how, even though it may have seemed for a while as if the inner life has receded, then we see how what the person has... how, at death, as a birth for the spiritual, the eternal, how that emerges at death as what he has developed valuably within himself, in his inwardness. Death is physical death, but spiritually for the spiritual world it is a new birth and... this is prepared in the second half of life. At this time, when the outer layers gradually die off, the human being shapes what remains, what is eternal about him. The great poet sensed that when the outer layers die away, the inner form, the spiritual form, that which is lasting and eternal, develops within. Great minds have always sensed and said what a wisdom that deeply penetrates the spiritual effects must confirm in every detail... What Schiller said cannot be presented to you as blind faith, but as fully valid knowledge. Today, only brief, cursory allusions could be given... about the course of human life... If we allow ourselves to be completely permeated by this practice of life, which can arise from spiritual science, then we will experience that life is shaped in such a way that we become hopeful, able to live and work through it, because we understand correctly in every moment:
Question and Answer
Rudolf Steiner: In this respect, we must learn to place the principle of freedom above all else in relation to the developing human being. It is easy to believe that these or those ideals are the right ones at first. But we must not create stereotyped ideals for ourselves. The developing human being is a mystery that the educator has to solve, and he learns just as much from the mysterious human being who is gradually emerging from his or her shells and allows himself to be guided by this human being to the ideals that are right for him or her. So we learn to respect the freely developing individuality when we know that the spirit is realizing itself... The question can only be solved by education in life in each individual case... However, there are certain basic ideals that are appropriate almost everywhere... above all, there is a beautiful ideal: a human being who is as complete as possible in every single detail, whom we can justifiably depict from history. ... when we create figures of world history and let our own powers be ignited by the great figures... but when we then come up with practical life, we can also ignite these ideals with practical life... what is important is to keep alive the sense of the transformation of the world, to maintain the sense that the world can change. ... On the real meaning of ideals: Fichte, “On the purpose of the scholar”. |
| 68d. The Nature of Man in the Light of Spiritual Science: The Mystery of the Human Temperaments
19 Jan 1909, Karlsruhe Translated by Frances E. Dawson Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 68d. The Nature of Man in the Light of Spiritual Science: The Mystery of the Human Temperaments
19 Jan 1909, Karlsruhe Translated by Frances E. Dawson Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
It is an oft-repeated and a justifiable opinion, with regard to all the realms of human spiritual life, that man's greatest riddle here in our physical life is man himself. And we may truly say that a large part of our scientific activity, of our reflection, and of much besides in man's life of thought, is applied to the solving of this human riddle, to discerning a little wherein the essence of human nature consists. Natural science and spiritual science try to solve from different sides this great riddle comprised in the word Man. In the main, all the more profound natural scientific research seeks to attain its final goal by bringing together all the processes of nature, and so forth, in order to comprehend the external laws. And all spiritual science seeks the sources of existence for the sake of comprehending, of fathoming, man's being and destiny. If then, on the one hand, it is unquestioned that in general man's greatest riddle is man himself, we may say that in relation to life this expression may have a still deeper significance, in that it is necessary on the other hand to emphasize what each of us feels upon meeting another person: namely, that fundamentally each single person is in turn an enigma for others and for himself because of his special nature and being. Ordinarily, when we speak of this human enigma, we have in mind man in general, man without distinction regarding this or that individuality; and certainly many problems appear for us when we wish to understand human nature in general. But today we have not to do with the general riddles of existence, but rather with that enigma, not less significant for life, which each person we meet presents to us. For how endlessly varied are human beings in their deepest individual essence! When we survey human life we shall have to be especially attentive to this riddle which each person presents, for our entire social life, our relation of man to man, must depend more upon how in individual cases we are able to approach with our feeling, with our sensibility, rather than merely with our intelligence, that individual human enigma which stands before us so often each day, with which we have to deal so often. How difficult it is regarding the people we meet to come to a clear knowledge of the various sides of their nature, and how much depends in life upon our coming to such clear knowledge regarding those people with whom we come in touch. We can of course only approach quite gradually the solution of the whole riddle of the human individual, of which each person presents a special phase, for there is a great gap between what is called human nature in general and that which confronts us in each human individual. Spiritual science, or as we call it more recently, Anthroposophy, will have a special task precisely regarding this individual enigma—man. Not only must it give us information about what man is in general, but it must be, as you know, a knowledge which flows directly into our daily life, into all our sensibilities and feelings. Since our feelings and sensibilities are unfolded in the most beautiful way in our attitude toward our fellow men, the fruit of spiritual science, of spiritual scientific knowledge, will be revealed the most beautifully in the view we take of our fellow men because of this knowledge. When in life a person stands before us, we must always, in the sense of this spiritual science, or Anthroposophy, take into consideration that what we perceive outwardly of the person is only one part, only one member, of the human being. To be sure, an outer material view of man regards as the whole man what this outer perception and the intellect connected with it are able to give us. Spiritual science shows us, however, that the human being is something very, very complicated. And often, when one goes more deeply into this complexity of human nature, the individual is then also seen in the right light. Spiritual science has the task of showing us what the innermost kernel of the human being is; what we can see with the eyes and grasp with the hands is only the outer expression, the outer shell. And we may hope to come to an understanding of the external also if we are able to penetrate into the spiritual inner part. In the great gap between what we may call human nature in general and what confronts us in each individual, we see nevertheless many homogeneous characteristics in whole human groups. To these belong those human qualities which today form the subject of our consideration, and which we usually call the temperament. We need only utter the word ‘temperament’ to see that there are as many riddles as men. Within the basic types, the basic colorings, we have such a multiplicity and variety among individuals that we can indeed say that the real enigma, of existence is expressed in the peculiar basic disposition of the human being which we call temperament. And when the riddles intervene directly in practical life, the basic coloring of the human being plays a role. When a person stands before us, we feel that we are confronted by something of this basic disposition. Therefore it is to be hoped that spiritual science is able to give also the necessary information about the nature of the temperaments. For though we must admit that the temperaments spring from within, they nevertheless express themselves in the whole external appearance of the individual. By means of an external observation of nature, however, the riddle of man is not to be solved; we can approach the characteristic coloring of the human being only when we learn what spiritual science has to say about him. It is of course true that each person confronts us with his own temperament, but we can still distinguish certain groups of temperaments. We speak chiefly of four types, as you know: the sanguine, the choleric, the phlegmatic, and the melancholic temperament. And even though this classification is not entirely correct in so far as we apply it to individuals—in individuals the temperaments are mixed in the most diverse way, so we can only say that one temperament or another predominates in certain traits—still we shall in general classify people in four groups according to their temperaments. The fact that the temperament is revealed on the one side as something which inclines toward the individual, which makes people different, and on the other side joins them again to groups, proves to us that the temperament must on the one side have something to do with the innermost essence of the human being, and on the other must belong to universal human nature. Man's temperament, then, is something which points in two directions; and therefore it will be necessary, if we wish to solve the mystery, to ask on the one hand: In how far does the temperament point to what belongs to universal human nature? and then again on the other: How does it point to the essential kernel, to the actual inner being of the individual? If we put the question, it is natural that spiritual science seems called upon to give enlightenment, for spiritual science must lead us to the innermost essential kernel of the human being. As he confronts us on earth, he appears to be placed in a universality, and again on the other side he appears as an independent entity. In the light of spiritual science man stands within two life streams which meet when he enters earth existence. And here we are at the focal point of the consideration of human nature according to the methods of spiritual science. We learn that we have in the human being, first of all, that which places him in his line of heredity. The one stream leads us from the individual man back to his parents, grandparents, and further ancestors. He shows the characteristics inherited from father, mother, grandparents, and all preceding ancestors farther and farther back. And these attributes he transmits again to his descendants. That which flows down from ancestors to the individual man we designate in life and in science as inherited attributes and characteristics. A man is placed in this way within what we may call the line of heredity; and it is known that an individual bears within him, even in the very kernel of his being, qualities which we must certainly trace back to heredity. Very much about an individual is explicable if we know his ancestry, so to speak. How deeply true are the words uttered with regard to his own personality by Goethe, who had such a deep knowledge of the soul:
Here we see how this great knower of human nature has to point even to moral qualities when he wishes to refer to inherited characteristics. Everything we find as transmitted from ancestors to descendants interprets for us the individual person in a certain respect, but only in a certain respect; for what he has inherited from his ancestors gives us only one side of the human being. Of course the present-day materialistic conception would like to seek in the line of ancestry for everything under the sun, would like even to trace back a man's spiritual being (his spiritual qualities) to ancestry; and it never wearies of declaring that even a man's qualities of genius are explicable if we find signs, indications, of such characteristics in this or that ancestor. Those who hold such a view would like to compile the human personality, so to speak, from what is found scattered among the ancestors. Anyone who penetrates more deeply into human nature will of course be struck by the fact that beside these inherited attributes, in each man something confronts us which we cannot characterize otherwise than by saying: That is his very own; we cannot say, as a result of close observation, that it is transmitted from this or that ancestor. Spiritual science comes in here and tells us what it has to say about it. Today we are able to present only sketchily what is involved in these questions, to indicate only sketchily the findings of spiritual science. Spiritual science tells us: Certainly it is true that the human being is placed in the stream which we may call the stream of heredity, the stream of inherited attributes. Besides that, however, something else appears in an individual, namely, the innermost spiritual kernel of his being. In this are united what the individual brings with him from the spiritual world and what the father and mother, the ancestors, are able to give to him. With that which flows down in the stream of the generations is united something else which has its origin, not in the immediate ancestors, the parents, and not in the grandparents, but which comes from quite other realms, something which passes from one existence to another. On the one side we may say: A man has this or that from his ancestors. But if we watch an individual develop from childhood on, we see how from the center of his nature something evolves which is the fruit of foregoing lives, something he never can have inherited from his ancestors. What we see in the individual, when we penetrate to the depths of his soul, we can only explain to ourselves when we know a great comprehensive law, which is really only the consequence of many natural laws. It is the law of repeated earth lives, so greatly tabooed at the present time. This law of re-embodiment, the succession of earth lives, is only a specific case of a general cosmic law. It will not appear so paradoxical to us when we think the matter over. Let us observe a lifeless mineral, a rock crystal. It has a regular form. If it is destroyed, nothing of its form remains which could pass over to other rock crystals. The new rock crystal receives nothing of its form. Now if we rise from the world of minerals to the world of plants, it becomes clear to us that a plant cannot originate according to the same law as a rock crystal. A plant can originate only when it is derived from the parent plant. Here the form is maintained and passes over to the other entity. If we rise to the animal world, we find that a development of species takes place. We see that the 19th century considered this discovery of the development of the species as among its greatest results. Not only does one form proceed from another, but each animal in the body of the mother repeats the earlier forms, the lower evolutionary phases of his ancestors. Among the animals we have a rising gradation of species. Among human beings, however, we have not only a gradation of species, a development of kinds, but we have a development of the individual. What a man acquires in the course of his life through education, through experience, is just as little lost as the animal's succession of ancestors. A time will come when a man's essential core is traced back to a previous existence. It will be recognized that the human being is a fruit of an earlier existence. This law will have a peculiar destiny in the world, a destiny similar to that of another law. The opposition against which this teaching has to assert itself will be overcome, just as the opinion of the scientists of earlier centuries was overcome: that the living can originate from the lifeless. Even into the 17th century the learned and the unlearned had no doubt whatever that from ordinary lifeless things not only lower animals could be evolved, but that earthworms, even fish, could originate from ordinary river slime. The first who declared energetically that the living can originate only from the living was the great Italian natural scientist, Francesco Redi (1627 to 1697), who showed that the living derives only from the living. That is a law which is only the forerunner of another: namely, that the soul-spiritual derives from the soul-spiritual. On account of this teaching he was attacked, and only with difficulty escaped the fate of Giordano Bruno. Today burning is no longer the custom; but anyone who appears with a new truth today, for instance, anyone who wishes to trace back the soul-spiritual element to the soul-spiritual, would not be burned, to be sure, but would be looked upon as a fool. A time will come when it will be considered nonsense to think that a man lives only once, that there is not something permanent which unites itself with his inherited characteristics. Spiritual science shows how that which is our own nature unites with what is given to us by heredity. That is the other stream into which the individual is placed, the stream with which the present civilization does not wish to have anything to do. Spiritual science leads us to the great facts of so-called re-embodiment, of reincarnation, and of karma. It shows us that we have to take into consideration the innermost essential kernel of man as that which descends from the spiritual world and unites with something which is given by the line of heredity, unites with what it is possible for the father and mother to give to the individual. For the spiritual scientist that which originates from the line of heredity envelops this essential kernel with outer sheaths. And as we must go back to father and mother and other ancestors for what we see in the physical man as form and stature, and so forth, for the characteristics which belong to his outer being, so we must go back to something entirely different, to an earlier life, if we wish to comprehend a man's innermost being; perhaps far, far back, beyond all hereditary transmission, we may have to seek the human being's spiritual kernel which has existed for thousands of years, and which during these thousands of years has entered again and again into existence, again and again has led an earth-life, and now in the present existence has united itself again to what it is possible for father and mother to give. Every single human being, when he enters into physical life, has a succession of lives behind him. And this has nothing to do with what belongs to the line of heredity. We should have to go back more than centuries if we wished to investigate what was his former life when he passed through the gate of death. After he has passed through the gate of death he lives in other forms of existence in the spiritual world. And when again the time comes to experience a life in the physical world, he seeks his parents. Thus we must go back to the spirit of man and his earlier incarnations, if we wish to explain what in him confronts us now as the soul-spiritual part. We must go back to his earlier incarnations, to what he acquired in course of them. We have to consider how he lived at that time, what he brought with him, as the causes of what the individual possesses today in the new life as tendencies, dispositions, abilities for this or that. For each person brings with him from his former life certain qualities of his life. Certain qualities and his destiny he brings with him to a certain degree. According as he has performed this or that deed, he calls forth the reaction, and feels himself thus to be surrounded by the new life. So he brings with him from earlier incarnations the inner kernel of his being and envelops it with what is given him by heredity. Certainly this one thing should be mentioned, because it is important, since actually our present time has little inclination to recognize this inner kernel of being, or to look upon the idea of reincarnation as anything but a fantastic thought. It is considered today to be poor logic, and we shall hear materialistic thinkers objecting over and over again that what is in man arises entirely through heredity. Just look at the ancestors, he says, and you will discover that this or that trait, this or that peculiarity, existed in some ancestor, that all the individual traits and qualities can be explained by tracing them in the ancestors. The spiritual scientist can also point to that fact, and he has done so. For example, in a musical family musical talent is inherited, etc. That is all supposed to support the theory of heredity. Indeed, the law is expressed point blank, that seldom does genius appear at the beginning of a generation; genius stands at the end of a line of heredity. And that is supposed to be a proof that genius is inherited. Here one proceeds from the standpoint that some person has a definite characteristic—he is a genius. Someone traces back the peculiar abilities of the genius, seeks in the past among his ancestors, finds in some ancestor signs of a similar characteristic, picks out something here and there, finds this quality in one, that in another, and then shows how they finally flowed together in the genius who appeared at the end of the generation; and he infers from it that genius is transmitted. For anyone whose thinking is direct and logical that could at best prove the opposite. If finding qualities of genius among the ancestors proves anything, what does it prove? Surely nothing else than that man's essential being is able to express itself in life according to the instrument of the body. It proves nothing more than that a man comes out wet if he falls into the water. Really it is no more intelligent than if some one wishes to call our special attention to the fact that if a man falls into the water he gets wet. It is only natural that he takes up something of the element into which he is placed. Surely it is quite self-evident that the qualities of the ancestors would be carried by that which has flowed down through the line of heredity, and has finally been given through father and mother to the particular human being who has descended from the spiritual world. The individual clothes himself in the sheaths which are given to him by his ancestors. What is intended to be presented as proof of heredity could much better be looked upon as proof that it is not heredity. For if genius were inherited, it would have to appear at the beginning of the generations and not stand at the end of a line of heredity. If anyone were to show that a genius has sons and grandchildren to whom the qualities of genius are transmitted, then he would be able to prove that genius is inherited; but that is just not the case. It is limping logic which wishes to trace back man's spiritual qualities to the succession of ancestors. We must trace back spiritual qualities to that which a man has brought with him from his earlier incarnations. If now we consider the one stream, that which lives in the line of heredity, we find that there the individual is drawn into a stream of existence through which he gets certain qualities: We have before us some one possessing the qualities of his family, his people, his race. The various children of the same parents have characteristics conditioned in this way. If we consider the true individual nature of a human being, we must say that the soul-spiritual essential kernel is born into the family, the people, the race; it envelops itself with what is given by the ancestors, but it brings with it purely individual characteristics. So we must ask ourselves: How is harmony established between a human essence which perhaps has acquired centuries earlier this or that quality and the outer covering with which it is now to envelop itself, and which bears the characteristics of family, people, race, and so forth? Is it possible for harmony to exist here? Is it not something in the highest sense individual which is thus brought into earth life, and is not the inherited part at variance with it? Thus the great question arises: How can that which has its origin in quite other worlds, which must seek father and mother for itself, unite with the physical body? How can it clothe itself with the physical attributes through which the human being is placed within the line of heredity? We see then in a person confronting us the flowing together of two streams; of these two streams each human being is composed. In him we see on the one side what comes to him from his family, and on the other what has developed from the individual's innermost being; namely, a number of predispositions, characteristics, inner capacities and outer destiny. An agreement must be effected. We find that a man must adapt himself to this union, in accordance with his innermost being on the one side, and on the other in accordance with that which is brought to him from the line of heredity. We see how a man bears to a great degree the physiognomy of his ancestors; we could put him together, so to speak, from the sum of his various ancestors. Since at first the inner essential kernel has nothing to do with what is inherited, but must merely adapt itself to what is most suitable to it, we shall see that it is necessary for a certain mediation to exist for that which has lived perhaps for centuries in an entirely different world and is again transplanted into another world; the spirit being of man must have something here below to which it is related; there must be a bond, a connecting link, between the special individual human being and humanity in general, into which he is born through family, people, race. Between these two, namely what we bring with us from our earlier life and what our family, ancestors and race imprint upon us, there is a mediation, something which bears more general characteristics, but at the same time is capable of being individualized. That which occupies this position between the line of heredity and the line which represents our individuality is expressed by the word TEMPERAMENT. In that which confronts us in the temperament of a person we have something in a certain way like a physiognomy of his innermost individuality. We understand thus how the individuality colors, by means of the qualities of temperament, the attributes inherited in the succession of generations. Temperament stands right in the middle between what we bring with us as individuals and what originates from the line of heredity. When the two streams unite, the one stream colors the other. They color each other reciprocally. Just as blue and yellow, let us say, unite in green, so do the two streams in man unite in what we call temperament. That which mediates between all inner characteristics which he brings with him from his earlier incarnation, on the one side, and on the other what the line of heredity brings to him, comes under the concept temperament. It now takes its place between the inherited characteristics and what he has absorbed into his inner essential being. It is as if upon its descent to earth this kernel of being were to envelop itself with a spiritual nuance of that which awaits it here below, so that in proportion as this kernel of being is able best to adapt itself to this covering for the human being, the kernel of being colors itself according to that into which it is born and to a quality which it brings with it. Here shine forth the soul qualities of man and his natural inherited attributes. Between the two is the temperament—between that by which a man is connected with his ancestors and that which he brings with him from his earlier incarnations. The temperament balances the eternal with the transitory. This balancing occurs through the fact that what we have learned to call the members of human nature come into relation with one another in a quite definite way. We understand this in detail, however, only when we place before our mind's eye the complete human nature in the sense of spiritual science. Only from spiritual science is the mystery of the human temperament to be discovered. This human being as he confronts us in life, formed by the flowing together of these two streams, we know as a four-membered being. So we shall be able to say when we consider the entire individual: This complete human being consists of the physical body, the etheric body or body of formative forces, the astral body, and the ego. In that part of man perceptible to the outer senses, which is all that materialistic thought is willing to recognize, we have first, according to spiritual science, only a single member of the human being, the physical body, which man has in common with the mineral world. That part which is subject to physical laws, which man has in common with all environing outer nature, the sum of chemical and physical laws, we designate in spiritual science as the physical body. Beyond this, however, we recognize higher super-sensible members of human nature which are as actual and essential as the outer physical body. As first super-sensible member, man has the etheric body, which becomes part of his organism and remains united with the physical body throughout the entire life; only at death does a separation of the two take place. Even this first super-sensible member of human nature—in spiritual science called the etheric or life body; we might also call it the glandular body—is no more visible to our outer eyes than are colors to those born blind. But it exists, actually and perceptibly exists, for that which Goethe calls the eyes of the spirit, and it is even more real than the outer physical body, for it is the builder, the moulder, of the physical body. During the entire time between birth and death this etheric or life body continuously combats the disintegration of the physical body. Any kind of mineral product of nature—a crystal, for example—is so constituted that it is permanently held together by its own forces, by the forces of its own substance. That is not the case with the physical body of a living being; here the physical forces work in such a way that they destroy the form of life, as we are able to observe after death, when the physical forces destroy the life-form. That this destruction does not occur during life, that the physical body does not conform to the physical and chemical forces and laws, is due to the fact that the etheric or life-body is ceaselessly combating these forces. The third member of the human being we recognize in the bearer of all pleasure and suffering, joy and pain, instincts, impulses, passions, desires, and all that surges to and fro as sensations and ideas, even all concepts of what we designate as moral ideals, and so on. That we call the astral body. Do not take exception to this expression. We could also call it the “nerve-body.” Spiritual science sees in it something real, and knows indeed that this body of impulses and desires is not an effect of the physical body, but the cause of this body. It knows that the soul-spiritual part has built up for itself the physical body. Thus we already have three members of the human being, and as man's highest member we recognize that by means of which he towers above all other beings, by means of which he is the crown of earth's creation: namely, the bearer of the human ego, which gives him in such a mysterious, but also in such a manifest way, the power of self-consciousness. Man has the physical body in common with his entire visible environment, the etheric body in common with the plants and animals, the astral body with the animals. The fourth member, however, the ego, he has for himself alone; and by means of it he towers above the other visible creatures. We recognize this fourth member as the ego-bearer, as that in human nature by means of which man is able to say “I” to himself, to come to independence. Now what we see physically, and what the intellect which is bound to the physical senses can know, is only an expression of these four members of the human being. Thus, the expression of the ego, of the actual ego-bearer, is the blood in its circulation. This “quite special fluid” is the expression of the ego. The physical sense expression of the astral body in man is, for example, among other things, the nervous system. The expression of the etheric body, or a part of this expression, is the glandular system; and the physical body expresses itself in the sense organs. These four members confront us in the human being. So we shall be able to say, when we observe the complete human being, that he consists of physical body, etheric body, astral body, and ego. That which is primarily physical body, which the human being carries in such a way that it is visible to physical eyes, clearly bears, first of all, when viewed from without, the marks of heredity. Also those characteristics which live in man's etheric body, in that fighter against the disintegration of the physical body, are in the line of heredity. Then we come to his astral body, which in its characteristics is much more closely bound to the essential kernel of the human being. If we turn to this innermost kernel, to the actual ego, we find what passes from incarnation to incarnation, and appears as an inner mediator, which rays forth its essential qualities. Now in the whole human nature all the separate members work into each other; they act reciprocally. Because two streams flow together in man when he enters the physical world, there arises a varied mixture of man's four members, and one, so to speak, gets the mastery over the others, and impresses its color upon them. Now according as one or another of these members comes especially into prominence, the individual confronts us with this or that temperament. The particular coloring of human nature, what we call the actual shade of the temperament, depends upon whether the forces, the different means of power, of one member or of another predominate, have a preponderance over the others. Man's eternal being, that which goes from incarnation to incarnation, so expresses itself in each new embodiment that it calls forth a certain reciprocal action among the four members of human nature: ego, astral body, etheric body and physical body; and from the interaction of these four members arises the nuance of human nature which we characterize as temperament. When the essential being has tinged the physical and etheric bodies, that which arises because of the coloring thus given will act upon each of the other members; so that the way an individual appears to us with his characteristics depends upon whether the inner kernel acts more strongly upon the physical body, or whether the physical body acts more strongly upon it. According to his nature the human being is able to influence one of the four members, and through the reaction upon the other members the temperament originates. The human essential kernel, when it comes into re-embodiment, is able through this peculiarity to introduce into one or another of its members a certain surplus of activity. Thus it can give to the ego a certain surplus strength; or again, the individual can influence his other members because of having had certain experiences in his former life. When the ego of the individual has become so strong through its destiny that its forces are noticeably dominant in the fourfold human nature, and it dominates the other members, then the choleric temperament results. If the person is especially subject to the influence of the forces of the astral body, then we attribute to him a sanguine temperament. If the etheric or life-body acts excessively upon the other members, and especially impresses its nature upon the person, the phlegmatic temperament arises. And when the physical body with its laws is especially predominant in the human nature, so that the spiritual essence of being is not able to overcome a certain hardness in the physical body, then we have to do with a melancholic temperament. Just as the eternal and the transitory intermingle, so does the relation of the members to one another appear. I have already told you how the four members express themselves outwardly in the physical body. Thus, a large part of the physical body is the direct expression of the physical life principle of man. The physical body as such comes to expression only in the physical body; hence it is the physical body which gives the keynote in a melancholic. We must regard the glandular system as the physical expression of the etheric body. The etheric body expresses itself physically in the glandular system. Hence in a phlegmatic person the glandular system gives the keynote in the physical body. The nervous system and, of course, what occurs through it we must regard as the physical expression of the astral body. The astral body finds its physical expression in the nervous system; therefore in a sanguine person the nervous system gives the keynote to the physical body. The blood in its circulation, the force of the pulsation of the blood, is the expression of the actual ego. The ego expresses itself in the circulation of the blood, in the predominating activity of the blood; it shows itself especially in the fiery vehement blood. One must try to penetrate more subtly into the connection which exists between the ego and the other members of the human being. Suppose, for example, that the ego exerts a peculiar force in the life of sensations, ideas, and the nervous system; suppose that in the case of a certain person everything arises from his ego, everything that he feels he feels strongly, because his ego is strong—we call that the choleric temperament. That which has received its character from the ego will make itself felt as the predominating quality. Hence, in a choleric the blood system is predominant. The choleric temperament will show itself as active in a strongly pulsating blood; in this the element of force in the individual makes its appearance, in the fact that he has a special influence upon his blood. In such a person, in whom spiritually the ego, physically the blood, is particularly active, we see the innermost force vigorously keeping the organization fit. And as he thus confronts the outer world, the force of his ego will wish to make itself felt. That is the effect of this ego. By reason of this, the choleric appears as one who wishes to assert his ego in all circumstances. All the aggressiveness of the choleric, everything connected with his strong will-nature, may be ascribed to the circulation of the blood. When the astral body predominates in an individual, the physical expression will lie in the functions of the nervous system, that instrument of the rising and falling waves of sensation; and that which the astral body accomplishes is the life of thoughts, of images, so that the person who is gifted with the sanguine temperament will have the predisposition to live in the surging sensations and feelings and in the images of his life of ideas. We must understand clearly the relation of the astral body to the ego. The astral body functions between the nervous system and the blood system. So it is perfectly clear what this relation is. If only the sanguine temperament were present, if only the nervous system were active, being quite especially prominent as the expression of the astral body, then the person would have a life of shifting images and ideas; in this way a chaos of images would come and go. He would be given over to all the restless flux from sensation to sensation, from image to image, from idea to idea. Something of that sort appears if the astral body predominates, that is, in a sanguine person, who in a certain sense is given over to the tide of sensations, images, etc., since in him the astral body and the nervous system predominate. It is the forces of the ego which prevent the images from darting about in a fantastic way. Only because these images are controlled by the ego does harmony and order enter in. Were man not to check them with his ego, they would surge up and down without any evidence of control by the individual. In the physical body it is the blood which principally limits, so to speak, the activity of the nervous system. Man's blood circulation, the blood flowing in man, is that which lays fetters, so to speak, upon what has its expression in the nervous system; it is the restrainer of the surging feelings and sensations; it is the tamer of the nerve-life. It would lead too far if I were to show you in all its details how the nervous system and the blood are related, and how the blood is the restrainer of this life of ideas. What occurs if the tamer is not present, if a man is deficient in red blood, is anemic? Well, even if we do not go into the more minute psychological details, from the simple fact that when a person's blood becomes too thin, that is, has a deficiency of red corpuscles, he is easily given over to the unrestrained surging back and forth of all kinds of fantastic images, even to illusion and hallucination—you can still conclude from this simple fact that the blood is the restrainer of the nerve-system. A balance must exist between the ego and the astral body—or speaking physiologically, between the blood and the nervous system—so that one may not become a slave of his nervous system, that is, to the surging life of sensation and feeling. If now the astral body has a certain excess of activity, if there is a predominance of the astral body and its expression, the nerve-system, which the blood restrains to be sure, but is not completely able to bring to a condition of absolute balance, then that peculiar condition arises in which human life easily arouses the individual's interest in a subject, but he soon drops it and quickly passes to another one; such a person cannot hold himself to an idea, and in consequence his interest can be immediately kindled in everything which meets him in the outer world, but the restraint is not applied to make it inwardly enduring; the interest which has been kindled quickly evaporates. In this quick kindling of interest and quick passing from one subject to another we see the expression of the predominating astral element, the sanguine temperament. The sanguine person cannot linger with an impression, he cannot hold fast to an image, cannot fix his attention upon one subject. He hurries from one life impression to another, from perception to perception, from idea to idea; he shows a fickle disposition. That can be especially observed with sanguine children, and in this case it may cause one anxiety. Interest is easily aroused, a picture begins easily to have an effect, quickly makes an impression, but the impression soon vanishes again. When there is a strong predominance in an individual of the etheric or life-body—that which inwardly regulates the processes of man's life and growth—and the expression of this etheric body—that system which brings about the feeling of inner well-being or of discomfort—then such a person will be tempted to wish just to remain in this feeling of inner comfort. The etheric body is a body which leads a sort of inner life, while the astral body expresses itself in outer interests, and the ego is the bearer of our activity and will, directed outward. If then this etheric body, which acts as life-body, and maintains the separate functions in equilibrium, an equilibrium which expresses itself in the feeling of life's general comfort—when this self-sustained inner life, which chiefly causes the sense of inner comfort, predominates, then it may occur that an individual lives chiefly in this feeling of inner comfort, that he has such a feeling of well-being, when everything in his organism is in order, that he feels little urgency to direct his inner being toward the outer world, is little inclined to develop a strong will. The more inwardly comfortable he feels, the more harmony will he create between the inner and outer. When this is the case, when it is even carried to excess, we have to do with a phlegmatic person. In a melancholic we have seen that the physical body, that is, the densest member of the human being, rules the others. A man must be master of his physical body, as he must be master of a machine if he wishes to use it. But when this densest part rules, the person always feels that he is not master of it, that he cannot manage it. For the physical body is the instrument which he should rule completely through his higher members. But now this physical body has dominion and sets up opposition to the others. In this case the person is not able to use his instrument perfectly, so that the other principles experience repression because of it, and disharmony exists between the physical body and the other members. This is the way the hardened physical system appears when it is in excess. The person is not able to bring about flexibility where it should exist. The inner man has no power over his physical system; he feels inner obstacles. They show themselves through the fact that the person is compelled to direct his strength upon these inner obstacles. What cannot be overcome is what causes sorrow and pain; and these make it impossible for the individual to look out upon his contemporary world in an unprejudiced way. This constraint becomes a source of inner grief, which is felt as pain and listlessness, as a sad mood. It is very easy to feel that life is filled with pain and sorrow. Certain thoughts and ideas begin to be enduring; the person becomes gloomy, melancholic. There is a constant arising of pain. This mood is caused by nothing else than that the physical body sets up opposition to the inner ease of the etheric body, to the mobility of the astral body, and to the ego's certainty of its goal. And if we thus comprehend the nature of the temperaments through sound knowledge, many a thing in life will become clear to us; but it will also become possible to handle in a practical way what we otherwise could not do. Look at much which directly confronts us in life! What we see there as the mixture of the four members of human nature meets us clearly and significantly in the outer picture. We need only observe how the temperament comes to expression externally. Let us, for instance, take the choleric person, who has a strong firm center in his inner being. If the ego predominates, the person will assert himself against all outer oppositions; he wants to be in evidence. This ego is the restrainer. Those pictures are consciousness-pictures. The physical body is formed according to its etheric body, the etheric body according to its astral body. This astral body would fashion man, so to speak, in the most varied way. But because growth is opposed by the ego in its blood forces, the balance is maintained between abundance and variety of growth. So when there is a surplus of ego, growth can be retarded. It positively retards the growth of the other members; it does not allow the astral body and the etheric body their full rights. In the choleric temperament you are able to recognize clearly in the outer growth, in all that confronts us outwardly, the expression of what is inwardly active, the actual deep inner force-nature of the man, of the complete ego. Choleric persons appear as a rule as if growth had been retarded. You can find in life example after example; for instance, from spiritual history the philosopher, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, the German choleric. Even in external appearance he is recognizable as such, since in his outer form he gave the impression of being retarded in growth. Thereby he reveals clearly that the other members of his being have been held back by the excess of ego. Not the astral body with its forming capacity is the predominant member, but the ego rules, the restrainer, the limiter of the formative forces. Hence we see as a rule in those who are preeminently men of strong will, where the ego restrains the free formative force of the astral body, a small compact figure. Take another classical example of the choleric: Napoleon, the “little General,” who remained so small because the ego held back the other members of his being. There you have the type of the retarded growth of the choleric. There you can see how this force of the ego works out of the spirit, so that the innermost being is manifest in the outer form. Observe the physiognomy of the choleric! Take in comparison the phlegmatic person! How indefinite are his features; how little reason you have to say that such a form of forehead is suited to the choleric. In one organ it is shown especially clearly whether the astral body or the ego works formatively, that is in the eye, in the steady, assured aspect of the eye of the choleric. As a rule we see how this strongly-kindled inner light, which turns everything luminously inward, sometimes is expressed in a black, a coal-black eye, because, according to a certain law, the choleric does not permit the astral body to color that very thing which his ego-force draws inward, that which is colored in another person. Observe such an individual in his whole bearing. One who is experienced can almost tell from the rear view whether a certain person is a choleric. The firm walk proclaims the choleric, so to speak. Even in the step we see the expression of strong ego-force. In the choleric child we already notice the firm tread; when he walks on the ground, he not only sets his foot on it, but he treads as if he wanted to go a little bit farther, into the ground. The complete human individual is a copy of this innermost being, which declares itself to us in such a way. But naturally, it is not a question of my maintaining that the choleric person is short and the sanguine tall. We may compare the form of a person only with his own growth. It depends upon the relation of the growth to the entire form. Notice the sanguine person! Observe what a strange glance even the sanguine child has; it quickly lights upon something, but just as quickly turns to something else; it is a merry glance; an inner joy and gaiety shine in it; in it is expressed what comes from the depths of the human nature, from the mobile astral body, which predominates in the sanguine person. In its mobile inner life this astral body will work upon the members; and it will also make the person's external appearance as flexible as possible. Indeed, we are able to recognize the entire outer physiognomy, the permanent form and also the gestures, as the expression of the mobile, volatile, fluidic astral body. The astral body has the tendency to fashion, to form. The inner reveals itself outwardly; hence the sanguine person is slender and supple. Even in the slender form, the bony structure; we see the inner mobility of the astral body in the whole person. It comes to expression for example in the slim muscles. It is also to be seen in his external expression. Even one who is not clairvoyant can recognize from the rear whether a person is of sanguine or choleric temperament; and to be able to do this one need not be a spiritual scientist. In a sanguine person we have an elastic and springing walk. In the hopping, dancing walk of the sanguine child we see the expression of the mobile astral body. The sanguine temperament manifests itself especially strongly in childhood. See how the formative tendency is expressed there; and even more delicate attributes are to be found in the outer form. If in the choleric person we have sharply-cut facial features, in the sanguine they are mobile, expressive, changeable. And likewise there appears in the sanguine child a certain inner possibility to alter his countenance. Even to the color of the eyes we could confirm the expression of the sanguine person. The inwardness of the ego-nature, the self-sufficient inwardness of the choleric, meets us in his black eye. Look at the sanguine person in whom the ego-nature is not so deep-rooted, in whom the astral body pours forth all its mobility—there the blue eye is predominant. These blue eyes are closely connected with the individual's invisible inner light, the light of the astral body. Thus many attributes could be pointed out which reveal the temperament in the external appearance. Through the four-membered human nature we learn to understand clearly this soul riddle of the temperaments. And indeed, a knowledge of the four temperaments, springing from a profound perception of human nature, has been handed down to us from ancient times. If we thus understand human nature, and know that the external is only the expression of the spiritual, then we learn to understand man in his relation even to the externalities, to understand him in his whole process of becoming; and we learn to recognize what we must do concerning ourself and the child with regard to temperament. In education especially notice must be taken of the kind of temperament that tends to develop in the child. For life's wisdom, as for pedagogy, an actual living knowledge of the nature of the temperaments is indispensable, and both would profit infinitely from it. And now let us go further. Again we see how the phlegmatic temperament also is brought to expression in the outer form. In this temperament there predominates the activity of the etheric body, which has its physical expression in the glandular system and its soul expression in a feeling of ease, in inner balance. If in such a person everything is not only normally in order within, but if, beyond this normality, these inner formative forces of ease are especially active, then their products are added to the human body; it becomes corpulent, it expands. In the largeness of the body, in the development of the fatty parts, we see that which the inner formative forces of the etheric body are especially working on. The inner sense of ease of the phlegmatic person meets us in all that. And who would not recognize in this lack of reciprocal action between the inner and the outer the cause of the ofttimes slovenly, dragging gait of the phlegmatic person, whose step will often not adapt itself to the ground; he does not step properly, so to speak; does not put himself in relation to things. That he has little control over the forms of his inner being you can observe in the whole man. The phlegmatic temperament confronts one in the immobile, indifferent countenance, even in the peculiarly dull, colorless appearance of the eye. While the eye of the choleric is fiery and sparkling, we can recognize in that of the phlegmatic the expression of the etheric body, focused only upon inner ease. The melancholic is one who cannot completely attain mastery over the physical instrument, one to whom the physical instrument offers resistance, one who cannot cope with the use of this instrument. Look at the melancholic, how he generally has a drooping head, has not the force in himself to stiffen his neck. The bowed head shows that the inner forces which adjust the head perpendicularly are never able to unfold freely. The glance is downward, the eye sad, unlike the black gleam of the choleric eye. We see in the peculiar appearance of the eye that the physical instrument makes difficulties for him. The walk, to be sure, is measured, firm, but not like the walk of the choleric, the firm tread of the choleric; it has a certain kind of dragging firmness. All this can be only indicated here; but the life of the human being will be much, much more understandable to us if we work in this way, if we see the spirit activating the forms in such a way that the external part of the individual can become an expression of his inner being. So you see how significantly spiritual science can contribute to the solution of this riddle; but only if you face the whole reality, to which the spiritual also belongs, and do not stop merely with the physical reality, can this knowledge be practically applied in life. Therefore only from spiritual science can this knowledge flow in such a way as to benefit the whole of humanity as well as the individual. Now if we know all that, we can also learn to apply it. Particularly it must be of interest to learn how we can handle the temperaments pedagogically in childhood. For in education the kind of temperament must be very carefully observed; with children it is especially important to be able to guide and direct the developing temperament. But later also it is still important, for anyone in self-education. For the person who wishes to train himself it is invaluable that he observe what is expressed in his temperament. I have pointed out to you here the fundamental types, but naturally in life they do not often appear thus pure. Each person has only the fundamental tone of a temperament, besides which he has something of the others. Napoleon, for example, had in him much of the phlegmatic temperament, although he was a choleric. If we would govern life practically, it is important to be able to allow that which expresses itself physically to work upon our soul. How important this is we can see best of all if we consider that the temperaments can degenerate, that what may appear to us as one-sidedness can also degenerate. What would the world be without the temperaments—if people had only one temperament? The most tiresome place you could imagine! The world would be dreary without the temperaments, not only in the physical, but also in the higher sense. All variety, beauty, and all the richness of life are possible only through the temperaments. Do we not see how everything great in life can be brought about just through the one-sidedness of the temperaments, but also how these can degenerate in their one-sidedness? Are we not troubled about the child because we see that the choleric temperament can degenerate to malice, the sanguine to fickleness, the melancholic to gloom, etc.? In the question of education in particular, and also in self-education, will not the knowledge and estimation of the temperaments be of essential value to the educator? We must not be misled into depreciating the value of the temperament because it is a one-sided characteristic. In education the important thing is not to equalize the temperaments, to level them, but to bring them into the right track. We must clearly understand that the temperament leads to one-sidedness, that the most radical phase of the melancholic temperament is madness; of the phlegmatic, imbecility; of the sanguine, insanity; of the choleric, all those explosions of diseased human nature which result in frenzy, and so forth. Much beautiful variety results from the temperaments, because opposites attract each other; nevertheless, the deification of the one-sidedness of temperament very easily causes harm between birth and death. In each temperament there exists a small and a great danger of degeneracy. With the choleric person there is the danger that in youth his ego will be determined by his irascibility, by his lack of self-control. That is the small danger. The great danger is the folly which wishes to pursue, from the impulse of his ego, some kind of individual goal. In the sanguine temperament the small danger is that the person will lapse into fickleness. The great danger is that the rising and falling tide of sensations may result in insanity. The small danger for the phlegmatic is lack of interest in the outer world; the great danger is stupidity or idiocy. The small danger in the melancholic is gloominess, the possibility that he may not be able to extricate himself from what rises up within him. The great danger is madness. When we contemplate all that, we shall see that a tremendously significant task in practical life lies in the directing and guiding of the temperaments. It is important for the educator to be able to say to himself: What will you do, for example, in the case of a sanguine child? Here one must try to learn from the knowledge of the entire nature of the sanguine temperament how to proceed. If other points of view must be considered concerning the education of the child, it is also necessary that temperament, as a subject in itself, be taken into account. But in order to guide the temperaments the principle to be observed is that we must always reckon with what is there and not with what is not there. We have a child of sanguine temperament before us, which could easily degenerate into fickleness, lack of interest in important things, and, instead, become quickly interested in other things. The sanguine child is the quickly comprehending, but also the quickly forgetting child, whose interest it is difficult to hold upon anything whatever, just because interest in one subject is quickly lost and passes over to another. This can grow into the most frightful one-sidedness, and it is possible to notice the danger if we look into the depths of human nature. In the case of such a child a material-minded person will immediately come forward with a prescription and say: If you have a sanguine child to bring up, you must bring it into reciprocal activity with other children. But a person who thinks realistically in the right sense says: If you begin with the sanguine child by working upon forces which it does not at all possess, you will accomplish nothing with it. You could exert your powers ever so seriously to develop the other members of human nature, but these simply do not predominate in this child. If a child has a sanguine temperament, we cannot help him along in development by trying to beat interests into him; we cannot pound in something different from what his sanguine temperament is. We should not ask, What does the child lack? What are we to beat into him? But we should ask, What as a rule does a sanguine child possess? And that is what we must reckon with. Then we shall say to ourselves: We do not alter these characteristics by trying to induce any sort of opposite quality in this child. With regard to these things which are rooted in the innermost nature of man we must take into consideration that we can only bend them. Thus we shall not be building upon what the child does not possess, but upon what he does possess. We shall build exactly upon that sanguine nature, upon that mobility of the astral body, and not try to beat into him what belongs to another member of human nature. With a sanguine child who has become one-sided we must just appeal to his sanguine temperament. If we wish to have the right relation with this child, we must take special notice of something. For from the first it becomes evident to the expert that if the child is ever so sanguine, there is still something or other in which he is interested, that there is one interest, one genuine interest for each sanguine child. It will generally be easy to arouse interest in this or that subject, but it will quickly be lost again. There is one interest, however, which can be enduring even for the sanguine child. Experience shows this; only it must be discovered. And that which is found to hold a special interest must be kept in mind. And whatever it is that the child does not pass by with fickle interest we must try to bring before him as a special fact, so that his temperament extends to something which is not a matter of indifference to him. Whatever he delights in, we must try to place in a special light; the child must learn to use his sanguineness. We can work in such a way that we begin first of all with the one thing that can always be found, with the forces which the child has. He will not be able to become lastingly interested in anything through punishment and remonstrance. For things, subjects, events, he will not easily show anything but a passing, changeable interest; but for one personality, especially suited to a sanguine child—experience will show this—there will be a permanent, continuous interest, even though the child is ever so fickle. If only we are the right personality, or if we are able to bring him into association with the right personality, the interest will appear. It is only necessary to search in the right way. Only by the indirect way of love for one personality, is it possible for interest to appear in the sanguine child. But if that interest, love for one person, is kindled in him, then through this love straightway a miracle happens. This love can cure a child's one-sided temperament. More than any other temperament, the sanguine child needs love for one personality. Everything must be done to awaken love in such a child. Love is the magic word. All education of the sanguine child must take this indirect path of attachment to a certain personality. Therefore parents and teachers must heed the fact that an enduring interest in things cannot be awakened by drumming it into the sanguine child, but they must see to it that this interest is won by the roundabout way of attachment to a personality. The child must develop this personal attachment; one must make himself lovable to the child; that is one's duty to the sanguine child. It is the responsibility of the teacher that such a child shall learn to love the personality. We can still further build up the education upon the child's sanguine nature itself. The sanguine nature reveals itself, you know, in the inability to find any interest which is lasting. We must observe what is there. We must see that all kinds of things are brought into the environment of the child in which he has shown more than the ordinary interest. We should keep the sanguine child busy at regular intervals with such subjects as warrant a passing interest, concerning which he is permitted to be sanguine, so to speak, subjects not worthy of sustained interest. These things must be permitted to affect the sanguine nature, permitted to work upon the child; then they must be removed so that he will desire them again, and they may again be given to him. We must cause these things to work upon the child as the objects of the ordinary world work upon the temperament. In other words, it is important to seek out for a sanguine child those objects toward which he is permitted to be sanguine. If we thus appeal to what exists rather than to something which does not exist, we shall see—and practical experience will prove it—that as matter of fact the sanguine force, if it becomes one-sided, actually permits itself to be captured by serious subjects. That is attained as by an indirect path. It is good if the temperament is developed in the right way during childhood, but often the adult himself has to take his education in hand later in life. As long, indeed, as the temperaments are held in normal bounds, they represent that which makes life beautiful, varied, and great. How dull would life be if all people were alike with regard to temperament. But in order to equalize a one-sidedness of temperament, a man must often take his self-education in hand in later life. Here again one should not insist upon pounding into oneself, as it were, a lasting interest in any sort of thing; but he must say to himself: According to my nature I am sanguine; I will now seek subjects in life which my interest may pass over quickly, in which it is right that the interest should not be lasting, and I will just occupy myself with that in which I may with complete justification lose interest in the very next moment. Let us suppose that a parent should fear that in his child the choleric temperament would express itself in a one-sided way. The same treatment cannot be prescribed as for the sanguine child; the choleric will not be able easily to acquire love for a personality. He must be reached through something else in the influence of person upon person. But in the case of the choleric child also there is an indirect way by which the development may always be guided. What will guide the education here with certainty is: Respect and esteem for an authority. For the choleric child one must be thoroughly worthy of esteem and respect in the highest sense of the word. Here it is not a question of making oneself loved through the personal qualities, as with the sanguine child, but the important thing is that the choleric child shall always have the belief that the teacher understands the matter in hand. The latter must show that he is well informed about the things that take place in the child's environment; he must not show a weak point. He must endeavor never to let the choleric child notice that he might be unable to give information or advice concerning what is to be done. The teacher must see to it that he holds the firm reins of authority in his hands, and never betray the fact that he is perhaps at his wits' end. The child must always keep the belief that the teacher knows. Otherwise he has lost the game. If love for the personality is the magic word for the sanguine child, then respect and esteem for the worth of a person is the magic word for the choleric. If we have a choleric child to train we must see to it before everything else that this child shall unfold, bring to development, his strong inner forces. It is necessary to acquaint him with what may present difficulties in the outer life. For the choleric child who threatens to degenerate into one-sidedness, it is especially necessary to introduce into the education that which is difficult to overcome, so as to call attention to the difficulties of life by producing serious obstacles for the child. Especially must such things be put in his way as will present opposition to him. Oppositions, difficulties, must be placed in the path of the choleric child. The effort must be put forth not to make life altogether easy for him. Hindrances must be created so that the choleric temperament is not repressed, but is obliged to come to expression through the very fact that certain difficulties are presented which the child must overcome. The teacher must not beat out, educate out, so to speak, a child's choleric temperament, but he must put before him just those things upon which he must use his strength, things in connection with which the choleric temperament is justified. The choleric child must of inner necessity learn to battle with the objective world. The teacher will therefore seek to arrange the environment in such a way that this choleric temperament can work itself out in overcoming obstacles; and it will be especially good if these obstacles pertain to little things, to trifles; if the child is made to do something on which he must expend tremendous strength, so that the choleric temperament is strongly expressed, but actually the facts are victorious, the strength employed is frittered away. In this way the child gains respect for the power of facts which oppose what is expressed in the choleric temperament. Here again there is another indirect way in which the choleric temperament can be trained. Here it is necessary first of all to awaken reverence, the feeling of awe, to approach the child in such a way as actually to arouse such respect, by showing him that we can overcome difficulties which he himself cannot yet overcome; reverence, esteem, particularly for what the teacher can accomplish, for his ability to overcome objective difficulties. That is the proper means: Respect for the ability of the teacher is the way by which the choleric child in particular may be reached in education. It is also very difficult to manage the melancholic child. What must we do if we fear the threatened one-sidedness of the melancholic temperament of the child, since we cannot cram in what he does not possess? We must reckon with the fact that it is just repressions and resistance that he has power within himself to cling to. If we wish to turn this peculiarity of his temperament in the right direction, we must divert this force from subjective to objective activity. Here it is of very special importance that we do not build upon the possibility, let us say, of being able to talk him out of his grief and pain, or otherwise educate them out of him; for the child has the tendency to this excessive reserve because the physical instrument presents hindrances. We must particularly build upon what is there, we must cultivate what exists. With the melancholic child it will be especially necessary for the teacher to attach great importance to showing him that there is suffering in the world. If we wish to approach this child as a teacher, we must find here also the point of contact. The melancholic child is capable of suffering, of moroseness; these qualities exist in him and we cannot flog them out, but we can divert them. For this temperament too there is one important point: Above all we must show the melancholic child how people can suffer. We must cause him to experience justifiable pain and suffering in external life, in order that he may come to know that there are things concerning which he can experience pain. That is the important thing. If you try to entertain him, you drive him back into his own corner. Whatever you do, you must not think you have to entertain such a child, to try to cheer him up. You should not divert him; in that way you harden the gloominess, the inner pain. If you take him where he can find pleasure, he will only become more and more shut up within himself. It is always good if you try to cure the young melancholic, not by giving him gay companionship, but by causing him to experience justifiable pain. Divert his attention from himself by showing him that sorrow exists. He must see that there are things in life which cause suffering. Although it must not be carried too far, the important point is to arouse pain in connection with external things in order to divert him. The melancholic child is not easy to guide; but here again there is a magic means. As with the sanguine child the magic word is love for a personality, with the choleric, esteem and respect for the worth of the teacher, so with the melancholic child the important thing is for the teachers to be personalities who in some way have been tried by life, who act and speak from a life of trial. The child must feel that the teacher has really experienced suffering. Bring to his attention in all the manifold occurrences of life the trials of your own destiny. Most fortunate is the melancholic child who can grow up beside a person who has much to give because of his own hard experiences; in such a case soul works upon soul in the most fortunate way. If therefore at the side of the melancholic child there stands a person who, in contrast to the child's merely subjective, sorrowful tendencies, knows how to tell in a legitimate way of pain and suffering that the outer world has brought him, then such a child is aroused by this shared experience, this sympathy with justified pain. A person who can show in the tone and feeling of his narration that he has been tried by destiny, is a blessing to such a melancholic child. Even in arranging the melancholic child's environment, so to speak, we should not leave his predispositions unconsidered. Hence, it is even advantageous if—strange as it may sound—we build up for the child actual hindrances, obstructions, so that he can experience legitimate suffering and pain with regard to certain things. It is the best education for such a child if the existing tendency to subjective suffering and grief can be diverted by being directed to outer hindrances and obstructions. Then the child, the soul of the child, will gradually take a different direction. In self-education also we can again use this method: we must always allow the existing tendencies, the forces present in us, to work themselves out, and not artificially repress them. If the choleric temperament, for example, expresses itself so strongly in us that it is a hindrance, we must permit this existing inner force to work itself out by seeking those things upon which we can in a certain sense shatter our force, dissipate our forces, preferably upon insignificant, unimportant things. If on the other hand we are melancholic, we shall do well to seek out justifiable pain and suffering in external life, in order that we may have opportunity to work out our melancholy in the external world; then we shall set ourselves right. Let us pass on to the phlegmatic temperament. With the phlegmatic child it will be very difficult for us if his education presents us with the task of conducting ourselves in an appropriate way toward him. It is difficult to gain any influence over a phlegmatic person. But there is one way in which an indirect approach may be made. Here again it would be wrong, very wrong indeed, if we insisted upon shaking up a person so inwardly at ease, if we thought we could pound in some kind of interests then and there. Again we must take account of what he has. There is something in each case which will hold the attention of the phlegmatic person, especially the phlegmatic child. If only through wise education we build up around him what he needs, we shall be able to accomplish much. It is necessary for the phlegmatic child to have much association with other children. If it is good for the others also to have playmates, it is especially so for the phlegmatic. He must have playmates with the most varied interests. There is nothing to appeal to in the phlegmatic child. He will not interest himself easily in objects and events. One must therefore bring this child into association with children of like age. He can be trained through the sharing of the interests—as many as possible—of other personalities. If he is indifferent to his environment, his interest can be kindled by the effect upon him of the interests of his playmates. Only by means of that peculiar suggestive effect, only through the interests of others, is it possible to arouse his interest. An awakening of the interest of the phlegmatic child will result through the incidental experiencing of the interest of others, the sharing of the interests of his playmates, just as sympathy, sharing of the experience of another human destiny, is effective for the melancholic. Once more: To be stimulated by the interest of others is the correct means of education for the phlegmatic. As the sanguine child must have attachment for one personality, so must the phlegmatic child have friendship, association with as many children as possible of his own age. That is the only way the slumbering force in him can be aroused. Things as such do not affect the phlegmatic. With a subject connected with the tasks of school and home you will not be able to interest the little phlegmatic; but indirectly, by way of the interests of other souls of similar age you can bring it about. If things are reflected in this way in others, these interests are reflected in the soul of the phlegmatic child. Then also we should particularly see to it that we surround him with things and cause events to occur near him concerning which apathy is appropriate. One must direct the apathy to the right objects, those toward which one may rightly be phlegmatic. In this way quite wonderful things can sometimes be accomplished in the young child. But also one's self-education may be taken in hand in the same way in later life, if it is noticed that apathy tends to express itself in a one-sided way; that is, by trying to observe people and their interests. One thing more can also be done, so long as we are still in a position to employ intelligence and reason at all: we can seek out the very subjects and events which are of the greatest indifference to us, toward which it is justifiable for us to be phlegmatic. We have now seen again how, in the methods of education based upon spiritual science, we build upon what one has and not upon what is lacking. So we may say that it is best for the sanguine child if he may grow up guided by a firm hand, if some one can show him externally aspects of character through which he is able to develop personal love. Love for a personality is the best remedy for the sanguine child. Not merely love, but respect and esteem for what a personality can accomplish is the best for the choleric child. A melancholic child may be considered fortunate if he can grow up beside some one who has a bitter destiny. In the corresponding contrast produced by the new insight, by the sympathy which arises for the person of authority, and in the sharing of the justifiably painful destiny,—in this consists what the melancholic needs. They develop well if they can indulge less in attachment to a personality, less in respect and esteem for the accomplishment of a personality, but can reach out in sympathy with suffering and justifiably painful destinies. The phlegmatic is reached best if we produce in him an inclination towards the interests of other personalities, if he can be stirred by the interests of others. The sanguine should be able to develop love and attachment for one personality. Thus do we see in these principles of education how spiritual science goes right into the practical questions of life; and when we come to speak about the intimate aspects of life, spiritual science shows just in these very things how it works in practice, shows here its eminently practical side. Infinitely much could we possess of the art of living, if we would adopt this realistic knowledge of spiritual science. When it is a case of mastering life, we must listen for life's secrets, and these lie behind the sense perceptible. Only real spiritual science can explain such a thing as the human temperaments, and so thoroughly fathom them that we are able to make this spiritual science serve as a benefit and actual blessing of life, whether in youth or in age. We can also take self-education in hand here; for when it is a question of self-education, the temperaments can be particularly useful to us. We become aware with our intellect that our sanguineness is playing us all kinds of tricks, and threatens to degenerate to an unstable way of life; we hurry from subject to subject. This condition can be countered if only we go about it in the right way. The sanguine person will not, however, reach his goal by saying to himself: You have a sanguine temperament and you must break yourself of it. The intellect applied directly is often a hindrance in this realm. On the other hand, used indirectly it can accomplish much. Here the intellect is the weakest soul-force of all. In presence of the stronger soul-forces, such as the temperaments, the intellect can do very little; it can work only indirectly. If some one exhorts himself ever so often: “For once now hold fast to one thing”—then the sanguine temperament will again and again play him bad tricks. He can reckon only with a force which he has. Behind the intellect there must be other forces. Can a sanguine person count upon anything at all but his sanguine temperament? And in self-education too it is necessary to try to do also what the intellect can do directly. A man must reckon with his sanguineness; self-exhortations are fruitless. The important thing is to show sanguineness in the right place. One must try to have no interest in certain things in which he is interested. We can with the intellect provide experiences for which the brief interest of the sanguine person is justified. Let him try to place himself artificially in such situations; to put in his way as much as possible what is of no interest to him. If then we bring about such situations in ever such small matters, concerning which a brief interest is warranted, it will call forth what is necessary. Then it will be noticed, if only one works at it long enough, that this temperament develops the force to change itself. The choleric can likewise cure himself in a particular way, if we consider the matter from the point of view of spiritual science. For the choleric temperament it is good to choose such subjects, to bring about through the intellect such conditions as are not changed if we rage, conditions in which we reduce ourselves ad absurdum by our raging. When the choleric notices that his fuming inner being wishes to express itself, he must try to find as many things as possible which require little force to be overcome; he must try to bring about easily superable outer facts, and must always try to bring his force to expression in the strongest way upon insignificant events and facts. If he thus seeks out insignificant things which offer him no resistance, then he will bring his one-sided choleric temperament again into the right course. If it is noticed that melancholia is producing one-sidedness, one must try directly to create for himself legitimate outer obstacles, and then will to examine these legitimate outer obstacles in their entire aspect, so that what one possesses of pain and the capacity for suffering is diverted to outer objects. The intellect can accomplish this. Thus the melancholic temperament must not pass by the pain and suffering of life, but must actually seek them, must experience sympathy, in order that his pain may be diverted to the right objects and events. If we are phlegmatic, have no interests, then it is good for us to occupy ourselves as much as possible with quite uninteresting things, to surround ourselves with many sources of ennui, so that we are thoroughly bored. Then we shall completely cure ourselves of our apathy, completely break ourselves of it. The phlegmatic person therefore does well to decide with his intellect that he must take interest in a certain thing, that he must search for things which are really only worthy to be ignored. He must seek occupations in which apathy is justified, in which he can work out his apathy. In this way he conquers it, even when it threatens to degenerate into one-sidedness. Thus we reckon with what is there and not with what is lacking. Those however who call themselves realists believe, for example, that the best thing for a melancholic is to produce conditions that are opposed to his temperament. But anyone who actually thinks realistically will appeal to what is already in him. So you see spiritual science does not divert us from reality and from actual life; but it will illuminate every step of the way to the truth; and it can also guide us everywhere in life to take reality into consideration. For those people are deluded who think they can stick to external sense appearance. We must go deeper if we wish to enter into this reality; and we shall acquire an understanding for the variety of life if we engage in such considerations. Our sense for the practical will become more and more individual if we are not impelled to apply a general prescription: namely, you must not drive out fickleness with seriousness, but see what kind of characteristics the person has which are to be stimulated. If then man is life's greatest riddle, and if we have hope that this riddle will be solved for us, we must turn to this spiritual science, which alone can solve it for us. Not only is man in general a riddle to us, but each single person who confronts us in life, each new individuality, presents a new riddle, which of course we cannot fathom by considering it with the intellect. We must penetrate to the individuality. And here too we can allow spiritual science to work out of the innermost center of our being; we can make spiritual science the greatest impulse of life. So long as it remains only theory, it is worthless. It must be applied in the life of the human being. The way to this goal is possible, but it is long. It becomes illuminated for us if it leads to reality. Then we become aware that our views are transformed. Knowledge is transformed. It is prejudice to believe that knowledge must remain abstract; on the contrary, when it enters the spiritual realm it permeates our whole life's work; our entire life becomes permeated by it. Then we face life in such a way that we have discernment for the individuality, which enters even into feeling and sensation and expresses itself in these, and which possesses great reverence and esteem. Patterns are easy to recognize; and to wish to govern life according to patterns is easy; but life does not permit itself to be treated as a pattern. Only insight will suffice, insight which is transformed into a feeling one must have toward the individuality of man, toward the individuality in the whole of life. Then will our conscientious spiritual knowledge flow into our feeling, so to speak, in such a way that we shall be able to estimate correctly the riddle which confronts us in each separate human being. How do we solve the riddle which each individual presents to us? We solve it by approaching each person in such a way that harmony results between him and us. If we thus permeate ourselves with life's wisdom, we shall be able to solve the fundamental riddle of life which is the individual man. It is not solved by setting up abstract ideas and concepts. The general human riddle can be solved in pictures; this individual riddle, however, is not to be solved by this setting up of abstract ideas and concepts; but rather must we approach each individual person in such a way that we bring to him direct understanding. That is possible, however, only when we know what lies in the depths of the soul. Spiritual science is something which slowly and gradually pours itself into our entire soul so that it renders the soul receptive not only to the large relations but also to the finer details. In spiritual science it is a fact that, when one soul approaches another, and this other requires love, love is given. If it requires something else, that will be given. Thus by means of such true life wisdom we create social foundations, and that means at each moment to solve a riddle. Anthroposophy works not by means of preaching, exhortation, harping on morals, but by creating a social basis on which one man is able to understand another. Spiritual science is thus the sub-soil of life, and love is the blossom and fruit of such a life, stimulated by spiritual science. Therefore spiritual science may claim that it is establishing something which will provide a base for the most beautiful goal of the mission of man: genuine, true, human love. In our sympathy, in our love, in the manner in which we approach the individual human being, in our conduct, we should learn the art of living through spiritual science. If we would permit life and love to stream into feeling and sensibility, human life would be a beautiful expression of the fruit of this spiritual science. We learn to know the individual human being in every respect when we perceive him in the light of spiritual science. We learn to perceive even the child in this way; we learn little by little to respect, to value, in the child the peculiarity, the enigmatic quality of the individuality, and we learn also how we must treat this individual in life, because spiritual science gives to us, so to speak, not merely general, theoretical directions, but it guides us in our relation to the individual in the solving of the riddles which are there to be solved: namely, to love him as we must love him if we not merely fathom him with the mind, but let him work upon us completely, let our spiritual scientific insight give wings to our feelings, our love. That is the only proper soil which can yield true, fruitful, genuine human love; and this is the basis from which we discover what we have to seek as the innermost essential kernel in each individual. And if we permeate ourselves thus with spiritual knowledge, our social life will be regulated in such a way that each single person, when he approaches any other in esteem and respect and understanding of the riddle “man,” will learn how to find and to regulate his relation to the individual. Only one who lives in abstractions as a matter of course can speak from prosaic concepts, but he who strives for genuine knowledge will find it, and will find the way to other people; he will find the solution of the riddle of the other person in his own attitude, in his own conduct. Thus we solve the individual riddle according as we relate ourselves to others. We find the essential being of another only with a view of life which comes from the spirit. Spiritual science must be a life-practice, a spiritual life-factor, entirely practical, entirely living, and not vague theory. This is knowledge which can work into all the fibers of man's being, which can rule each single act in life. Thus only does spiritual science become the true art of living—and that could be particularly shown in the consideration of those intimate peculiarities of man, the temperaments. Thus the finest relation is engendered between man and man when we look a person in the face and understand not only how to fathom the riddle, but how to love, that is, to let love flow from individuality to individuality. Spiritual science needs no theoretical proofs; life brings the proofs. Spiritual science knows that something can be said “for” and “against” everything, but the true proofs are those which life brings; and only step by step can life show the truth of what we think when we consider the human being in the light of spiritual-scientific knowledge; for this truth exists as a harmonious, life-inspired insight which penetrates into the deepest mysteries of life. |
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Jesuit and Rosicrucian Training
05 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Jesuit and Rosicrucian Training
05 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The object of these lectures is to place before you an idea of the Christ-Event in so far as it is connected with the historical appearance of the Christ in the person of Jesus of Nazareth. So many questions of the spiritual life are bound up with this subject that the choice of it will enable us to make a wide survey of the realm of Spiritual Science and its mission, and to discuss the significance of the Anthroposophical Movement for the spiritual life of the present time. We shall also have the opportunity of learning what the content of religion is. And since this content must spring from the common heritage of mankind, we shall seek to know it in its relation to the deeper sources of religious life, and to what the sources of occult science have to tell us concerning the foundation of all religious and philosophic endeavours. Much that we shall have to discuss will seem to lie very far from the theme itself, but it will all lead us back to our main purpose. We shall best come to a more precise understanding of our subject—modern religious life on the one hand and the spiritual-scientific deepening of spiritual life on the other—if we glance at the origins both of religious life and of occult spiritual life in recent centuries. For as regards spiritual development in Europe during this period, we can discern two directions of thought which have been cultivated with the utmost intensity: on the one hand an exaggeration of the Jesus-Principle, and on the other a most careful, conscientious preservation of the Christ-Principle. When we place before our minds these two recent streams, we must see in the exaggeration of the Jesus-Principle a great and dangerous error in the spiritual life of those times, and on the other side a movement of deep significance, a movement which seeks above all the true paths and is careful to avoid the paths of error. From the outset, therefore, in our judgment of two entirely different spiritual movements, we have to ascribe serious errors to one of them and most earnest efforts after truth to the other. The movement which interests us in connection with our spiritual-scientific point of view, and which we may call an extraordinarily dangerous error in a certain sense, is the movement known in the external world as Jesuitism. In Jesuitism we encounter a dangerous exaggeration of the Jesus-Principle. In the other movement, which for centuries has existed in Europe as Rosicrucianism, we have an inward Christ-movement which above all seeks carefully for the ways of truth. Ever since a Jesuitical current arose in Europe, much has been said and written in exoteric life about Jesuitism. Those who wish to study spiritual life from its deeper sources will thus be concerned to see how far Jesuitism signifies a dangerous exaggeration of the Jesus-Principle. If we wish to arrive at a true characterisation of Jesuitism, we must get to know how the three chief principles of world-evolution, which are indicated in the most varied ways in the different world-outlooks, find practical expression in human life, including exoteric life. Today we will first of all turn quite away from the deeper significance and characterisation of these three fundamental streams, which run through all life and all evolution, and will review them from an external point of view. First of all we have the cognitional element in our soul-life. Now, whatever may be said against the abstractions of a one-sided intellectual search for truth, or against the alienation from life of many scientific, philosophical, and theosophical endeavours, anyone who is clear in his own mind as to what he wills and what he can will, knows that Cognition belongs to the most deeply rooted activities of the soul. For whether we seek knowledge chiefly through thinking, or more through sensation or feeling, Cognition always signifies a taking account of the world around us, and also of ourselves. Hence we must say that whether we are satisfied for the moment with the simplest experiences of the soul, or whether we wish to devote ourselves to the most complicated analysis of the mysteries of existence, Cognition is the primary and most significant question. For it is basically through Cognition that we form a picture of the content of the world—a picture we live by and from which our entire soul-life is nourished. The very first sense-impression, in fact all sense-life, must be included in the realm of Cognition, along with the highest formulations of the intellect. Under Cognition we must include also the impulse to distinguish between the beautiful and the ugly, for although it is true in a certain sense that there is no disputing about taste, yet cognition is involved when someone has adopted a certain judgment in a question of taste and can distinguish between the beautiful and the ugly. Again, our moral impulses—those which prompt us to do good and abstain from evil—must be seen as moral ideas, as cognition, or as impulses to do the one and avoid the other. Even what we call our conscience, however vague the impulses from it may be, comes under the heading of cognition. In short, the world we are consciously aware of, whether it be reality or maya; the world we live in consciously, everything we are conscious of—all this can be embraced under the heading: cognitive spiritual life. Everyone, however, must acknowledge that under the surface of this cognitive life something else can be discerned; that in our everyday existence our soul-life gives evidence of many things which are not part of our conscious life. When we wake up in the morning, our soul-life is always strengthened and refreshed and newly born from sleep. During the unconsciousness of sleep we have gained something which is outside the realm of conscious cognition, but comes from a region where our soul is active below the level of consciousness. In waking life, too, we must admit that we are impelled by impulses, instincts and forces which throw up their waves into our conscious life, while they work and have their being below it. We become aware that they work below the conscious when they rise above the surface which separates the conscious from the subconscious. And indeed our moral life also makes us aware of a subconscious soul-life of this kind, for we can see how in the moral realm this or that ideal comes to birth. It takes only a little self-knowledge to realise that these ideals do rise up into our soul-life, but that we are far from always knowing how our great moral ideals are connected with the deepest questions of existence, or how they belong to the will of God, in which they must ultimately be grounded. We might indeed compare our soul-life in its totality with a deep ocean. The depths of this oceanic soul-life throw up waves to the surface, and those that break out into the realm of air, which we can compare with normal consciousness, are brought within the range of conscious cognition. All conscious life is rooted in a subconscious soul-life. Fundamentally, the whole evolution of mankind can be understood only if a subconscious soul-life of this kind is acknowledged. For what does the progress of spiritual life signify save that many things which have long dwelt down below take form for the first time when they are brought to surface level? So it is, for example, when an inventive idea arises in the form of an impulse towards discovery. Subconscious soul-life, as real as our conscious life, must therefore be recognised as a second element in our life of soul. If we place this subconscious soul-life in a realm that is at first unknown—but not unknowable—we must contrast it with a third element. This element is immediately apparent to external, exoteric observation, for if we turn our attention to the outer world through our senses, or approach it through our intellect or any form of mental activity, we come to know all sorts of things. But a more exact consideration of every age of cognition compels us to realise that behind everything we can know about the world at large something else lies hidden: something that is certainly not unknowable but in every epoch has to be described as not yet known. And this not-yet-known, which lies below the surface of the known in the mineral, plant, and animal kingdoms, belongs as much to ourselves as it does to external nature. It belongs to us in so far as we absorb and work up in our physical organism the materials and forces of the outer world; and inasmuch as we have within us a portion of nature, we have also within us a portion of the unknown in nature. So in the world wherein we live we must distinguish a triad: our conscious spiritual life; our subconscious soul-life below the threshold of consciousness; and that which, as the unknown in nature and at the same time in man, lives in us as part of the great unknown Nature. This triad emerges directly from a rational observation of the world. And if looking away from all dogmatic statements, from all philosophical or theosophical traditions, in so far as these are clothed in conceptual definitions or formulations, we may ask: How has the human mind always expressed the fact that this triad is present not only in the immediate environment, but in the whole world to which man himself belongs? We must then reply: Man gives the name of Spirit to all that can be known within the horizon of the conscious. He designates as the Son or the Logos that which works in the subconscious and throws up only its waves from down below. And to that which belongs equally to the unknown in Nature, and to the part of our own being which is of one kind with Nature, the name of the Father-Principle has always been given, because it was felt to express the relation of the third principle to the other two. Besides what has now been said concerning the Spirit, the Son, and the Father-Principle, it can be taken for granted that other differentiations we have formerly made, and also the differentiations made in this or that philosophy, have their justifications. But we can say that the most widely accepted idea of this differentiation corresponds with the account of it given here. Now let us ask: How can we characterise the transition from that which belongs to the Spirit, and so plays directly into the conscious life of the soul, to the subconscious element which belongs to the Son-Principle? We shall best grasp this transition if we realise that into ordinary human consciousness there plays quite distinctly the element we designate as Will, in contrast to the elements of ideation and feeling. If we rightly interpret the Bible saying, ‘The Spirit is willing, but the flesh is weak’, it indicates that everything grasped by consciousness lies in the realm of the Spirit, whereas by ‘the flesh’ is meant everything that lies more in the subconscious. As to the nature of the Will, we need only think of that which plays up from the subconscious and enters into our consciousness only when we form concepts of it. Only when we transform into concepts and ideas the dark impelling forces which are rooted in the elemental part of the soul—only then do they enter the realm of the Spirit; otherwise they remain in the realm of the Son-Principle. And since the Will plays through our feelings into the life of ideas, we see quite clearly the breaking out into the conscious of the waves from the subconscious ocean. In our threefold soul-life we have two elements, ideation and feeling, which belong to conscious life, but feeling descends directly into the realm of the Will, and the nearer we come to the impulses of Will, the further we descend into the subconscious, the dark realms into which we sink completely when consciousness is engulfed in deep, dreamless sleep. Thus we see that the Will-element, because it descends into the realm of the subconscious, stands towards the individual being of man in a relationship quite different from that of cognition, the realm of the Spirit. And so, when we differentiate between Spirit and Son, we may be impelled to surmise that man's relationship to the Spirit is different from his relationship to the Son. How is this to be understood? Even in exoteric life it is quite easy to understand. Certainly the realm of cognition has given rise to all kinds of debate, but if people would only come to understand one another concerning the concepts and ideas they formulate for themselves, controversy over questions of cognition would gradually cease. I have often emphasised that we no longer dispute over mathematics, because we have raised mathematics entirely into consciousness. The things we dispute about are those not yet raised into consciousness: we still allow our subconscious impulses, instincts, and passions to play into them. So we see that in the realm of cognition we have to do with something more universally human than anything to be found in the subconscious realm. When we meet another human being and enter into the most varied relationships with him, it is in the realm of conscious spiritual life that understanding should be possible. And a mark of a healthy soul-life is that it will always wish and hope to reach an understanding with the other person concerning things that belong to conscious spiritual life. It will be unhealthy for the soul if that hope is lost. On the other hand, we must recognise the Will-element, and everything in another person's subconscious, as something which should on no account be intruded upon; it must be regarded as his innermost sanctuary. We need consider only how unpleasant to a healthy soul-life is the feeling that the Will of another man is being put under compulsion. It is not only aesthetically but morally unpleasant to see the conscious soul-life of anyone eliminated by hypnotism or any other powerful means; or to see the will-power of one person working directly on the Will of another. The only healthy way to gain influence over another person's Will is through cognition. Cognition should be the means whereby one soul comes to an understanding with another. A person must first translate his wishes into a conceptual form; then they may influence another person's cognition, and they should touch his Will only by this indirect route. Nothing else can be satisfactory in the highest, most ideal sense to a healthy life of soul. Every kind of forcible working of Will upon Will must evoke an unpleasant impression. In other words, human nature strives, in so far as it is healthy, to develop in the realm of the Spirit the life it has in common with others, and to cherish and respect the realm of the subconscious, in so far as it comes to expression in the human organism, as an inviolable sanctuary that should rest in the personality, the individuality, of each man and should not be approached save through the door of conscious cognition. So at least a modern consciousness, attuned to our epoch, must feel if it is to know itself to be healthy. In later lectures we shall see whether this was so in all periods of human evolution. What has been said today will help us to think clearly about what is outside us and what is within us, at least for our own period. This leads to the conclusion that fundamentally the realm of the Son—embracing everything that we designate as the Son or Logos—must be awakened in each individual as a quite personal concern; and that the realm of common life, where men may be influenced by one another, is the realm of the Spirit. We see this expressed in the grandest, most significant way in the New Testament accounts of the attitude of Christ Jesus towards His first disciples and followers. From all that is told concerning the Christ-Event we can gather that the followers who had hastened to Jesus during his life-time were bewildered when His life ended with the crucifixion; with that form of death which, in the land where the Christ-Event took its course, was regarded as the only possible expiation for the greatest crimes. And although this death on the cross did not affect everyone as it did Saul, who later became Paul, and as Saul had concluded that someone who suffered such a death could not be the Messiah, or the Christ—for the crucifixion had made a milder impression on the disciples, one might say—yet it is obvious that the writers of the Gospels wished to give the impression that Christ Jesus, through his subjection to the shameful death on the cross, had forfeited some of the effect he had had on the hearts of those around him. But with this account something else is connected. The influence that Christ Jesus had acquired—an influence we must characterise more exactly during these lectures—was restored to Him after the Resurrection. Whatever may be our present thoughts about the Resurrection, we shall have to discuss it here in the light of occult science; and then, if we simply go by the Gospel narratives, one thing will be clear: for those to whom Christ appeared after the Resurrection He had become someone who was present in a quite special way, different entirely from His previous presence. In speaking on the Gospel of St. John I have already pointed out how impossible it would have been for anyone who knew Jesus not to recognise Him after three days, or to confuse Him with someone else, if He had not appeared in an altered form. The Evangelists wish particularly to evoke the impression that the Christ appeared in this altered form. But they also wish to indicate something else. For the Christ to exert influence on human souls, a certain receptivity in those souls was necessary. And this receptivity had to be acted on not merely by an influence from the realm of the Spirit but by the actual sight of the Christ-Being. If we ask what this signifies, we must realise that when a person stands before us, his effect upon us goes beyond anything we are conscious of. Whenever a human being or other being works upon us, unconscious elements affect our soul-life; they are produced by the other being indirectly through consciousness, but he can produce them only if he stands before us in actuality. What the Christ brought about from person to person after the so-called Resurrection was something that worked up from the unconscious soul-powers of the disciples into their soul-life: an acquaintance with the Son. Hence the differences in the portrayal of the risen Christ; hence, too, the variations in the accounts, showing how the Christ appeared to one or other person, according to the disposition of the person concerned. Here we see the Christ-Being acting on the subconscious part of the souls of the disciples; hence the appearances are quite individual, and we should not complain because they are not uniform. If, however, the significance of the Christ for the world was to be His bringing to all men something common to all of them, then not only this individual working of the Son had to proceed from the Christ, but the element of Spirit, which can encompass something that belongs to all men, had to be renewed by Him. This is indicated by the statement that after the Christ had worked upon the Logos-nature of man. He sent forth the Spirit in the form of the renewed or ‘holy Spirit’. Thus was created that element common to all men which is characterised when we are told that the disciples, after they had received the Spirit, began to speak in the most diverse tongues. Here we are shown how the common element resides in the outpouring of the Holy Spirit. And something else is indicated: how different is this outpouring of the Spirit from the simple imparting of the power of the Son, for in the Acts of the Apostles we are told that certain persons to whom the apostles came had already received the Jesus-baptism, and yet they had now to receive for the first time the Spirit, symbolically indicated by the laying on of hands. In the characterisation of the Christ-Event we are made very precisely aware of the difference between the working we have to designate as the Christ-working, which acts upon the subconscious impulses of the soul and so must have a personal, inward character, and the Spirit-element, which represents something common to all mankind. It is this Spirit-element that those who have named themselves ‘Rosicrucians’ have sought to preserve most carefully, as far as human weakness permits. The Rosicrucians have always wished to adhere strictly to the rule that even in the highest regions of Initiation nothing must be worked upon except the Spirit-element which, as common between man and man, is available in the evolution of humanity. The Initiation of the Rosicrucians was an Initiation of the Spirit. It was never an Initiation of the Will, for the Will of man was to be respected as a sanctuary in the innermost part of the soul. Hence the individual was led to those Initiations which were to take him beyond the stage of Imagination, Inspiration, and Intuition, but always so that he could recognise within himself the response which the development of the Spirit-element was to call forth. No influence was to be exerted on the Will. We must not mistake this attitude for one of indifference towards the Will. The point is that by excluding all direct working upon the Will, the purest spiritual influence was imparted indirectly through the Spirit. When we come to an understanding with another man with regard to entering on the path of knowledge of the Spirit, light and warmth are radiated from the spiritual path, and they then enkindle the Will, but always by the indirect path through the Spirit—never otherwise. In Rosicrucianism, therefore, we can observe in the highest sense that impulse of Christianity which finds twofold expression: on the one hand in the Son-element, in the Christ-working which goes down deeply into the subconscious; on the other, in the Spirit-working which embraces all that falls within the horizon of our consciousness. We must indeed bear the Christ in our Will; but the way in which men should come to an understanding with each other in life concerning the Christ can be found only—in the Rosicrucian sense—through a conscious soul-life which penetrates ever more deeply into the occult. In reaction against many other spiritual streams in Europe, the opposite way was taken by those who are usually called Jesuits. The radical, fundamental difference between what we justifiably call the Christian way of the Spirit and the Jesuit way of the Spirit, which gives a one-sided exaggeration to the Jesus-Principle, is that the intention of the Jesuit way is to work directly, at all times, upon the Will. The difference is clearly shown in the method by which the pupil of Jesuitism is educated. Jesuitism is not to be taken lightly, or merely exoterically, but also esoterically, for it is rooted in esotericism. It is not, however, rooted in the spiritual life that is poured out through the symbol of Pentecost, but it seeks to root itself directly in the Jesus-element of the Son, which means in the Will; and thereby it exaggerates the Jesus-element of the Will. This will be seen when we now enquire into the esoteric part of Jesuitism, its various spiritual exercises. How were these exercises arranged? The essential point is that every single pupil of Jesuitism goes through exercises which lead into the occult life, but into the Will, and within the field of occultism they hold the Will in severe discipline; they ‘break it in’, one might say. And the significant fact is that this discipline of the Will does not arise merely from the surface of life, but from something deeper, because the pupil has been led into the occult, in the way just indicated. If now, leaving aside the exercises of prayer preparatory to all Jesuit exercises, we consider these occult exercises, at least in their chief points, we find that the pupil has first to call up a vivid Imagination of Christ Jesus as the King of the Worlds—mark this carefully: an Imagination. And no one would be received into the degrees of Jesuitism who had not gone through such exercises, and had not experienced in his soul the transformation which such psychic exercises mean for the whole man. But this Imaginative presentation of Christ Jesus as King of the Worlds has to be preceded by something else. The pupil has to call up for himself, in absolute solitude and seclusion, a picture of man as he was created in the world, and how by falling into sin he incurred the possibility of most terrible punishments. And it is strictly prescribed how one must picture such a man; how if he were left to himself he would incur the utmost of torturing penalties. The rules are extraordinarily severe. With all other concepts or ideas excluded, this picture must live uninterruptedly within the soul of the future Jesuit, the picture of the God-forsaken man, the man exposed to the most fearful punishments, together with the feeling: ‘That am I, since I have come into the world and have forsaken God, and have exposed myself to the possibility of the most fearful punishments.’ This must call forth the fear of being forsaken by God, and detestation of man as he is according to his own nature. Then, in a further Imagination, over against the picture of the outcast, God-forsaken man, must be set the picture of the God full of pity who then became Christ, and through His acts on earth atones for what man has brought about by forsaking the divine path. In contrast to the Imagination of the God-forsaken man, there must arise that of the all-merciful, loving Being, Christ Jesus, to whom alone it is due that man is not exposed to all possible punishments working upon his soul. And, just as vividly as a feeling of contempt for the forsaking of the divine path had first to become fixed in the soul of the Jesuit pupil, so must a feeling of humility and contrition now take hold of him in the presence of Christ. When these two feelings have been called forth in the pupil, then for several weeks he has to practise severe exercises, picturing to himself in Imagination all details of the life of Jesus from his birth to the Crucifixion and Resurrection. And all that can arise in the soul emerges when the pupil lives in rigorous seclusion and, except for necessary meals, lets nothing else work upon his soul than the pictures which the Gospels give of the compassionate life of Jesus. But these pictures do not merely appear before him in thoughts and ideas; they must work upon his soul in vivid, living Imaginations. Only someone who really knows how the human soul is transformed through Imaginations which work with full living power—only he knows that under such conditions the soul is in fact completely changed. Such Imaginations, because they are concentrated in the most intense, one-sided way, first on sinful man, secondly on the compassionate God, and then only on the pictures from the New Testament, evoke precisely, through the law of polarity, a strengthened Will. These pictures produce their effect directly, at first hand, for any reflection upon them must be dutifully excluded. It is solely a matter of holding before one's mind these Imaginations, as they have just been described. What then follows is this. In the further exercises Christ Jesus—and now we may no longer say Christ but exclusively Jesus—is represented as the universal King of the Worlds, and thereby the Jesus element is exaggerated. Because Christ had to be incarnated in a human body, the purely spiritual took part in the physical world; but over against this participation stand the monumental and most significant words: ‘My kingdom is not of this world.’ We can exaggerate the Jesus element by making Jesus into a king of this world, by making Him that which He would have become if He had not resisted the tempter who wished to give Him ‘all the kingdoms of the world and the glory thereof’. Then Jesus of Nazareth would have been a king who, unlike other kings who possess only a portion of the earth, would have had the whole earth under his sway. If we think of this king portrayed in this guise, his kingly power so increased that the whole earth is his domain, then we should have the very picture that followed the other exercises through which the personal will of each Jesuit pupil had been sufficiently strengthened. To prepare for this picture of ‘King Jesus’, this Ruler over all the kingdoms of the earth, the pupil had to form an Imagination of Babylon and the plain around Babylon as a living picture, and, enthroned over Babylon, Lucifer with his banner. This picture had to be visualised with great exactitude, for it is a powerful Imagination: King Lucifer, with his banner and his hosts of Luciferic angels, seated amidst fire and dense smoke, as he sends out his angels to conquer the kingdoms of the earth. And the whole danger that issues from the ‘banner of Lucifer’ must first of all be imagined by itself, without casting a glance upon Christ Jesus. The soul must be entirely engrossed in the Imagination of the danger which issues from the banner of Lucifer. The soul must learn to feel that the greatest danger to the world's existence that could be conjured forth would be a victory for the banner of Lucifer. And when this picture has had its effect, the other Imagination, ‘The banner of Jesus’, must take its place. The pupil must now visualise Jerusalem and the plain around Jerusalem; King Jesus with His hosts, how He sends out His hosts, how He conquers and drives off the hosts of Lucifer and makes Himself King of the whole earth—the victory of the banner of Jesus over the banner of Lucifer. These are the strength-giving Imaginations for the Will which are brought before the soul of the Jesuit pupil. This is what completely changes his Will; makes him such that in his Will, because it is trained occultly, he turns away from everything else and surrenders absolutely to the idea: ‘King Jesus must become the Ruler upon earth, and we who belong to His army have to employ every means to make Him Ruler of the earth. To this we pledge ourselves, we who belong to His host assembled on the plain of Jerusalem, against the host of Lucifer assembled on the plain of Babylon. And the greatest disgrace for a soldier of King Jesus is to forsake His banner.’ These ideas, gathered up into a single resolution of the Will, can certainly give the Will immense strength. But we must ask: what is it in the soul-life that has been directly attacked? The element that ought to be regarded as intrinsically holy, the element that ought not to be touched—the Will-element. In so far as this Jesuit training lays hold of the Will-element, while the Jesus-idea seizes the Will-element completely, in so far is the concept of the dominion of Jesus exaggerated in the most dangerous way—dangerous because through it the Will becomes so strong that it can work directly upon the Will of another. For where the Will becomes so strong through Imaginations, which means by occult methods, it acquires the capacity for working directly upon the Will of another, and hence also along all the other occult paths to which such a Will can have recourse. Thus we see how in recent centuries we encounter these two movements, among many others: one has exaggerated the Jesus-element and sees in ‘King Jesus’ the sole ideal of Christianity, while the other looks solely at the Christ-element and carefully sets aside anything that could go beyond it. This second outlook has been much calumniated because it maintains that Christ has sent the Spirit, so that, indirectly through the Spirit, Christ can enter into the hearts and minds of men. In the development of civilisation during the last few centuries there is hardly a greater contrast than that between Jesuitism and Rosicrucianism, for Jesuitism contains nothing of what Rosicrucianism regards as the highest ideal concerning human worth and human dignity, while Rosicrucianism has always sought to guard itself from any influence which could in the remotest sense be called Jesuitical. In this lecture I wished to show how even so lofty an element as the Jesus-principle can be exaggerated and then becomes dangerous, and how necessary it is to sink oneself into the depths of the Christ-Being if we wish to understand how the strength of Christianity must reside in esteeming, to the very highest degree, human dignity and human worth, and in strictly refraining from groping our clumsy way into man's inmost sanctuary. Rosicrucianism, even more than Christian mysticism, is attacked by the Jesuit element, because the Jesuits feel that true Christianity is being sought elsewhere than in the setting which offers merely ‘King Jesus’ in the leading role. But the Imaginations here indicated, together with the prescribed exercises, have made the Will so strong that even protests brought against it in the name of the Spirit can be defeated. |
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Rosicrucian Training and Anthroposophical Training
06 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Rosicrucian Training and Anthroposophical Training
06 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Yesterday I tried to give you a picture of a form of Initiation which ought not to exist, according to our valuation of human nature. This Initiation, as we have seen it in Jesuitism, leads to the acquisition of certain occult faculties, but if we bring a cleansed and purified occult vision to bear upon these faculties, they cannot be considered good. It will now be my task to show that the Rosicrucian way is characterised by all that high regard for human nature which we recognise as equally our own. But we must first be clear on certain points. From explanations given previously in various forms, we know that the Rosicrucian Initiation is essentially a development of the Christian Initiation, so that we can speak of it as a Christian-Rosicrucian Initiation. In earlier lecture-courses the purely Christian Initiation; with its seven degrees, and the Rosicrucian Initiation, also with seven degrees, have been compared. But now we must note that with regard to Initiation the principle of the progress of the human soul must be strictly maintained. We know that the Rosicrucian Initiation had its proper beginning somewhere about the thirteenth century. At that time it was recognised by those individualities who have to guide the deeper destinies of human evolution as the right Initiation for the more advanced human souls. This shows that the Initiation of the Rose-Cross takes full account of the continuous progress of the human soul and must therefore pay particular attention to the fact that since the thirteenth century the human soul has developed further. Souls which are to be led to Initiation in our day can no longer adopt the standpoint of the thirteenth century. I want especially to point this out because in our time there is such a strong desire to label everything with some mark or other, with some catchword. From this bad habit, and not for any justified reason, our anthroposophical movement has been given a label which could lead gradually to something like a calamity. It is true that within our movement the principle of Rosicrucianism can be found in all completeness, so that we can penetrate into the sources of Rosicrucianism. So it is that persons who by means of our anthroposophical training penetrate into these sources can properly call themselves Rosicrucians. But it must be emphasised just as strongly that outsiders have no right to designate as Rosicrucian the anthroposophical stream we represent, simply because our movement has been given—consciously or unconsciously—an entirely false label. We are no longer standing where the Rosicrucians stood in the thirteenth century and on through the following centuries, for we take into account the progress of the human soul. Hence the way indicated in my book, Knowledge of the Higher Worlds, as the way best adapted for gaining access to the Higher Worlds must not without further explanation be equated with what may be called the Rosicrucian way. Through our movement we can penetrate into true Rosicrucianism, but our movement extends over a far wider domain, for it embraces the whole of Theosophy; hence it should not be labeled Rosicrucian. Our movement must be described simply as the spiritual science of today, the anthroposophical spiritual science of the twentieth century. Outsiders, particularly, will fall—more or less unconsciously—into some kind of misunderstanding if they describe our movement simply as Rosicrucian. But an outstanding achievement of Rosicrucianism since the dawn of modern spiritual life in the thirteenth century has been to establish a rule which must also be ours: the rule that all modern Initiation in the deepest sense of the word must recognise and treasure the independence of the most holy element in man's inner life, his Will-centre, as indicated yesterday. The occult methods there described are designed to overcome and enslave the human will and to set it on a predetermined course; hence a true occultism will rigorously avoid them. Before characterising Rosicrucianism and present-day Initiation, we must mention a decisively relevant point: the Rosicrucianism of the thirteenth, fourteenth and even of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries has again had to be modified for our time. The Rosicrucianism of those earlier centuries could not reckon with a spiritual element which has since entered into human evolution. Without this element today we can no longer understand rightly the fundamentals of all those spiritual streams which arise from the ground of occultism, including therefore any theosophical stream. For reasons we shall see more exactly in the course of these lectures, the teaching of reincarnation and karma, of repeated earth-lives, was excluded for many centuries from the external, exoteric teachings of Christianity. In the thirteenth century the teaching of reincarnation and karma had not yet entered, in the highest sense, into the first stages of Rosicrucian initiation. One could go far, up to the fourth or fifth degree; one could go through what was called the Rosicrucian studium—the acquiring of Imagination, the reading of the occult script, the finding of the philosopher's stone—and one could experience something of what is called the mystical death. One could reach this stage and acquire exceptionally high occult knowledge, but without needing to achieve full clarity concerning the illuminating teachings of reincarnation and karma. We must be clear that human thinking progresses and now embraces forms of thought which, if only we follow them out logically—and this can easily be done on the external, exoteric level—lead unconditionally to a recognition of repeated earth-lives and so to the idea of karma. The words spoken through the lips of Strader in my second Rosicrucian drama, The Soul's Probation, are absolutely true: namely that a logical thinker today, if he is not to break with everything that the thought-forms of the last century have brought in, must come finally to a recognition of karma and reincarnation. This is something deeply rooted in present-day spiritual life. Just because this knowledge has been slowly prepared and has these deep roots, it emerges little by little, as though independently, in the West. It is indeed remarkable how the necessity of recognising repeated earth-lives has independently made itself felt—though certainly only by outstanding individual thinkers. We need only call attention to certain facts which are quite forgotten, intentionally or unintentionally, in our present-day literature. Take, for example, what comes out so wonderfully in Lessing's Education of the Human Race. We see how Lessing, that great mind of the eighteenth century who at the zenith of his life gathered up his thoughts and wrote the Education of the Human Race, came as though by inspiration to the thought of repeated earth-lives. So does the idea of repeated earth-lives find its way, as though by inner necessity, into modern life. It has to be taken into consideration, but certainly not in the way that ideas of this kind are considered in our history books or in cultured circles nowadays. For in such cases resort is had to the familiar formula that when a clever man grows old, excuses must be made for him. So it is said that although we may appreciate Lessing in his earlier works, we must allow that in later years, when he came to the idea of repeated earth-lives, he had become somewhat feeble. In more recent times the idea occurs sporadically. Drossbach, a nineteenth-century psychologist, spoke of it in the only way then possible. Without occultism, simply by observing nature, he tried in his own way as a psychologist to establish the idea of repeated earth-lives. Again, in the middle of the last century, a small society offered a prize for the best essay on the immortality of the soul. This was a remarkable occurrence in German spiritual life, and is very little known. Moreover, the prize went to an essay by Wiedenmann which tried to prove the immortality of the soul in the sense of repeated earth-lives: certainly an imperfect attempt, but it could not be otherwise in the fifties of the last century, when the necessary thought-forms had not developed far enough. One could quote various other instances where the idea of repeated earth-lives springs up, as though in response to a postulate, a demand, of the nineteenth century. Hence in my little book, Reincarnation and Karma, and also in my book, Theosophy, the ideas of repeated earth-lives and of karma could be worked out in relation to the thought-forms of natural science, but with reference to human individuality in contrast to the animal species. We must, however, be clear on one essential point: there is an immense difference between the way in which Western men have come to this idea simply through thinking, and the way in which it figures in Buddhism, for instance. It is most interesting to see how Lessing came to the idea of repeated earth-lives. The result can of course be compared with the idea of repeated earth-lives in Buddhism, and even given the same name; but the way taken by Lessing is very different and is not generally known. How did he come to this idea? We can see this quite clearly if we go through the Education of the Human Race. There is no doubt that human evolution gives evidence of progress in the strictest sense. Lessing argued that this progress is an education of humanity by the Divine Powers. God gave into men's hands a first elementary book, the Old Testament. Thereby a certain stage of evolution was achieved. When the human race had gone further, it was given the second elementary book, the New Testament. And then Lessing sees in our time something that goes beyond the New Testament: an independent feeling in the human soul for the true, the good, and the beautiful. This marks for him a third stage in the education of the human race. The thought of the education of mankind by the Divine Powers is worked out in a lofty style. Lessing then asks himself: What is the one and only way to explain this progress? He cannot explain it otherwise than by allowing every soul to participate in each epoch of human evolution, if human progress is to have any meaning at all. For it would have no meaning if one soul lived only in the epoch of Old Testament civilisation and another soul only in the New Testament epoch. It has meaning only if souls are taken through all the epochs of civilisation and share in all the stages of human education. In other words, if the soul lives through repeated earth-lives, the progressive education of the human race makes good sense. So the idea of repeated earth-lives springs up in Lessing's mind as something that belongs to human destiny. In a deeper sense the following underlies his thinking. If a soul was incarnated at the time of the Old Testament, it took into itself whatever it could take; when it reappears in a later time it carries the fruits of its previous life into the next life, and the fruits of that life into the one following, and so on. Thus the successive stages of evolution are interlocked. And whatever a soul achieves is achieved not only for itself, but for all mankind. Humanity is a great organism, and for Lessing reincarnation is necessary in order that the whole human race can progress. Thus it is historical evolution, the concern of humanity as a whole, that he takes as his starting-point, and from there he is impelled to a recognition of reincarnation. It is different if we trace out the same idea in Buddhism. There, a person is concerned merely with himself, with his own psyche. The individual says to himself: I am placed in the world of maya; desire brought me into it, and in the course of repeated incarnations I shall free myself as an individual soul from the necessity of living again on earth. This applies to the single individual; all the attention is centred on him. That is the great difference. Whether a person looks at the process from within, as in Buddhism, or from without, as Lessing does, his gaze takes in the whole of human evolution. In both cases the same idea emerges, but in the West the path to it is quite different. While the Buddhist limits himself to concern for the individual, the man of the West is concerned with the whole of humanity. He feels himself bound up with all men as a single organism. What is it that has taught Western man the necessity of realising, above all, that his concern is with all mankind? The reason is that into the sphere of the heart, into his world of feeling, he has received the words of Christ Jesus concerning human brotherhood: that it is beyond all nationality, beyond all racial characteristics, and that humanity is a great organism. Hence it is interesting to see how Drossbach, although his thinking is still imperfect, because the scientific ideas of the first half of the nineteenth century had not yet produced the corresponding thought-forms, does not take the Buddhistic path, but a universal cosmic one. Drossbach starts from the thoughts of natural science and observes the soul in its cosmic aspect. He cannot think otherwise of the soul than as a seed which goes through an external form and reappears in other external forms, and so is reincarnated. With him, this idea turns into fantasy, for he thinks that the world itself must be transformed, whereas Lessing thought correctly of short periods of time. Wiedenmann, too, in his prize essay, brings the immortality of the soul into logical connection with the question of reincarnation. So we see that these ideas appear quite sporadically, and it is right that in spite of faulty modes of thinking they should spring up in minds such as these, and in others also. The great evolutionary change which the human soul has undergone from the eighteenth to the twentieth century is such that everyone today who begins the study of world progress must above all assimilate those thought-forms which lead quite naturally to the acceptance and making credible of the ideas of reincarnation and karma. Between the thirteenth and eighteenth centuries human thought was not sufficiently advanced to come by itself to a recognition of reincarnation. One has always to start from the stage reached by the most highly developed thought of the period. Today the starting point must be that form of thinking which, on the basis of natural science, regards the idea of repeated earth-lives as logical—which means hypothetically true. So do the times advance. Without describing the Rosicrucian path in detail today, we will bring out what is essential both to it and to the way of knowledge at the present time. The characteristic of both is that everyone who gives advice and guidance for Initiation will value in the deepest sense the independence and inviolability of the sphere of the human Will. Hence the essential point is that through a special kind of moral and spiritual culture the ordinary interweaving of the physical body, etheric body, astral body, and ego must be changed. And those directions which are given for the training of the moral feelings, as also those for concentration in thinking, for meditation—all this makes finally for the one goal of loosening the spiritual texture which binds together the physical and etheric bodies, so that the etheric body does not remain so firmly fitted into the physical body as it naturally is. All the exercises strive after this lifting out, this loosening, of the etheric body. Thereby another union between the astral body and the etheric body is brought about. It is because in ordinary life the etheric body and the physical body are so firmly united that the astral body cannot normally feel or experience what is going on in the etheric body. Because the etheric body has its seat within the physical body, our astral body, and our ego perceive only what the physical body brings them from the world and enables them to think of through the instrument of the brain. The etheric body is too deeply embedded in the physical body for it to be experienced in ordinary life as an independent entity, as an independent instrument of cognition, or as an instrument of feeling and willing. The efforts in concentrated thinking, according to the instructions given nowadays—and given also by the Rosicrucians—the efforts in meditation, the cleansing of the moral feelings: all these finally produce on the etheric body the effect described in my book, Knowledge of the Higher Worlds. As we use our eyes for seeing and our hands for grasping, so eventually we shall use the etheric body with its organs, but for looking into the spiritual, not the physical, world. The way in which we gather together and concentrate our inner life works for the independence of the etheric body. It is necessary, however, that we should first permeate ourselves, at least tentatively, with the idea of karma. And we do this when we establish a certain moral equilibrium, a balance of the soul-forces of feeling. A person who cannot to a certain extent grasp the thought that ‘in the long run I myself am to blame for my impulses’, will not be able to make good progress. A certain equanimity and understanding with regard to karma, even if only a purely hypothetical understanding, are necessary as a starting-point. A person who never gets away from his ego, who is so dependent upon his narrowly limited ways of feeling and perception that when things go wrong he always blames others and never himself; a person who is always filled with the idea that the world, or a part of his environment, is against him; a man who never gets beyond the results of applying ordinary thinking to whatever can be learnt from exoteric Theosophy—such a person will find progress particularly difficult. Hence it is well that in order to develop equanimity and calmness of soul we should make ourselves familiar with the idea that when something does not succeed, particularly on the occult path, we must blame not others but ourselves. This does most to help our progress. What helps least is always wanting to lay the blame on the world outside, or always wanting to change our training methods. Our attitude in such matters is more important than perhaps appears. It is better to test carefully, at all times, how little we have learnt, and to seek the fault in ourselves when progress is not made. It is a quite significant advance when we can make up our minds always to seek the fault in ourselves. Then we shall see that we are making progress not only in farther off things but also in matters of external life. Those who have some experience in this field will always be able to testify that by accepting the blame for their own non-success, they have found something that makes precisely their external life easy and bearable. We shall get on much more easily with our environment when we can truly grasp this fact. We shall rise above much grumbling and hypochondria, above complaining and lamenting, and pursue our way more calmly. For we should reflect that in every true modern Initiation he who gives advice is under the strictest obligation not to penetrate into the innermost sanctuary of the soul. With regard to this most inward part of the soul, therefore, we have from the start to undertake something for ourselves, and we should not complain that we are perhaps not getting the right advice. The advice may be right and yet the results may not be satisfactory, if we fail to make the resolve I have indicated. This equanimity, this calmness, once we have made our choice—and the choice should come only from a serious resolve—is a good ground for meditation concerned with thoughts and feelings. In everything founded on Rosicrucianism an important point is that in meditation and concentration we are always directed not to dogma but to the universally human. The deviation of which we spoke yesterday takes its start from subject-matter that is first given to the aspirant for holding in his mind. But what if this subject-matter had first to be tested by occult cognition? What if it were not in any way firmly established in advance? We must take our stand on Rosicrucian principles, one of which is that we are not in a position to decide about anything which is supported only by external documents, for example, the accounts of what took place as the Event of Golgotha. We must come to know these things first by the occult path; we may not assume them beforehand. Hence we should start from the universally human, from that which can be justified by every soul. A glance into the great world, marveling at the revelation of light in the sun, feeling that what our eyes see of light is only the external veil of the light, its external revelation, or, as is said in Christian esotericism, the glory of light, and then yielding oneself up to the thought that behind the external sensible light something quite different is hidden—all this is fundamentally human. To think of, to gaze on, the light spread out through infinite space, and then clearly to feel that in this infinitely extended element of the light something spiritual must live, something which weaves this web of light in space; to concentrate upon these thoughts, to live in them—here we have something universally human, presented not through dogma but through universal feeling. Or again, to perceive the warmth of nature, to feel how through the universe, along with the warmth, something moves in which there is spirit. Then, out of certain relationships in our own organism with the feeling of love, to concentrate on the thought of how warmth can exist spiritually, how it lives pulsing through the world. Then, to sink oneself into what we can learn from intuitions given to us by modern occult teaching. Then to take counsel with those who know something in this realm as to concentrating in the right way upon world thoughts, cosmic thoughts. And further, the ennobling, the cleansing, of moral perceptions, whereby we come to understand that what we feel to be moral is reality. So we rise above the prejudice that these moral feelings are something transitory; we realise that they live on, are stamped into us as moral realities. We learn to feel the responsibility of being placed in the world as conscious beings, together with our moral feelings. All esoteric life is fundamentally directed towards universally human experiences of this kind. I will now describe how far we can go through exercises which take their start in this way from human nature, if only we devote ourselves to a clear-sighted examination of our own human nature. From this beginning we come to a loosening of the connection between the physical body and the etheric body, and to a new kind of knowledge. We give birth as it were, to a second man within ourselves, so that we are no longer so firmly connected with the physical body as before. And in the finest moments of life we feel the etheric and astral bodies as though enclosed in an external sheath, and thereby know ourselves to be free from the instrument of the physical body. That is what we attain. We shall then be led to see our physical body in its true being, and to recognise how it affects us when we are within it. We become aware of the whole working of the physical body upon us only when we have in a certain sense come out of it, like the snake which after casting its skin can look upon the skin from outside, though feeling it as a part of itself. Through the first stages of Initiation we learn in like manner to feel ourselves free from the physical body, and learn to recognise it. At this moment quite special feelings will steal over us, which may be described as follows. (There are so many different experiences along the path of Initiation that it has not yet been possible to describe them all. In Knowledge of the Higher Worlds you will find much on the subject, but there is a great deal more.) The first experience, open to nearly everyone who turns from ordinary life to pursue the path of knowledge, leads us to say, in accordance with our feeling: ‘This physical body as it is, as it appears to me, has not been formed by myself. Most certainly I have not made this physical body, through which I have been brought to be what I am in the world. Without this body, the Ego which I now regard as my great ideal, would not have arisen within me. I have become what I am only through having kept my physical body riveted upon me.’ At first all this gives rise to something like resentment, bitterness, against the Cosmic Powers. It is easy to say, ‘I will not cherish this resentment.’ But when there arises before us in melancholy majesty a picture of what we have become through being bound up with the physical body, the effect is overwhelming. We feel something like bitter hatred for the Cosmic Powers on this account. But now our occult training must be so far advanced that we overcome this hatred and on a higher level can say with our whole being, with our individuality which has already come down into repeated incarnations, that we ourselves are responsible for what our physical body has become. When we have mastered the bitterness, we experience the perception, already often described: ‘Now I know I am that very thing which appears there as the changed form of my physical being. That I am myself. But because my physical being was crushing me to death, I knew nothing of it.’ We stand here before the significant meeting with the Guardian of the Threshold. But if we come so far, if through the strenuousness of our exercises we experience what has just been said, then from out of what is common to human nature we recognise that we are as we are in our present form as the result of preceding incarnations. But we also recognise that we can experience the deepest pain and must work our way out beyond this pain to the overcoming of our present existence. And for every man who is sufficiently far advanced and has experienced these feelings in all their intensity, who has looked upon the Guardian of the Threshold, there arises of necessity an Imaginative picture, a picture not painted by constraint, as in Jesuitism, from passages in the Bible but a picture that each man experiences through having felt, in a general human sense, what he is. Through these experiences he will quite naturally come to know the picture of the Divine Ideal-Man, who like us lived in a physical body, and who like us in this physical body felt all that a physical body can bring about. The Temptation, and the picture of it as presented to us in the synoptic Gospels, the leading of Christ Jesus to the mountain, the promise of all external realities, the desire to cling to these outer realities, the temptation to remain attached to matter: in short, the temptation to remain with the Guardian of the Threshold and not to pass beyond him appears to us in the great Imaginative picture of Christ Jesus standing on the mountain, with the Tempter beside Him—a picture that would have arisen before us even if we had never heard of the Gospels. And then we know that he who wrote the story of the Temptation depicted his own experience of seeing, in the spirit, Christ Jesus and the Tempter. Then we know it is true in the Spirit that the writer of the Gospel has described something that we ourselves can experience even if we knew nothing of the Gospels. Thus we shall be led to a picture which is similar to the picture in the Gospels. We gain for ourselves what stands in the Gospels. Nothing is forced upon us; everything is drawn forth from the depths of our own nature. We proceed from the universally human and bring forth the Gospels afresh through our occult life. We feel ourselves at one with the writers of the Gospels. Then there arises within us another feeling, a next step along the occult path. We feel how the Tempter has grown into a powerful Being who is behind all the phenomena of the world. Yes, we learn indeed to know the Tempter, but by degrees we learn in a certain way to value him. We learn to say: ‘The world spread out before us, whether it be Maya or something else, has its right to exist; it has revealed something to me.’ Then comes a second feeling, a quite definite one for every person who fulfils the conditions of a Rosicrucian initiation. The feeling arises: ‘We belong to the Spirit Who lives in all things, and with Whom we have to reckon. We cannot in the least comprehend the Spirit if we do not surrender ourselves to it.’ Then fear comes over us. We experience fear such as every real knower must undergo; a feeling for the greatness of the Cosmic Spirit who pervades the world. We are in the presence of this greatness and we feel our own powerlessness. We feel also what we might have become in the course of the earth's history, or in that of the Cosmos. We feel our own impotent existence so far removed from Divine existence. We feel fear in face of the ideal we must come to resemble, and of the magnitude of the effort which should lead us to that ideal. As through esotericism we must feel the whole magnitude of the effort, so must we feel this fear as a struggle we take upon ourselves, a wrestling with the Spirit of the Cosmos. When we feel our own littleness, and the necessary struggle laid upon us to attain our ideal, to become one with that which works and weaves in the world—when we experience this with fear, then only may we lay fear aside and betake ourselves to the path, to the paths which lead us to our ideal. And if we feel this completely and rightly, there comes before us yet another significant Imagination. If we had never read a Gospel, if mankind had never had such an external book, a spiritual picture would rise before our clairvoyant sight. We are led out into the solitude which stands clearly before the inner eye, and we are brought before the picture of the Ideal Man who in a human body experienced all the immeasurable fears and anguish that we ourselves can taste in this moment. The picture of Christ in Gethsemane stands before us, as He experienced fear to an overwhelmingly intensified degree, the fear that we ourselves must feel on the path of Initiation, the fear that wrung from His brow the Bloody Sweat. That is the picture we encounter at a certain point on our occult path, independently of all external documents. So we have, standing before us like two great pillars on the occult path, the story of the Temptation experienced spiritually, and the scene on the Mount of Olives experienced spiritually. And then we understand the words: Watch and pray, and live in prayer, so that you will never be tempted to remain standing at any one point, but will continually stride forward. This means that first of all we experience the Gospel; we experience everything so that we could write it down just as the writers of the Gospels have described it. For we do not need to take these two pictures from the Gospel; we can take them out of our own inner consciousness; we can bring them forth out of the Holy of Holies of the soul. No teacher is needed to come and say: ‘You must place before yourself in imagination the Temptation, and the scene on the Mount of Olives.’ We need only bring before ourselves that which can be developed in our consciousness through meditation, purification of our common human feelings, and so on. Then, without constraint from anyone, we call forth the Imaginations which are contained in the Gospels. In the Jesuit spiritual movement the pupil had the Gospels given to him first, and afterwards he experienced what the Gospels describe. The way we have indicated today shows that when a man has taken the path of the spiritual life, he experiences occultly that which is connected with his own life, and thereby can experience through himself the pictures, the Imaginations, of the Gospels. |
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Sources of Knowledge of Christ, Lord of Karma
07 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Sources of Knowledge of Christ, Lord of Karma
07 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
We must now turn our attention to the relation between ordinary religious consciousness and the knowledge that can be gained through higher clairvoyant powers concerning the higher worlds in general, and in particular—this is specially relevant to our theme—concerning the relation of Christ Jesus to these higher worlds. It will be clear to you all that the evolution of Christianity so far has been such that most persons have not been able to attain through their own clairvoyant knowledge to the mysteries of the Christ-Event. It must be granted that Christianity has entered into the hearts of countless human beings, and to a certain degree its essential nature has been recognised by countless souls; but these hearts and souls have not been able to look up to the higher worlds and so to receive clairvoyant vision of what really took place in human evolution through the Mystery of Golgotha and everything connected with it. Hence the knowledge that can be gained through clairvoyant consciousness itself, or through a person having accepted on one or other ground the communications of the seer concerning the mysteries of Christianity, must be carefully distinguished from the religious inclination to Christ and the intellectual leanings towards Him of a person who knows nothing of clairvoyant investigation. Now you will all agree that during the centuries since the Mystery of Golgotha there have been men of all degrees of intellectual culture who have accepted the mysteries of Christianity in a deep inner way, and from what has been said lately in various lectures you will have felt that this is quite natural, for—as has been emphasised again and again—it is only in the twentieth century that a renewal of the Christ-Event will take place, for this is when a certain general heightening of human powers of cognition begins. It brings with it the possibility that in the course of the next 3,000 years, and without special clairvoyant preparation, more and more persons will be able to attain a direct vision of Christ Jesus. This has never happened before. Until now there have been only two—or later on today we may perhaps discover three—sources of knowledge concerning the Christian mysteries for persons who could not rise by training to clairvoyant observation. One source was the Gospels and all that comes from the communications in the Gospels, or in the traditions connected with them. The second source of knowledge arose because there have always been clairvoyant individuals who could see into the higher worlds, and through their own knowledge brought down the facts of the Christ-Event. Other persons followed these individuals, receiving from them a ‘never-ending Gospel’, which could continually come into the world through those who were clairvoyant. These two seem at first to be the only two sources in the evolution of Christian humanity up to the present time. And, now from the twentieth century onwards, a third begins. It arises because for more and more people an extension, an enhancement, of their cognitional powers, not brought about through meditation, concentration and other exercises will occur. As we have often said, more and more persons will be able to renew for themselves the experience of Paul on the road to Damascus. Hence we can say of the ensuing period that it will provide a direct means of perceiving the significance and the Being of Christ Jesus. Now the first question that will naturally occur to you is this: What is the essential difference between the clairvoyant vision of Christ which has always been possible as a result of the esoteric development described yesterday, and the vision of Christ which will come to people, without esoteric development, in the next 3,000 years, beginning from our twentieth century? There is certainly an important difference. And it would be false to believe that what the seer through his clairvoyant development sees today in the higher worlds concerning the Christ-Event, and what has been seen clairvoyantly concerning the Christ-Event since the Mystery of Golgotha, is exactly the same as the vision which will come to an ever greater and greater number of people. These are two quite different things. As to how far they differ, we must ask clairvoyant research how it is that from the twentieth century onwards Christ Jesus will enter more and more into the ordinary consciousness of men. The reason is as follows. Just as on the physical plane in Palestine, at the beginning of our era, an event occurred in which the most important part was taken by Christ Himself—an event which has its significance for the whole of humanity—so in the course of the twentieth century, towards the end of the twentieth century, a significant event will again take place, not in the physical world, but in the world we usually call the world of the etheric. And this event will have as fundamental a significance for the evolution of humanity as the event of Palestine had at the beginning of our era. Just as we must say that for Christ Himself the event of Golgotha had a significance that with this very event a God died, a God overcame death—we will speak later concerning the way this is to be understood; the deed had not happened before and it is an accomplished fact which will not happen again—so an event of profound significance will take place in the etheric world. And the occurrence of this event, an event connected with the Christ Himself, will make it possible for men to learn to see the Christ, to look upon Him. What is this event? It consists in the fact that a certain office in the Cosmos, connected with the evolution of humanity in the twentieth century, passes over in a heightened form to the Christ. Occult clairvoyant research tells us that in our epoch Christ becomes the Lord of Karma for human evolution. This event marks the beginning of something that we find intimated also in the New Testament: He will come again to separate, or to bring about the crisis for, the living and the dead.1 Only, according to occult research, this is not to be understood as though it were a single event for all time which takes place on the physical plane. It is connected with the whole future evolution of humanity. And whereas Christianity and Christian evolution were hitherto a kind of preparation, we now have the significant fact that Christ becomes the Lord of Karma, so that in the future it will rest with Him to decide what our karmic account is, how our credit and debit in life are related. This has been common knowledge in Western occultism for many centuries, and is denied by no occultist who knows these things. But recently it has been verified again with the utmost care, by every means available to occult research. We will now enter more exactly into these matters. Ask all those who know something of the truth about these things, and you will find everywhere one fact confirmed, but a fact which only at this present stage in the development of our Movement could be made known. Everything which can make our minds receptive towards such a fact had first to be gathered together. You can find in occult literature information concerning these matters if you wish to search for it. However, I shall take no account of the literature; I shall only bring forward the corresponding facts. When certain conditions are described, including those I have dealt with myself, a picture has to be given of the world a man enters on passing through the gate of death. Now there are a great many men, especially those who have gone through the development of Western civilisation—these things are not the same for all peoples—who experience a quite definite event in the moment following the separation of the etheric body after death. We know that on passing through the gate of death we separate ourselves from the physical body. The individual is at first still connected for a time with his etheric body, but afterwards lie separates his astral body and also his Ego from the etheric body. We know that he takes with him an extract of his etheric body; we know also that the main part of the etheric body goes another way; generally it becomes part of the cosmic ether, either dissolving completely—this happens only under imperfect conditions—or continuing to work on as an enduring active form. When the individual has stripped off his etheric body he passes over into the Kamaloka region for the period of purification in the soul-world. Before this, however, he undergoes a quite special experience which has not previously been mentioned, because, as I said, the time was not ripe for it. Now, however, these things will be fully accepted by all who are qualified to judge them. Before entering Kamaloka, the individual experiences a meeting with a quite definite Being who presents him with his karmic account. And this Being, who stood there as a kind of bookkeeper for the karmic Powers, had for many men the form of Moses. Hence the mediaeval formula which originated in Rosicrucianism: Moses presents man in the hour of death—the phrase is not quite accurate, but that is immaterial here—Moses presents man in the hour of his death with the record of his sins, and at the same time points to the ‘stern law’. Thus the man can recognise how he has departed from this stern law which he ought to have followed. In the course of our time—and this is the significant point—this office passes over to Christ Jesus, and man will ever more and more meet Christ Jesus as his Judge, his karmic Judge. That is the super-sensible event. Just as on the physical plane, at the beginning of our era, the event of Palestine took place, so in our time the office of Karmic Judge passes over to Christ Jesus in the higher world next to our own. This event works into the physical world, on the physical plane, in such a way that men will develop towards it the feeling that by all their actions they will be causing something for which they will be accountable to the judgment of Christ. This feeling, now appearing quite naturally in the course of human development, will be transformed so that it permeates the soul with a light which little by little will shine out from the individual himself, and will illuminate the form of Christ in the etheric world. And the more this feeling is developed—a feeling that will have stronger significance than the abstract conscience—the more will the etheric Form of Christ be visible in the coming centuries. We shall have to characterise this fact more exactly in the next few days, and we shall then see that a quite new event has come to pass, an event which works into the Christ-development of humanity. With regard to the evolution of Christianity on the physical plane, let us now ask whether for the non-clairvoyant consciousness there was not also a third way, over against the two already given. Such a third way was in fact always there, for all Christian evolution. It had to be there. The objective evolution of humanity is not directed in accordance with the opinions of men, but in accordance with objective facts. Concerning Christ Jesus there have been many opinions in the course of the centuries, or the Councils and Church assemblies and theologians would not have disputed so much among themselves; and in no period, perhaps, have so many people held various views of the Christ as in our own. Facts, however, are not determined by human opinions, but by the forces actually present in human evolution. These facts could be recognised by many more people simply through noticing what the Gospels have to say, if people had the patience and perseverance to look at things really without prejudice, and if they were not too quick and biased in considering the objective facts. Most people, however, do not want to form a picture of Christ according to the facts, but one that suits their own likings and represents their own ideal. And it must be said that in a certain respect Theosophists of all shades of opinion do this very thing today. When, for example, certain highly developed individuals who have attained an advanced stage of human evolution are spoken of in theosophical literature as Masters, or Adepts, this is a truth that cannot be disputed by anyone who knows the facts. It applies to individuals who have had many incarnations; through exercises and holy life they have pressed on in advance of mankind and have acquired powers which the rest of humanity will acquire only in the future. It is natural and right that a student of Theosophy who has acquired some knowledge concerning the Masters, the Adepts, should feel the highest respect for such lofty individuals. If we go on to contemplate so sublime a life as that of Buddha, we must agree that Buddha should be looked on as one of the highest Adepts. And we shall then be able to gain through our minds and feelings an inward relationship to such a person. Now because the Theosophist approaches the figure of Christ Jesus on the ground of this theosophical knowledge and feeling, he will naturally feel a certain need—and a very comprehensible need—to connect with his Christ Jesus the same concept he has formed of a Master, of an Adept, perhaps of Buddha; and he may be impelled to say: ‘Jesus of Nazareth must be thought of as a great Adept!’ This preconceived opinion would turn upside down any knowledge of the real nature of Christ. And it would be no more than a preconceived opinion only prejudice, although an understandable one. How shall someone who has won the deepest, most intimate relationship to the Christ not place the bearer of the Christ-Being in the same rank as the Master, the Adept, or the Buddha? Why should he not? This must seem to us quite comprehensible. Perhaps to such a person it would seem like a depreciation of Jesus of Nazareth if we were not to do so. But by applying this concept to Jesus of Nazareth we are led away from directing our thought according to the facts, at least as these facts have found their way to us through tradition. Anyone who examines without bias the traditional records—disregarding all opinions offered by Church Councils and Fathers and so on—will not fail to recognise one fact: Jesus of Nazareth cannot be called an Adept. Where in tradition do we find anything which allows us to apply to Jesus of Nazareth the concept of the Adept as we have it in theosophical teaching? In the first periods of Christianity one thing was emphasised: that Jesus of Nazareth was a man like any other, a weak man like any other. And those who uphold the saying, ‘Jesus was truly man’ understand most nearly who it was that came into the world. Thus if we pay proper heed to the tradition, no idea of ‘Adept’ is to be found there. And if you remember all that has been said in past lectures concerning the development of Jesus of Nazareth—the history of the Jesus-child in whom up to his twelfth year Zarathustra lived, and the history of the other Jesus-child in whom Zarathustra then lived up to his thirtieth year—you will certainly say: Here we have to do with a special man, a man for whose existence the world's history, the world's evolution, made the greatest preparations, evident from the fact that two human bodies were formed, and in one of them up to the twelfth year, and in the other from the twelfth to the thirtieth year, the Zarathustra-individuality dwelt. Since these two Jesus-figures were such significant individualities, Jesus of Nazareth certainly stands high; but not in the same way as an Adept does, for the Adept goes forward continuously from incarnation to incarnation. And apart from this: in the thirtieth year, when the Christ-Individuality enters into the body of Jesus of Nazareth, this very Jesus of Nazareth forsakes his body, and from the moment of the Baptism by John—even if we do not now speak of the Christ—we have to do with a human being who must be designated in the truest sense of the word as a ‘mere man’, save that he is the bearer of the Christ. But we must distinguish between the bearer of the Christ and the Christ Himself. Once the body which was to be the bearer of the Christ had been forsaken by the Zarathustra-individuality, there dwelt in it no human individuality who had attained any specially high development. The stage of development shown by Jesus of Nazareth sprang from the fact that the Zarathustra-individuality dwelt in him. As we know, however, this human nature was forsaken by the Zarathustra-individuality. Thus it was that this human nature, directly the Christ-Individuality had taken possession of it, brought against Him all that otherwise comes forth from human nature—the Tempter. That is why the Christ could go through the extremities of despair and sorrow, as shown to us in the happenings on the Mount of Olives. Anyone who leaves out of account these essential points cannot come to a real knowledge of the Being of the Christ. The Christ-bearer was truly man—not an Adept. Recognition of this fact will open for us a first glimpse into the whole nature of the events of Golgotha, the events of Palestine. If we were to look upon Christ Jesus simply as a high Adept, we should have to place Him in a line with other Adept-natures. Some people may perhaps tell us that we do not do this because from the very outset, owing to some preconceived idea, we want to place Christ Jesus beyond all other Adepts, as a still higher Adept. Those who might say this are not aware of what we have to impart as the results of occult research in our time. The question is not in the very least whether the prestige of other Adepts would be impaired. Within the world-conception to which we must adhere according to the occult results of the present time, we know just as well as others that there existed as a contemporary of Christ Jesus another significant individuality whom we regard as a true Adept. And unless we go into exact details, it is even difficult for us to distinguish inwardly this human being from Christ Jesus, for he really appears quite like Him. When, for instance, we hear that this contemporary of Christ Jesus was announced before his birth by a heavenly vision, it reminds us of the annunciation of the birth of Jesus, as told in the Gospels. When we hear that he was not designated merely as of human birth, but as a son of the Gods, this reminds us again of the beginning of the Gospels of Matthew and Luke. When we hear that the birth of this individuality took his mother by surprise, so that she was overwhelmed, we are reminded of the birth of Jesus of Nazareth, and of the events in Bethlehem, as told in the Gospels. When we hear that the individuality grew up and surprised all around him by his wise answers to the questions from the priests, it reminds us of the scene of the twelve-year-old Jesus in the Temple. When we are told that this individuality came to Rome and met there the funeral procession of a young girl, that the procession was brought to a halt and that he awakened the dead, we are reminded of an awakening from the dead in the Gospel of Luke. And if we wish to speak of miracles, numberless miracles are recorded in connection with this individuality, who was a contemporary of Christ Jesus. Indeed, the similarity goes so far that after the death of this individuality he is said to have appeared to men, as Christ Jesus appeared after His death to the disciples. And when from the Christian side all possible reasons are brought forward either to depreciate this being or to deny altogether his historical existence, this is no less ingenious than what is said against the historical existence of Christ Jesus Himself. The individuality in question is Apollonius of Tyana, and of him we speak as a really high Adept. If we now ask about the essential difference between the Christ Jesus event and the Apollonius event, we must be clear what the important point in the Apollonius event is. Apollonius of Tyana is an individuality who went through many incarnations; he won for himself high powers and reached a certain climax in his incarnation at the beginning of our era. Hence the individual we are considering is he who lived in the body of Apollonius of Tyana and had therein his earthly field of action. It is with him that we are concerned. Now we know that a human individuality takes part in the building up of his earthly body. Hence we must say: the body of this individuality was built up by him to a certain form for his own particular use. This we cannot say of Christ Jesus. In the thirtieth year of Jesus of Nazareth the Christ came into the physical body, etheric body, and astral body of Jesus; hence He had not himself built up this body from childhood. The relationship between the Christ-Individuality and this body is quite different from that between the Apollonius-individuality and his body. When in the spirit we turn our gaze to Apollonius of Tyana, we say: ‘It is the concern of this individuality, and his concern plays itself out as the life of Apollonius of Tyana.’ If we want to represent in a diagram a life-course of this kind, we can do it like this:  Let the continuous individuality be shown by the horizontal line; then we have in (a) a first incarnation, in (b) a life between death and a new birth, in (c) a second incarnation followed again by (d) a life between death and a new birth, then a third incarnation, (e) and so on. That which passes through all these incarnations—the human individuality—is like a thread of human life, independent of the sheaths of the astral body, etheric body and physical body, and also, between death and a new birth, independent of those parts of the etheric body and astral body which remain behind. Thus the life-thread is always separated from the external Cosmos. 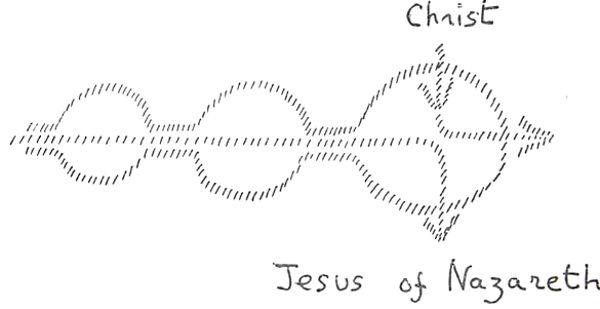 If we want to represent the nature of the Christ-life, we must draw it otherwise. When we consider the preceding incarnations of Jesus of Nazareth, the Christ-life certainly develops in a certain way. But when we draw the life-thread, we have to show that in the thirtieth year of the life of Jesus of Nazareth the individuality forsakes this body, so that from now onwards we have only the sheaths of physical body, etheric body and astral body. The forces which the individuality develops, however, are not in the external sheaths. They lie in the life-thread of the Ego, which goes from incarnation to incarnation. Thus the forces which belonged to the Zarathustra-individuality, and were present in the body of Jesus of Nazareth, preparing that body, pass out with the Zarathustra-individuality. Hence the sheaths which remain are a normal human organism, not in any sense the organism of an Adept, but the organism of a simple man, a weak man. And now the objective event occurs: whereas in other cases the life-thread simply goes farther, as in (a) and (b), it now turns along a side path (c); for through the Baptism by John in Jordan the Christ-Being entered into the threefold organism. In this organism the Christ-Being lived from the Baptism until the thirty-third year, until the Event of Golgotha, as we have often described. Whose concern, then, is the life of Christ Jesus from the thirtieth to the thirty-third year? It is not the concern of the individuality who went from incarnation to incarnation, but of that Individuality who from out of the Cosmos entered into the body of Jesus of Nazareth; the concern of an Individuality, a Being who was never before connected with the earth, who from out of the Universe connected Himself with a human body. In this sense the event which took place between the thirtieth and thirty-third years of the life of Christ Jesus, between the John-Baptism and the Mystery of Golgotha, are those of the Divine Being, Christ, not of a man. Hence this event was not a concern of the earth but a concern of the super-sensible worlds, for it had nothing to do with a man. As a sign of this—that it had to do with no man—the human being who had dwelt in this body up to the thirtieth year forsook it. These happenings have originally something to do with events that took place before such a life-thread as our human one had passed into a physical human organization. We must go back to the ancient Lemurian time, into the age wherein human individualities, coming from Divine heights, incarnated for the first time in earthly bodies; back to the event which is indicated for us in the Old Testament as the Temptation through the Serpent. This event is of a very remarkable kind. From its outcome all men suffer as long as they are subject to incarnation. For if this event had not happened, the whole evolution of mankind on the earth would have been different, and men would have passed in a much more perfect condition from incarnation to incarnation. Through this event, however, they become more closely entangled in matter, allegorically designated as the ‘Fall of Man’. But it was the Fall that first called man to his present individuality; so that, as he goes as an individuality from incarnation to incarnation, he is not responsible for the Fall. We know that the Luciferic spirits were responsible for the Fall. Hence we must say that before man became man in the earthly sense, there occurred the divine, super-sensible event by which a deeper entanglement in matter was laid upon him. Through this event man has indeed attained to the power of love and to freedom, but through it something was laid upon him that he could not lay upon himself by his own power. This becoming entangled in matter was not a human act, but a deed of the Gods, which happened before men could cooperate in their own fate. It is something which the Higher Powers of progressive evolution arranged with the Luciferic powers. We shall have to go into all these events and characterise them more exactly. Today we will place only the chief point before our minds. What happened at that time needed a counterpoise. The pre-human event—the Fall of Man—needed a counterpoise, but this again was a concern not of human beings, but of the Gods among themselves. And we shall see that this action had to take its course as deeply in matter as the first action had taken place above it. The God had to descend as deeply into matter as He had allowed man to sink into matter. Let this fact work upon you with its full weight; then you will understand that this incarnation of the Christ in Jesus of Nazareth was something that concerned Christ Himself. And what part was man called upon to take in it? First of all, as spectator, to see how the God compensates for the Fall, how He provides the compensating act. It would not have been possible to do this within the personality of an Adept, for an Adept is one who by his own efforts has worked his way out of the Fall. It was possible only in a personality who was truly man—who, as man, did not surpass other men. This personality had surpassed them before he was thirty years of age—but no longer. Through that which then took place, a Divine event was accomplished in the evolution of mankind, just as had been done at the beginning of human evolution in the Lemurian time. And men were partakers in a transaction which had taken place among Gods; men could look upon it, because the Gods had to make use of the world of the physical plane in order to let their transaction play itself out to the end. Hence it is much better to say: ‘Christ offered to the Gods the atonement which He could offer only in a physical human body’, than to use any other form of words. Man was a spectator of a Divine occasion. Through this atonement something had happened for human nature. Men simply experienced it in the course of their development. Thereby the third way was opened, besides the two already indicated. Men who have gone deeply into the nature of Christianity have often pointed out these three ways. From among the large number of those who could be named I will mention only two who have given eminent testimony to the fact that Christ—who from the twentieth century onwards will be seen through the more highly developed faculties—can be recognised, felt, experienced, through feelings which were not possible in the same form before the Event of Golgotha. There is, for example, a man who in his whole cast of mind can be looked upon as a sharp opponent of what we have characterised as Jesuitism: Blaise Pascal, a great figure in spiritual history, standing forth as one who has set aside all that had arisen to the detriment of the old Churches, but has also absorbed nothing of modern rationalism. As always with great minds, he really remained alone with his thoughts. But what is the fundamental feature of his thinking at the beginning of the modern period? When we look into the matter we see from the writings he left behind, particularly from his inspiring Pensées—a book accessible to anyone—how he perceived and felt what man must have become if the Christ-Event had not taken place in the world. In the secrecy of his soul, Pascal set himself the question: What would have become of man if no Christ had entered into human evolution? And he replied: We can feel that in his soul man encounters two dangers. One danger is that he should recognise God as identical with his own being: knowledge of God in knowledge of man. Whither does this lead? When it arises so that man recognises himself as God, it leads to pride, haughtiness, arrogance; and man destroys his best powers because he hardens them in haughtiness and pride. This is a knowledge of God that would always have been possible, even if no Christ had come, even if the Christ-Event had not worked as an impulse in the hearts of all men. Human beings would always have been able to recognize God, but they would have become proud through this consciousness in their own breasts. Or there might be human beings who hide themselves from the knowledge of God, who want to know nothing about God. Their gaze falls on something else; it falls on human powerlessness, on human misery, and then of necessity there follows human despair. That would have been the other danger, the danger of those who had put away from them the knowledge of God. Only these two ways, said Pascal, are possible: pride and arrogance, or despair. Then the Christ-Event entered into human evolution, and worked so that every man received a power which not only enabled him to experience God, but the very God who had become like unto men, who had lived with men. That is the sole remedy for pride: when we turn our gaze upon the God who bowed Himself to the Cross; when the soul looks to Christ bowing Himself to death on the Cross. And that, too, is the only healing for despair. For this is not a humility that makes a man weak, but a humility that gives healing strength which transcends despair. As the mediator between pride and despair, there dawns in the human soul the Helper, the Saviour, as Pascal understood Him. This can be felt by every man, even without clairvoyance. This is the preparation for the Christ who from the twentieth century onwards will be visible for all men; who as the Healer for pride and despair will arise in every human breast, but earlier could not be felt in the same way. The second witness I would summon from the long line of men who have this feeling, a feeling that every Christian can make his own, is one already mentioned in many other connections, Vladimir Soloviev. Soloviev also points to two powers in human nature, between which the personal Christ must stand as a mediator. There is a duality, he says, for which the human soul longs: immortality, and wisdom or moral perfection; but neither belongs to human nature from the start. Human nature shares the characteristic of all natures, and nature leads not to immortality, but to death. In beautiful meditations this great thinker of modern times works out how external science shows that death extends over everything. If we look at external nature, our knowledge replies, ‘Death is!’ But within us lives the longing for immortality. Why? Because of our longing for perfection. We have only to glance into the human soul to see that a longing for perfection lives in us. Just as truly, says Soloviev, as the red rose is endowed with red colour, so truly is the human soul endowed with the longing for perfection. But to strive after perfection without longing for immortality, he continues, is to give the lie to existence. It would be meaningless if the soul were to end with death, as all natural being ends. Yet all natural existence tells us, ‘Death is!’ Hence the human soul is under the necessity of going beyond natural existence and seeking the answer elsewhere. Proceeding from this thought, Soloviev says: Look at the natural scientists, what answer do they give when they wish to teach the connection of the human soul with nature? A mechanical natural order, they say, prevails and man is part of it. And what do the philosophers answer? That the spiritual, meaning an empty abstract thought-world which pervades all the facts of nature, is to be recognised philosophically. Neither of these statements is an answer for a man who is conscious of himself, and asks from out of his consciousness, ‘What is perfection?’ If he is conscious that he has a longing for perfection, a longing for the life of truth, if he asks what Power can satisfy this longing, there opens for him an outlook into a realm, the realm of Grace over and above nature, which at first stands before the soul as a riddle; and unless the answer to it can be found, the soul is constrained to regard itself as a falsehood. No philosophy, no natural science, can connect the realm of Grace with existence, for natural forces work mechanically, and thought-powers have only thought-reality. But what is it that is able, with full reality, to unite the soul with nature? He Who is the personal Christ working in the world. And only the living Christ, not one that is merely thought of, can give the answer. Anything that works merely in the soul leaves the soul alone, for the soul cannot of itself give birth to the kingdom of Grace. That which transcends nature, which like nature itself stands there as a real fact, the personal historic Christ—He it is who gives not an intellectual answer but a real answer. And now Soloviev comes to the most complete, the most fully spiritual answer that can be given at the end of the period now closing, before the doors open to that which has so often been intimated to you: the vision of Christ which will have its beginning in the twentieth century. In the light of these facts, a name can be given to the consciousness which Pascal and Soloviev have so memorably described: we can call it Faith. So, too, it has been named by others. With the concept of Faith we can come from two directions into a strange conflict regarding the human soul. Go through the evolution of the concept of Faith and see what the critics have said about it. Today men are so far advanced that they say Faith must be guided by knowledge, and a Faith not supported by knowledge must be put aside. Faith must be dethroned, as it were, and replaced by knowledge. In the Middle Ages the things of the Higher Worlds were apprehended by Faith, and Faith was held to be justified on its own account. The fundamental principle of Protestantism, also, is that Faith, alongside knowledge, is to be looked upon as justified. Faith is something which goes forth from the human soul, and alongside of it is the knowledge which ought to be common to all. It is interesting to see how Kant, whom many consider a great philosopher, did not get beyond this concept of Faith. His idea is that what a man should attain concerning such matters as God, immortality and so forth, ought to shine in from quite other regions, but only through a moral faith, not through knowledge. The highest development of the concept of Faith comes with Soloviev, who stands before the closed door as the most significant thinker of his time, pointing already to the modern world. For Soloviev knows a Faith quite different from all previous concepts of it. Whither has the prevailing concept of Faith led humanity? It has brought humanity to the atheistic, materialistic demand for mere knowledge of the external world, in line with Lutheran and Kantian ideas, or in the sense of the Monistic philosophy of the nineteenth century; to the demand for the knowledge which boasts of knowledge, and considers Faith as something that the human soul had framed for itself out of its necessary weakness up to a certain time in the past. The concept of Faith has finally come to this, because Faith was regarded as merely subjective. In the preceding centuries Faith had been demanded as a necessity. In the nineteenth century Faith is attacked just because it finds itself in opposition to the universally valid knowledge which should stem from the human soul. And then comes a philosopher who recognises and prizes the concept Faith in order to attain a relationship to Christ that had not previously been possible. He sees this Faith, in so far as it relates to Christ, as an act of necessity, of inner duty. For with Soloviev the question is not, ‘to believe or not to believe’; Faith is for him a necessity in itself. His view is that we have a duty to believe in Christ, for otherwise we paralyse ourselves and give the lie to our existence. As the crystal form emerges in a mineral substance, so does Faith arise in the human soul as something natural to itself. Hence the soul must say: ‘If I recognise the truth, and not a lie about myself, then in my own soul I must realise Faith. Faith is a duty laid upon me, but I cannot do otherwise than come to it through my own free act.’ And therein Soloviev sees the distinctive mark of the Christ-Deed, that Faith is both a necessity and at the same time a morally free act. It is as though it were said to the soul: You can do nothing else. If you do not wish to extinguish the self within you, you must acquire Faith for yourself; but it must be by your own free act! And, like Pascal, Soloviev brings that which the soul experiences, in order not to feel itself a lie, into connection with the historic Christ Jesus as He entered into human evolution through the events in Palestine. Because of this, Soloviev says: If Christ had not entered into human evolution, so that He has to be thought of as the historic Christ; if He had not brought it about that the soul perceives the inwardly free act as much as the lawful necessity of Faith, the human soul in our post-Christian times would feel itself bound to extinguish itself and to say, not ‘I am’, but ‘I am not’. That, according to this philosopher, would have been the course of evolution in post-Christian times: an inner consciousness would have permeated the human soul with the ‘I am not’.1 Directly the soul pulls itself together to the point of attributing real existence to itself, it cannot do otherwise than turn back to the historic Christ Jesus. Here we have, for exoteric thought also, a step forward along the path of Faith in establishing the third way. Through the message of the Gospels, a person not able to look into the spiritual world can come to recognition of Christ. Through that which the consciousness of the seer can impart to him, he can likewise come to a recognition of the Christ. But there was also a third way, the way of self-knowledge, and as the witnesses cited, together with thousands and thousands of other human beings, can testify from their own experience, it leads to a recognition that self-knowledge in post-Christian time is impossible without placing Christ Jesus by the side of man and a corresponding recognition that the soul must either deny itself, or, if it wills to affirm itself, it must at the same time affirm Christ Jesus. Why this was not so in pre-Christian times will be shown in the next few days.
|
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Experiencing the Christ Impulse, Jerome and the Gospel of St. Matthew
08 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Experiencing the Christ Impulse, Jerome and the Gospel of St. Matthew
08 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
We can perhaps sum up the outcome of the last lecture in the following way. From the Mystery of Golgotha until the coming of the epoch at whose portal we now stand, a man could attain by various exoteric means to an experience of the Christ-Impulse—an experience preceding any actual Initiation. One of these exoteric ways is through the Gospels, through the New Testament. The contents of the Gospels, when they are received into our souls and permitted to work upon us, can in fact bring about for each one of us an inner experience, and this inner experience may indeed be called the Christ-Experience. The second way for the exotericist was described as that of accepting what an esotericist—he who in a certain sense has been initiated—could make known from the spiritual worlds. By this way also the man who as yet was standing before the gate of Initiation could come to the Christ-Event, not through the traditional Gospels, but through continuous revelations from the spiritual worlds. Yesterday, too, we spoke of a third way, that of the inner deepening of heart and soul, and we pointed out that this way must arise in the soul from feelings; but with the proviso that if a man feels within him only the Divine spark, he may be driven to pride and arrogance. On the other hand, if he is not conscious of his connection with the Divine, he can be driven to despair. We have seen how in fact the swaying between despair on the one hand, and pride and arrogance on the other, if at the same time a man fixes his gaze upon the events in Palestine, can lead on to the birth of the Christ-Event within him. It was then pointed out that within the next 3,000 years, beginning from our own epoch, everything concerning the evolution of humanity will change. We also indicated the significant event which follows from the Mystery of Golgotha, but will be seen only in the super-sensible worlds. We pointed out that the capacities of human beings will be enhanced, and that, from our own epoch onwards, a sufficiently large number of persons will grow up able to look on the Christ. That which has hitherto had a justified place in the world as Faith will be replaced by what may be called the Vision of Christ. Now it will be our task to show further how from the usual way of experiencing Christ, as an experience of the heart, the path opens out quite naturally to what may be called the Christian Initiation. In the next few days we shall speak more exactly about the gradual building up of the Christian Initiation and we shall also need to characterise more closely the nature of the Christ-Event. Thus a picture of the Christian-Initiation, and of the Christ-Event, from the Baptism by John to the consummation of the Mystery of Golgotha, should come before our souls. If you keep this summary in mind, the following quite justified question may arise. What is the relation between external Christianity, Christian evolution, as it appears in world history, and the Christ-Event itself? To everyone who stands consciously in the present, who has gone through no special soul-experience of a mystical kind, or has perhaps the preliminary stages of esotericism behind him, it must appear strange that in every human being a quite definite kind of soul-experience should be so dependent upon an historic fact—the events in Palestine, on Golgotha—and that previously for these human souls something was not possible which afterwards, through these events, became possible, namely the inner Christ-Experience. The leaders of the first Christians, and also the first Christians generally, had a very distinct consciousness of these facts, and in preparation for the coming days it will be well to consider a little how these things appeared to their minds. One can easily believe—and later this belief turned more and more into an orthodox, very one-sided view—that human beings of the pre-Christian times were radically different from those of the post-Christian period. That this view is one-sided you can gather from the words of Augustine: ‘What we now call the Christian religion existed already among the ancients, and was not lacking in the earliest days of the human race. When Christ appeared in the flesh, the true religion, which was already in existence, received the name of Christianity.’ In the days of Augustine it was well known that there was not so radical a difference between pre-Christian and post-Christian times as orthodoxy maintained. Justin Martyr, too, makes a quite remarkable statement in his writings. Justin, who is recognised by the Church as one of the Fathers and a martyr, enlarges upon the relation of Socrates and Heraclitus to Christ. With a certain simple clarity he sees in Christ that which we set forth yesterday in the relation of Christ to Jesus of Nazareth, and he works out his idea of the Christ Being accordingly. In his Apologia he says, in the context of his own time, something we can repeat today in the same words: Christ, or the Logos, was incarnated in the man, Jesus of Nazareth. Justin then asks: Was the Logos not present in eminent personalities of pre-Christian times? Was man in pre-Christian times quite unacquainted with the Logos? To this question Justin Martyr answers No. Socrates and Heraclitus were also men in whom the Logos lived. They did not possess the Logos completely; but through the Christ-Event it became possible for a man to experience inwardly the Logos in its complete original form. From such a passage by a recognised Father of the Church we can gather, first, that the early Christians were acquainted with something which, after having been, as Augustine says, ‘always there’, had entered into the evolution of the earth in an enhanced form through the Mystery of Golgotha. Secondly, we have an answer from the earliest Christian centuries to the question we ourselves have raised today. Men such as Justin Martyr were still near to the Event of Golgotha, and they knew much more than we can about the nature of those who were but a few centuries removed from them, as Heraclitus and Socrates were. Justin held that in the time of Socrates, although such an eminent man could experience the Logos with himself, he could not experience it fully in its most intense form. And that is important. As testimony from those early times it indicates—if we look away from the event of Golgotha—how it was felt that between the centuries before and after Christ there was something whereby pre-Christian men could be distinguished from post-Christian. It can be shown from numerous other historical instances that men in earlier centuries consciously said, ‘Human nature has indeed changed; it has acquired another quality.’ Someone living in the third century after Christ, looking back to men who had lived in the third century before Christ, could say that although in their own way they could penetrate deeply into the secrets of existence, yet something that could happen in men living after the time of Christ could not have happened previously. The message of John the Baptist, ‘Change your outlook on the world, your idea of the world, for the times have become other than they were’—a statement confirmed by occult science—continued to be strongly and intensely felt. It must be grasped quite clearly that if we want to understand human evolution, we must give up the false idea that man has always been as he is today. For—apart from the fact that in the West no meaning could then be attached to the idea of reincarnation—tradition and occult science are at one in showing that in early times human beings really possessed something which now exists only in the subconscious, namely a certain power of clairvoyance; that later they descended from this height of clairvoyance, and that the lowest point in this descending evolution, when those forces developed which obscured the old clairvoyant powers, lies in the time of the Mystery of Golgotha. We know that in the material sphere a great quantity of fluid can be affected by the infusion of a very small quantity of a given substance. If you put a drop of some substance into a suitable fluid, it spreads through the fluid and colours the whole of it. In the material sphere, everyone understands this. But it is impossible to understand spiritual life if this principle is not understood in a spiritual sense. Our earth is not merely the material body we see with our eyes; it has a spiritual sheath. As we ourselves have an etheric body and an astral body, so the earth has such higher bodies. And just as a small quantity of substance spreads through a fluid, so that which rayed forth spiritually from the Act on Golgotha spread through the spiritual atmosphere of the earth, permeated it, and is still there. Something new has thus been imparted to our earth. And since souls do not merely live everywhere enclosed by matter, but are like drops in the sea of the earthly-spiritual, even so are human beings embedded in the spiritual atmosphere of our earth, which is permeated by the Christ-Impulse. That was not so before the Mystery of Golgotha, and it marks the great difference between pre-Christian and post-Christian life. If a person cannot imagine such a thing happening in spiritual life, he is not yet far enough advanced to grasp Christianity truly as a mystical fact, the full meaning of which can be recognised and acknowledged only in the spiritual world. Anyone who looks back over the unedifying disputes concerning the being and personality of Jesus of Nazareth, and the Being and Individuality of the Christ, will be able to feel everywhere in the gnostic and mystical views of the early Christian centuries that the most advanced of those who were concerned to extend Christianity stood with reverent awe before this mystical fact. Even though the words and phrases of Christian teachers are often abstruse, we can see clearly that these teachers stand in reverent awe before all that came to pass for the world's evolution through Christianity. Again and again they declare that weak human understanding, and the feeble powers of human feeling and perception, are inadequate to express truly the immense significance and depth of all that happened through the Mystery of Golgotha. A powerlessness to give real expression to the highest truths that man has to grope for—this is something that passes like a magic breath through the first Christian teachings. The reading of such writings is a good lesson for anyone, even in our times. We can learn thereby to exercise a certain modesty with regard to the highest truths. If we have the necessary humility and modesty towards things that are more easily recognised at the portal of a new Christian epoch than they were in the first Christian centuries, we can say: Certainly it is now possible to know more than could be known then, but no one who ventures to speak of the mysteries of Christianity should remain unconscious of the fact that what we are able to say today concerning the deepest truths of human evolution will in a comparatively short time be imperfect again. And because we wish to come gradually to a deeper characterisation of Christianity, we must pay special attention at this juncture to a person's inward attitude towards the spiritual world, if he accepts or wishes to spread abroad the truths which since the nineteenth and the beginning of the twentieth century can stream into us. Thus, even if we do not speak much about the concept of Grace, we must make great use of it in practice. Every occultist today clearly understands that this concept of Grace must belong to his inner practice of life in a quite special degree. What does this mean? It means that today investigations can be made concerning the deepest truths of Christianity, quite independently of the Gospels and of every tradition. Everything, however, which is connected with a certain thirst for knowledge, with a passion for gaining as quickly as possible a certain number of ideas, will lead, if not into complete error, quite certainly to a distortion of the truth. Anyone who says that since he is occultly prepared, he must provide an explanation, for example of the Pauline Epistles or the Gospel of Matthew, showing how their content is to be understood—anyone who set out to do that and believed he could complete it within a fixed time would quite certainly deceive himself. In a human way we can go deeply into these documents, but all that can be known about them cannot be made known today. For there is a golden saying which applies precisely to the occult investigator: ‘Have patience and wait, until you no longer wish to grasp the fruits by your own efforts, but they come to you.’ Many a person can approach the Pauline Epistles feeling himself ready to understand this or that, because in the spiritual world it meets his opened eyes. Should he wish at the same time to understand another passage, perhaps quite close to it, he may not be able to do so. A curbing of this thirst for knowledge is necessary today. One should rather say to oneself: ‘Grace has brought me to a certain number of truths. I will wait patiently until further truths flow to me.’ Today there is really more need for a certain passive attitude towards these truths than there was perhaps twenty years ago. This attitude is necessary because our minds must first completely ripen in order to allow truths to enter into us in their right form. This is a practical lesson regarding investigation of the spiritual worlds, especially in their relation to the Christ-Event. It is fundamentally wrong when people think they can grasp at that which ought to stream towards them in a certain passive way. For we must be conscious that we can be what we ought to be only in so far as we are judged worthy by the spiritual Powers to be this or that. And all that we can do by way of meditation, contemplation, and so forth, is really done only to open our eyes, not in order to seize the truths, but to let them come to us, for we may not run after them. Those who through this inward passivity have developed feelings of whole-hearted devotion in the sense described—and with no other feelings can one enter the spiritual world—are ready to understand the fact we have placed in the fore-front of our subject today: the fact that something like a drop of spiritual substance flowed from the Deed on Golgotha. In our time souls are ripe for this understanding. If it were not so we would have lacked many things that our modern period has brought forth. I need mention only one example: if the soul of Richard Wagner had not ripened in a certain passive way, if concerning the Mystery of Golgotha he had not in some sense surmised the flowing forth of that which came drop by drop into the spiritual atmosphere of earthly humanity, we could not have had his Parsifal. We can discern this in the passages where he refers to the significance of the Blood of Christ. In our day we can find many such minds which show how the spiritual substance which hovers in the atmosphere is grasped by the souls into which it penetrates. Spiritual Science is here because many more souls now have the possibility of being able, without realising it, to gather from the spiritual world the influences described above; but they need to have their difficulties lightened by an understanding of the spiritual world. In fact, no one whose heart is unripe enters into Spiritual Science; no one who has not more or less of a sincere longing to know something of what has just been mentioned. It may indeed be that some are impelled into our Movement by curiosity or the like, but those who come in with upright hearts feel the longing to be able to open their souls towards that which is making ready for the future epoch of human evolution which begins in our time. People need Spiritual Science today because their souls are becoming different from what they were a short time ago. Just as souls underwent a great change during the period in which the Event of Golgotha fell, so will they again experience a great change in this millennium and in the succeeding ones. The rise of our Movement is connected with the fact that souls, even if they are not clearly conscious of it, have an obscure feeling that something of the kind is going on in our time. For this reason it became necessary, on the ground of anthroposophical development, that a certain explanation of the foundations of the Gospels should be begun. And if you can convince yourselves through honest inner feeling that there is something true in the Christ Event, as it was described in the last lecture, you will find you can understand what has happened as regarding the explanation of the Gospels. You will understand that the anthroposophical interpretation of the Gospels differs radically from all previous interpretations. Anyone who takes up our printed lecture-cycles on the Gospels, or recalls them from memory, will see that everywhere a return has been made to true meanings, which can no longer be found simply by reading the present-day Gospel texts. From the existing translations, in fact, we can no longer reach that which the Gospels wish to indicate. To a certain extent, as they exist today, they are no longer fully of use. What, then, has been done towards reaching an explanation of the Christ event, and what must be done? To those who approach an understanding of the Christ-Event by the path of Spiritual Science, it must be clear that these Gospels were written by men who could look upon the Christ-Event spiritually with spiritual eyes. Hence they had no wish to write an external biography, but followed the old Initiation writings. (This connection is shown in greater detail in my book, Christianity as Mystical Fact.) They maintained that what had taken place in the depths of the Mysteries had, in the Christ-Event, occurred on the plane of history through the divine ordering of human evolution. What had happened on a small scale within the Mysteries to the candidates for Initiation was carried out by the Being we call the Christ on the great stage of world history, without the preparation that was necessary for human beings, and without the seclusion of the Mysteries. That which had previously been seen only by the pupil of the Mysteries, in their innermost sanctuary, was enacted before all eyes. This again is something for which the first Christian teachers felt a reverential awe. When they considered what the Gospels ought to be, there arose in the genuine Christian teachers a feeling of their own unworthiness, of their inability to grasp the true kernel and meaning of the Gospels. This fact is the cause of something else connected with the necessity of interpreting the Gospels as we do today in our Movement. If you have followed the explanations of the Gospels given here, you will have noticed that the traditional books of the Gospels are not, in the first place, taken as the basis, for what they say is regarded as something altogether unreliable. Instead, through the reading of the Akashic record, we are taken back to the spiritual writing as it is given out by those who can themselves read spiritually. Only when explanatory reference is made to some passage do we take into account the sentence as it stands in the printed books. We then examine whether, or how far, it agrees with the form that can be recovered from the Akashic record. The Gospels of Matthew, Mark, and Luke must be reconstructed in this way from the Akashic record. Only a comparison of the tradition with the original form can show how this or that passage must be read. Every tradition which rests only upon the printed text is bound to go astray and to fall into error. In the future the Gospels must be not only explained, but first reconstructed in their true original form. Then, when anyone examines what is there set forth, he will no longer be able to say that this may or may not be true, for where agreement is shown it will be clear why for us it is only the reading in the Akashic record which can guarantee the right text of the Gospels. And then the Gospels will again be evidence for the correctness of what stands written there. This can be shown in numberless passages. As an example let us take the following: When at the condemnation of Christ Jesus He was asked whether He was a king sent from God, He replied: ‘Thou sayest it!’ Now anyone who thinks straightforwardly, and does not wish to explain the Gospels according to the professorial methods of the present day, must admit that with this answer of Christ Jesus no clear sense can be connected in terms either of feeling or of reason. From the side of feeling, we must ask why Christ Jesus speaks so indefinitely that no one can recognise what He means by saying ‘Thou sayest it’. If He means ‘Thou art right’, there is no meaning m it, for the words of the interrogator are not a declaration but a question. How then can this be an answer full of meaning? Or, from the side of reason, how can we think that He whom we imagine to be possessed of all-comprehending wisdom should choose such a form for His answer? When, however, these words are given as they stand in the Akashic record, they have quite another sense. For in the Akashic record it is not ‘Thou sayest it’, but, ‘This, thou alone mayest give as answer’, which means, when we understand it rightly, ‘To thy question I should have to give an answer that no one may ever give with reference to himself: it can be given only by someone who stands opposite him. Whether the answer is true or not true, of that I cannot speak; the acknowledgement of this truth lies not with me but with thee. Thou must say it; then and then only would it have a meaning.’ Now you may say: ‘That may be true or may not be true.’ As an abstract judgment that would certainly be correct. But if we look at the whole scene and ask ourselves, ‘Can we understand it better when we take the version from the Akashic record?’, it will be apparent to everyone that this scene can be understood only in this way. We can say, too, that the last transcriber or translator of this passage did not understand it, because of its difficulty, and so wrote down something inaccurate. Anyone who knows how many things in the world are inexactly written down will not be surprised that here we have to do with an inaccurate version. Have we then no right, when a new epoch of humanity is beginning, to lead the Gospels back to their original form, which can be authenticated from the Akashic record? The whole thing comes out clearly—and this can be shown even from external history—if we consider in this connection the Matthew Gospel. The best that has been said about the origin of the Matthew Gospel may be read in the third volume of Blavatsky's Secret Doctrine, a work which must be understood if we are to judge and value it correctly. There was a certain Father of the Church, Jerome, who wrote towards the end of the fourth century. From what he writes we learn something that can be fully confirmed by occult research: the Gospel of Matthew was originally written in Hebrew. In the copy that Jerome had obtained, or, as we should perhaps say nowadays, in the edition he possessed, he had before him the original language of this Gospel, written in the Hebrew letters still in use, though its language was not the customary Hebrew of that time. Jerome's Bishop had given him the task of translating this version of the Matthew Gospel for his Christians. As a translator Jerome behaved in a most singular way. In the first place he thought it would be dangerous to translate this Gospel of Matthew as it was, because there were things in it which those who up to then had possessed it as their sacred writing wished to keep from the profane world. He thought that this Gospel, if it were translated complete, would cause disturbance rather than edification. So he omitted the things which, according to his own and the ecclesiastical views of that period, might have a disturbing effect, and replaced them by others. But we can learn still more from his writings, and this is the most serious aspect of the whole proceeding: Jerome knew that the Gospel of Matthew could be understood only by those who were initiated into certain secrets. He knew, too, that he was not one of those. In other words, he admitted that he did not understand this Gospel! Yet he translated it. Thus the Matthew Gospel lies before us today in the dress given to it by a man who did not understand it, but who became so accustomed to this version that he afterwards condemned as heresy anything asserted about this Gospel if it was not in accord with his own rendering. These are absolute facts. The next point of interest we must examine is the following. Why, in the very earliest days of Christianity, did those who held specially to the Gospel of Matthew communicate it only to such persons as were initiated into the secret meaning of certain things? It is possible to understand why this was so only if we are somewhat familiar with the character of Initiation. Such things have often been spoken of to you in one connection or another, and in particular you have heard that Initiation, when by means of it a man attains clairvoyant power, leads him to acquire knowledge of certain fundamental truths concerning the world. These fundamental truths are such that to the ordinary consciousness they at first appear absurd. All it can say about them is: That is a paradox. But there is more to it than that. If the highest truths, i.e. those accessible to an Initiate, were to become known to an unprepared individual—either if he were to conjecture them, which in a certain case might be possible, or if they were imparted to him when he was in an imperfect condition to receive them—then, even if they were the most elementary truths, they would be in the highest degree dangerous for him. Even if the purest, the highest, truth concerning the world were set before him, it would work destructively on him and on his surroundings. For this reason, anyone today who is in possession of the highest truths knows that it cannot be right merely to call someone to him and impart to him the highest mysteries of the world. The highest truths cannot be so imparted that a mouth simply pronounces them and an ear simply hears them. The way in which the highest truths are imparted is quite different. A person who wishes to become a pupil is slowly and gradually prepared, and this preparation takes place in such a way that the last conclusion, the imparting of the mystery, does not pass from mouth to ear. At a definite point of time the pupil is so conditioned by preparation that the secret, the mystery, rises up before him. It does not need to be pronounced by a mouth, nor does it need to be heard by an ear; it must be born in the soul through what has passed between teacher and pupil. There are no means of wringing from an Initiate the last things of the Mysteries, for no one can be compelled—by any means available on the physical plane—to betray with his mouth anything of the higher Mysteries. So it is with the higher Mysteries. And if that which should be born from the soul, as the higher Mysteries must be, were to be communicated to an unripe person through the mouth of another, it would be full of danger for this other person also. For he who had imparted the knowledge would be given completely into the power of his hearer for the rest of his incarnation. This, however, can never happen if the teacher simply prepares the pupil, and the pupil allows the truths to be born from out of his own soul. When we know this, we understand that the original Gospel of Matthew could not be imparted without further preparation because men were not ripe to receive what was in it. For if Jerome, a Father of the Church, was himself not ripe for what it contained, then certainly other men were not. Those who were originally in possession of these communications, the Ebionites, did not impart them because, if received by unripe persons, they would have been so distorted that they must have led to what Jerome meant when he said that they would serve not for edification but for destruction. Now Jerome understood this; yet he allowed himself to impart in a certain way the Gospel of Matthew to the world. Hence we must realise that this Gospel has been imparted in a certain way and has had a corresponding effect upon the world. Now if we look round and see what influence it has had, then in the light of occult truths we shall find many things comprehensible. Who, standing on the ground of occultism, would care to say that all the persecutions and so on in the Christian world could be connected with the principles of Christ Jesus? Who, standing on the ground of occultism, would not say that into external evolution there must have flowed something not in accordance with Christian evolution? In short, a great misunderstanding must here exist. We mentioned yesterday how on the ground of Christianity we should speak, for example, of Apollonius of Tyana; we set before us his greatness and significance and even called him an Adept. Yet when we go through early Christian literature we find everywhere accusations against Apollonius, as though everything he did, everything he accomplished, had been achieved only under the influence of the devil. There we have something that must be called misrepresentation, not only a misunderstanding of the personality and acts of Apollonius of Tyana. This is only one example among many. We understand it only when we see that the Gospels have been handed down in a way that must lead to misunderstandings, and that today, on the ground of occultism, our task is to go back to the true meaning of Christianity, concerning which the first teachers made many mistakes. It will then appear understandable that the next epoch of Christianity will be experienced differently from the earlier epochs. On the other hand, as already indicated, many things are stated here which can be said only because the listeners have taken part in the development of our Spiritual Science during the last few years, or are rightly disposed to enter into it: persons in whose souls there is a corresponding feeling and mood which will allow what is imparted to work upon them. Because souls have gone through at least one period of teaching, one incarnation between the Mystery of Golgotha and the present time, the Gospels can be spoken of today without fear that harm may result. Thus we have before us the singular fact that the Gospels had to be communicated, but that Christianity could be understood only in its most imperfect form. Hence the Gospels have been subject to a method of research which can no longer determine what is historical and what is not, so that finally everything is denied. In their original form they must enter our hearts and souls, and this must give rise to a new power whereby the findings that will now be presented to men can be accepted by those who have been able worthily to feel the events from the Baptism of John to the Event of Golgotha. An interpretation of the Christ-Event from the occult standpoint is thus a necessary preparation for the souls that in the near future are to experience something new, souls that are to look out on the world with new faculties. The old form of the Gospels will first receive its true value through our learning to read the Gospels with the aid of the Akashic record; through this alone will their full value be restored. In particular, the true significance of the Event of Golgotha can be fully demonstrated only by occult research. Only when the original significance of this Event is understood through occult research will the results it can have for human souls be recognised. Our task in the next few days will be to throw light, as far as is possible in one short lecture-cycle, on everything the human soul can experience under the influence of the Christ-Impulse, so that we may come to a deeper knowledge than was previously possible of all that took place in Palestine and on Golgotha. |
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Redemption of the Physical Body
09 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: Redemption of the Physical Body
09 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
If you recall that in the course of our lectures we have come to look upon the Christ-Impulse as the most profound event in human evolution, you will doubtless agree that some exertion of our powers of mind and spirit is needed to understand its full meaning and range of influence. Certainly in the widest circles we find the bad habit of saying that the highest things in the world must be comprehensible in the simplest terms. If what someone is constrained to say about the sources of existence appears complicated, people turn away from it because ‘the truth must be simple’. In the last resort it certainly is simple. But if at a certain stage we wish to learn to know the highest things, it is not hard to see that we must first clear the way to understanding them. And in order to enter into the full greatness, the full significance, of the Christ-Impulse, from a particular point of view, we must bring together many different matters. We need only turn to the Pauline Epistles and we shall soon see that Paul, who sought especially to bring within range of human minds the super-sensible nature of the Christ-Being, has drawn into the concept, the idea, of the Christ, the whole of human evolution, so to speak. If we let the Pauline Epistles work upon us, we have finally something which, through its extraordinary simplicity and through the deeply penetrating quality of the words and sentences, makes a most significant impression. But this is so only because Paul, through his own initiation, had worked his way up to that simplicity which is not the starting-point of what is true, but the consequence, the goal. If we wish to penetrate into what Paul was able finally to express in wonderful, monumental, simple words concerning the Christ-Being, we must come nearer to an understanding of human nature, for whose further development on Earth the Christ-Impulse came. Let us therefore consider what we already know concerning human nature, as shown through occult sight. We divide the life of Man into two parts: the period between birth and death, and the period which runs its course between death and a new birth. Let us first of all look at man in his physical body. We know that occult sight sees him as a four-fold being, but as a four-fold being in process of development. Occult sight sees the physical body, etheric body, astral body and the Ego. We know that in order to understand human evolution we must learn the occult truth that this Ego, of which we become aware in our feelings and perceptions when we simply look away from the external world and try to live within ourselves, goes on from incarnation to incarnation. But we also know that this Ego is, as it were, ensheathed—although ‘ensheathed’ is not a good expression, we can use it for the present—by three other members of human nature, the astral body, the etheric body and the physical body. Of the astral body we know that in a certain respect it is the companion of the Ego through the various incarnations. For though during the Kamaloka time much of the astral body must be shed, it remains as a kind of force-body, which holds together the moral, intellectual and aesthetic progress we have stored up during an incarnation. Whatever constitutes true progress is held together by the power of the astral body, is carried from one incarnation to another, and is linked, as it were, with the Ego, which passes as the fundamentally eternal in us from incarnation to incarnation. Further, we know that from the etheric body, too, very much is cast off immediately after death, but an extract of this etheric body remains with us, an extract we take with us from one incarnation to another. In the first days directly after death we have before us a kind of backward review, like a great tableau, of our life up to that time, and we take with us a concentrated etheric extract. The rest of the etheric body is given over into the general etheric world in one form or another, according to the development of the person concerned. When, however, we look at the fourth member of the human being, the physical body, it seems at first as if the physical body simply disappears into the physical world. One might say that this can be externally demonstrated, for to external sight the physical body is brought in one way or another to dissolution. The question, however, which everyone who occupies himself with Spiritual Science must put to himself is the following. Is not all that external physical cognition can tell us about the fate of our physical body perhaps only Maya? The answer does not lie very far away for anyone who has begun to understand Spiritual Science. When a man can say to himself, ‘All that is offered by sense-appearance is Maya, external illusion’, how can he think it really true that the physical body, delivered over to the grave or to the fire, disappears without trace, however crudely the appearance may obtrude on his senses? Perhaps, behind the external Maya, there lies something much deeper. Let us go further into this. You will realise that in order to understand the evolution of the Earth, we must know the earlier embodiments of our planet; we must study the Saturn, Sun, and Moon embodiments of the Earth. We know that the Earth has gone through its ‘incarnations’ just as every human being has done. Our physical body was prepared in the course of human evolution from the Saturn period of the Earth. With regard to the ancient Saturn time we cannot speak at all of etheric body, astral body, and Ego in the sense of the present day. But the germ for the physical body was already sown, was embodied, during the Saturn evolution. During the Sun period of the Earth this germ was transformed, and then in this germ, in its altered form, the etheric was embodied. During the Moon period of the Earth the physical body was again transformed, and in it, and at the same time in the etheric body, which also came forth in an altered form, the astral body was incorporated. During the Earth period the Ego was incorporated. And is it conceivable that the part of us which was embodied during the Saturn period, our physical body, simply decomposes or is burned up and disappears into the elements, after the most significant endeavours had been made by divine-spiritual Beings through millions and millions of years, during the Saturn, Sun and Moon periods, in order to produce this physical body? If this were true, we should have before us the very remarkable fact that through three planetary stages, Saturn, Sun, Moon, a whole host of divine Beings worked to produce a cosmic element, such as our physical body is, and that during the Earth period this cosmic element is destined to vanish every time a person dies. It would be a remarkable drama if Maya—and external observation knows nothing else—were right. So now we ask: Can Maya be right? At first it certainly seems as though occult knowledge declares Maya to be correct, for, strangely enough, occult knowledge seems in this case to harmonise with Maya. When we study the description given by spiritual knowledge of the development of man after death, we find that scarcely any notice is taken of the physical body. We are told that the physical body is thrown off, is given over to the elements of the Earth. We are told about the etheric body, the astral body, the Ego. The physical body is not further touched upon, and it seems as though the silence of spiritual knowledge were giving tacit assent to Maya-knowledge. So it seems, and in a certain way we are justified by Spiritual Science in speaking thus, for everything further must be left to a deeper grounding in Christology. For concerning what goes beyond Maya with regard to the physical body we cannot speak at all correctly unless the Christ-Impulse and everything connected with it has first been sufficiently explained. If we observe how this physical body was experienced at some definite moment in the past, we shall reach a quite remarkable result. Let us enquire into three kinds of folk-consciousness, three different forms of human consciousness concerning all that is connected with our physical body, during decisive periods in human evolution. We will enquire first of all among the Greeks. We know that the Greeks were that remarkable people who rose to their highest development in the fourth post-Atlantean epoch of civilisation. We know that this epoch began about the eighth century before our era, and ended in the thirteenth, fourteenth, and fifteenth centuries after the Event of Palestine. We can easily confirm what is said about this period from external information, traditions, and documents. The first dimly clear accounts concerning Greece hardly go back farther than the sixth or seventh century before our era, though legendary accounts come down from still earlier times. We know that the greatness of the historical period of Greece has its source in the preceding period, the third post-Atlantean epoch. The inspired utterances of Homer reach back into the period preceding the fourth post-Atlantean epoch; and Aeschylus, who lived so early that a number of his works have been lost, points back to the drama of the Mysteries, of which he offers us but an echo. The third post-Atlantean epoch extends into the Greek age, but in that age the fourth epoch comes to full expression. The wonderful Greek culture is the purest expression of the fourth post-Atlantean epoch. Now there falls upon our ear a remarkable saying from this land of Greece, a saying which permits us to see deeply into the soul of the man who felt himself truly a Greek, the saying of the hero (Achilles, in the Odyssey): ‘Better a beggar in the upper world, than a king in the land of shades.’ Here is a saying which betrays the deep susceptibility of the Greek soul. One might say that everything preserved to us of Greek classical beauty and classical greatness, of the gradual formation of the human ideal in the external world—all this resounds to us from that saying. Let us recall the wonderful training of the human body in Greek gymnastics and in the great Games, which are only caricatured in these days by persons who understand nothing of what Greece really was. Every period has its own ideal, and we must keep this in mind if we want to understand how this development of the external physical body, as it stands there in its own form on the physical plane, was a peculiar privilege of the Greek spirit. So, too, was the creation of human ideals in plastic art, the enhancement of the human form in sculpture. And if we then look at the character of the Greek consciousness, as it held sway in a Pericles, for example, when a man had a feeling for the universally human and yet could stand firmly on his own feet and feel like a lord and king in the domain of his city—when we let all this work upon us, then we must say that the real love of the Greek was for the human form as it stood there before him on the physical plane, and that aesthetics, too, were turned to account in the development of this form. Where this human form was so well loved and understood, one could give oneself up to the thought: ‘When that which gives to man this beautiful form on the physical plane is taken away from human nature, one cannot value the remainder as highly as the part destroyed by death.’ This supreme love for the external form led unavoidably to a pessimistic view of what remains of man when he has passed through the gate of death. And we can fully understand that the Greek soul, having looked with so great a love upon the outer form, felt sad when compelled to think: ‘This form is taken away from the human individuality. The human individuality lives on without this form!’ If for the moment one looks at it solely from the point of view of feeling, then we must say: We have in Greece that branch of the human race which most loved and valued the human body, and underwent the deepest sorrow when the body perished in death. Now let us consider another consciousness which developed about the same time, the Buddha consciousness, which had passed over from Buddha to his followers. There we have almost the opposite of the Greek attitude. We need only remember one thing: the kernel of the four great truths of Buddha is that human individuality is drawn by longing, by desire, into the existence where it is enshrouded by an external form. Into what kind of existence? Into an existence described in the Buddha-teaching as ‘Birth is sorrow, sickness is sorrow, old age is sorrow, death is sorrow!’ The underlying thought in this kernel of Buddhism is that by being enshrouded in an external bodily sheath, our individuality, which at birth comes down from divine-spiritual heights and returns to divine-spiritual heights at death, is exposed to the pain of existence, to the sorrow of existence. Only one way of salvation for men is expressed in the four great holy truths of Buddha: to become free from external existence, to throw off the external sheath. This means transforming the individuality so that it comes as soon as possible into a condition which will permit this throwing off. We note that the active feeling here is the reverse of the feeling dominant among the Greeks. Just as strongly as the Greek loved and valued the external bodily sheath, and felt the sadness of casting it aside, just as little did the adherent of Buddhism value it, regarding it as something to be cast aside as quickly as possible. And linked with this attitude was the struggle to overcome the craving for existence, an existence enshrouded by a bodily sheath. Let us go a little more deeply into these Buddhist thoughts. A kind of theoretical view meets us in Buddhism concerning the successive incarnations of man. It is not so much a question of what the individual thinks about the theory, as of what has penetrated into the consciousness of the adherents of Buddhism. I have often described this. I have said that we have perhaps no better opportunity of feeling what an adherent of Buddhism must have felt in regard to the continual incarnations of man, than by immersing ourselves in the traditional conversation between King Milinda and a Buddhist sage. ‘Thou hast come in thy carriage: then reflect, O great King,’ said the sage Nagasena, ‘that all thou hast in the carriage is nothing but the wheels, the shaft, the body of the carriage and the seat, and beyond these nothing else exists except a word which covers wheels, shaft, body of carriage, seat, and so on. Thus thou canst not speak of a special individuality of the carriage, but thou must clearly understand that “carriage” is an empty word if thou thinkest of anything else than its parts, its members.’ And another simile was chosen by Nagasena for King Milinda. ‘Consider the almond-fruit which grows on the tree, and reflect that out of another fruit a seed was taken and laid in the earth and has decayed; out of that seed the tree has grown, and the almond-fruit upon it. Canst thou say that the fruit on the tree has anything else in common other than name and external form with the fruit from which the seed was taken and laid in the earth, where it decayed?’ A man, Nagasena meant to say, has just as much in common with the man of his preceding incarnation as the almond-fruit on the tree has with the almond-fruit which, as seed, was laid in the earth. Anyone who believes that the form which stands before us as man, and is wafted away by death, is anything else than name and form, believes something as false as he who thinks that in the carriage—in the name ‘carriage’—something else is contained than the parts of the carriage—the wheels, shaft, and so on. From the preceding incarnation nothing of what man calls his Ego passes over into the new incarnation. That is important! And we must repeatedly emphasise that it is not to the point how this or that person chooses to interpret this or that saying of the Buddha, but how Buddhism worked in the consciousness of the people, what it gave to their souls. And what it gave to their souls is indeed expressed with intense clearness and significance in this parable of King Milinda and the Buddhist sage. Of what we call the ‘Ego’, and of which we say that it is first felt and perceived by man when he reflects upon his inner being, the Buddhist says that fundamentally it is something that flows into him, and belongs to Maya as much as everything else that does not go from incarnation to incarnation. I have elsewhere mentioned that if a Christian sage were to be compared with the Buddhist one, he would have spoken differently to King Milinda. The Buddhist said to the King: ‘Consider the carriage, wheels, shaft, and so on; they are parts of the carriage, and beyond these parts carriage is only a name and form. With the word carriage thou hast named nothing real in the carriage. If thou wilt speak of what is real, thou must name the parts.’ In the same case the Christian sage would have said: ‘O wise King Milinda, thou hast come in thy carriage; look at it! In it thou canst see only the wheels, the shaft, the body of the carriage and so on, but I ask thee now: Canst thou travel hither with the wheels only? Or with the shaft only, or with the seat only? Thou canst not travel hither on any of the separate parts. So far as they are parts they make the carriage, but on the parts thou canst not come hither. In order that the assembled parts can make the carriage, something else is necessary than their being merely parts. There must first be the quite definite thought of the carriage, for it is this that brings together wheels, shaft, and so on. And the thought of the carriage is something very necessary: thou canst indeed not see the thought, but thou must recognise it!’ The Christian sage would then turn to man and say: ‘Of the individual person thou canst see only the external body, the external acts, and the external soul-experiences; thou seest in man just as little of his Ego as in the name carriage thou seest its separate parts. Something quite different is established within the parts, namely that which enables thee to travel hither. So also in man: within all his parts something quite different is established, namely that which constitutes the Ego. The Ego is something real which as a super-sensible entity goes from one incarnation to another.’ How can we make a diagram of the Buddhist teaching of reincarnation, so that it will represent the corresponding Buddhist theory? With the circle we indicate a man between birth and death. The man dies. The time when he dies is marked by the point where the circle touches the line A–B. Now what remains of all that has been spellbound within his existence between birth and death? A summation of causes: the results of acts, of everything a man has  done, good or bad, beautiful or ugly, clever or stupid. All that remains over in this way works on as a set of causes, and so forms the causal nucleus (C) for the next incarnation. Round this causal nucleus new body-sheaths (D) are woven for the next incarnation. These body-sheaths go through new experiences, as did the body-sheaths around the earlier causal nucleus. From these experiences there remains again a causal nucleus (E). It includes experiences that have come into it from earlier incarnations, together with experiences from its last life. Hence it serves as the causal nucleus for the next incarnation, and so on. This means that what goes through the incarnations consists of nothing but causes and effects. There is no continuing Ego to connect the incarnations; nothing but causes and effects working over from one incarnation into the next. So when in this incarnation I call myself an ‘Ego’, this is not because the same Ego was there in the preceding incarnation. What I call my Ego is only a Maya of the present incarnation. Anyone who really knows Buddhism must picture it in this way, and he must clearly understand that what we call the Ego has no place in Buddhism. Now let us go on to what we know through anthroposophical cognition. How has man ever been able to develop his Ego? Through the Earth-evolution. Only in the course of the Earth-evolution has he reached the stage of developing his Ego. It was added to his physical body, etheric body and astral body on the Earth. Now, if we remember all we had to say concerning the evolutionary phases of man during the Saturn, Sun and Moon periods, we know that during the Moon period the human physical body had not yet acquired a quite definite form; it received this first on Earth. Hence we speak of the Earth-existence as the epoch in which the Spirits of Form first took part, and metamorphosed the physical body of man so that it has its present form. This forming of the human physical body was necessary if the Ego were to find a place in man. The physical Earth-body, set down on the physical Earth, provided the foundation for the dawn of the Ego as we know it. If we keep this in mind, what follows will no longer seem incomprehensible. With regard to the valuation of the Ego among the Greeks, we saw that for them it was expressed externally in the human form. Let us now recall that Buddhism, according to its knowledge, sets out to overcome and cast off as quickly as possible the external form of the human physical body. Can we then wonder that in Buddhism we find no value attached to anything connected with this bodily form? It is the essence of Buddhism to value the external form of the physical body as little as it values the external form which the Ego needs in order to come into being: indeed, all this is completely set aside. Buddhism lost the form of the Ego through the way in which it undervalued the physical body.  Thus we see how these two spiritual currents are polarically opposed: the Greek current, which set the highest value on the external form of the physical body as the external form of the Ego, and Buddhism, which requires that the external form of the physical body, with all craving after existence, shall be overcome as soon as possible, so that in its theory it has completely lost the Ego. Between these two opposite world-philosophies stands ancient Hebraism. Ancient Hebraism is far from thinking so poorly of the Ego as Buddhism does. In Buddhism, it is heresy to recognise a continuous Ego, going on from one incarnation to the next. But ancient Hebraism held very strongly to this so called heresy, and it would never have entered the mind of an adherent of that religion to suppose that his personal divine spark, with which he connected his concept of the Ego, is lost when he goes through the gate of death. If we want to make clear how the ancient Hebrew regarded the matter, we must say that he felt himself connected in his inner being with the Godhead, intimately connected; he knew that through the finest threads of his soul-life, as it were, he was dependent on the being of this Godhead. With regard to the concept of the Ego, the ancient Hebrew was quite different from the Buddhist, but in another respect he was also very different from the Greek. When we survey those ancient times as a whole, we find that the estimation of human personality, and hence that valuation of the external human form which was peculiar to the Greek, is not present in ancient Hebraism. For the Greek it would have been absolute nonsense to say: ‘Thou shalt not make to thyself any image of thy God.’ He would not have understood if someone had said to him: ‘Thou shalt not make to thyself any image of thy Zeus, or thy Apollo.’ For he felt that the highest thing was the external form, and that the highest tribute a man could offer to the Gods was to clothe them with this human form which he himself valued so much. Nothing would have seemed more absurd to him than the commandment: ‘Thou shalt make to thyself no image of God.’ As artist, the Greek gave his human form to his gods. He thought of himself as made in the likeness of the Divine, and he carried out his contests, his wrestling, his gymnastics and so on, in order to become a real copy of the God. But the ancient Hebrew had the commandment, ‘Thou shalt make to thyself no image of God!’ This was because he did not value the external form as the Greeks had done; he regarded it as unworthy in relation to the Divine. The ancient Hebrew was as far removed on the one side from the disciple of Buddhism, who would have much preferred to cast off the human form entirely on passing through death, as he was on the other side from the Greek. He was mindful of the fact that it was this form that gave expression to the commands, the laws, of the Divine Being, and he clearly understood that a ‘righteous man’ handed down through the following generations what he, as a righteous man, had gathered together. Not the extinguishing of the form, but the handing on of the form through the generations was what concerned the ancient Hebrew. His point of view stood midway between that of the Buddhist, who had lost the value of the Ego, and that of the Greek, who saw in the form of the body the very highest, and felt it as sorrowful when the bodily form had to disappear with death. So these three views stand over against one another. And for a closer understanding of ancient Hebraism we must make it clear that what the Hebrew valued as his Ego was in a certain sense also the Divine Ego. The God lived on in humanity, lived within man. In his union with the God, the Hebrew felt at the same time his own Ego, and felt it to be coincident with the Divine Ego. The Divine Ego sustained him; the Divine Ego was active within him. The Greek said: ‘I value my Ego so greatly that I look with horror on what will happen to it after death.’ The Buddhist said: ‘That which is the cause of the external form of man must fall away from man as soon as possible.’ The Hebrew said: ‘I am united with God; that is my fate, and as long as I am united with Him I bear my fate. I know nothing else than the identification of my Ego with the Divine Ego.’ This old Judaic mode of thought, standing midway between Greek thought and Buddhism, does not involve, as Greek thought does from the outset, a predisposition to tragedy in face of the phenomenon of death, but tragic feeling is indirectly present in it. It is truly Greek for the hero to say: ‘Better a beggar in the upper world’—i.e. with the human bodily form—‘than a king in the realm of shades’, but a Hebrew could not have said it without something more. For the Hebrew knows that when in death his bodily form falls away, he remains united with God. He cannot fall into a tragic mood simply through the fact of death. Still, the predisposition to tragedy is present indirectly in ancient Hebraism, and is expressed in the most wonderfully dramatic story ever written in ancient times, the story of Job. We see there how the Ego of Job feels bound up with his God, how it comes into conflict with his God, but differently from the way in which the Greek Ego comes into conflict. We are shown how misfortune after misfortune falls upon Job, although he is conscious that he is a righteous man and has done all he can to maintain the connection of his Ego with the Divine Ego. And while it seems that his existence is blessed and ought to be blessed, a tragic fate breaks over him. Job is not aware of any sin; he is conscious that he has acted as a righteous man must act towards his God. Word is brought to him that all his possessions have been destroyed, all his family slain. Then his external body, this divine form, is stricken with grievous disease. There he stands, the man who can consciously say to himself: “Through the inward connection I feel with my God, I have striven to be righteous before my God. My fate, decreed to me by this God, has placed me in the world. It is the acts of this God which have fallen so heavily upon me.” And his wife stands there beside him, and calls upon him in strange words to deny his God. These words are handed down correctly. They are one of the sayings which correspond exactly with the Akashic record: ‘Renounce thy God, since thou hast to suffer so much, since He has brought these sufferings upon thee, and die!’ What endless depth lies in these words: Lose the consciousness of the connection with thy God; then thou wilt fall out of the Divine connection, like a leaf from the tree, and thy God can no longer punish thee! But loss of the connection with God is at the same time death! For as long as the Ego feels itself connected with God, death cannot touch it. The Ego must first tear itself away from connection with God; then only can death touch it. According to outward appearance everything is against righteous Job; his wife sees his suffering and advises him to renounce God and die; his friends come and say: ‘You must have done this or that, for God never punishes a righteous man.’ But he is aware, as far as his personal consciousness is concerned, that he has done nothing unrighteous. Through the events he encounters in the external world he stands before an immense tragedy: the tragedy of not being able to understand human existence, of feeling himself bound up with God and not understanding how what he is experiencing can have its source in God. Let us think of all this lying with its full weight upon a human soul. Let us think of this soul breaking forth into the words which have come down to us from the traditional story of Job: ‘I know that my Redeemer liveth! I know that one day I shall again be clothed with my bones, with my skin, and that I shall look upon God with whom I am united.’ This consciousness of the indestructibility of the human individuality breaks forth from the soul of Job in spite of all the pain and suffering. So powerful is the consciousness of the Ego as the inner content of the ancient Hebrew belief! But here we meet with something in the highest degree remarkable. ‘I know that my Redeemer liveth,’ says Job, ‘I know that one day I shall again be covered with my skin, and that with mine eyes I shall behold the glory of my God.’ Job brings into connection with the Redeemer-thought the external body, skin and bones, eyes which see physically. Strange! Suddenly, in this consciousness that stands midway between Greek thought and Buddhism—this ancient Hebrew consciousness—we meet a consciousness of the significance of the physical bodily form in connection with the Redeemer-thought, which then becomes the foundation, the basis, for the Christ-thought. And when we take the answer of Job's wife, still more light falls on everything Job says. ‘Renounce thy God and die.’ This signifies that he who does not renounce his God does not die. That is implied in these words. But then, what does ‘die’ mean? To die means to throw off the physical body. External Maya seems to say that the physical body passes over into the elements of the earth, and, so to speak, disappears. Thus in the answer of Job's wife there lies the following: ‘Do what is necessary that thy physical body may disappear!’ It could not mean anything else, or the words of Job that follow would have no sense. For man can understand anything only if he can understand the means whereby God has placed us in the world; if, that is, he can understand the significance of the physical body. And Job himself says, for this too lies in his words: ‘O, I know full well that I need not do anything that would bring about the complete disappearance of my physical body, for that would be only an external appearance. There is a possibility that my body may be saved, because my Redeemer liveth. This I cannot express otherwise than in the words: My skin, my bones, will one day be recreated. With my eyes I shall behold the Glory of my God. I can lawfully keep my physical body, but for this I must have the consciousness that my Redeemer liveth.’ So in this story of Job there comes before us for the first time a connection between the Form of the physical body, which the Buddhist would strip off, which sadly the Greek sees pass away, and the Ego-consciousness. We meet for the first time with something like a prospect of deliverance for that which the host of Gods from ancient Saturn, Sun, and Moon, down to the Earth itself, have brought forth as the Form of the physical body. And if the Form is to be preserved, if we are to say of it that what has been given us of bones, skin and sense-organs is to have an outcome, then we must add: ‘I know that my Redeemer liveth.’ This is strange, someone might now say. Does it really follow from the story of Job that Christ awakens the dead and rescues the bodily Form which the Greeks believed would disappear? And is there perhaps anything in the story to indicate that for the general evolution of humanity it is not right, in the full sense of the word, that the external bodily Form should disappear completely? May it not be interwoven with the whole human evolutionary process? Has this connection a part to play in the future? Does it depend upon the Christ-Being? These questions are set before us. And they mean that we shall have to widen in a certain connection what we have so far learnt from Spiritual Science. We know that when we pass through the gate of death we retain at least the etheric body, but we strip off the physical body entirely; we see it delivered up to the elements. But its Form, which has been worked upon through millions and millions of years—is that lost in nothingness, or is it in some way retained? We will consider this question in the light of the explanations you have heard today, and tomorrow we will approach it by asking: How is the impulse given to human evolution by the Christ related to the significance of the external physical body—that body which throughout Earth evolution is consigned to the grave, the fire or the air, although the preservation of its Form is necessary for the future of mankind? |
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: St. John and St. Paul, First Adam and Second Adam
10 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: St. John and St. Paul, First Adam and Second Adam
10 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
By taking our start from what was said yesterday, we shall be able to come nearer to the fundamental questions of Christianity and to penetrate into its essential nature. We shall see that only by this means can we see into the heart of what the Christ-Impulse has become for the evolution of humanity and what it will become in the future. People are always insisting that the answers to the highest questions must not be complicated; the truth must be brought directly to each person in the simplest way. In support of this they argue, for example, that the Apostle John in his last years expressed the quintessence of Christianity in words of truth: ‘Children, love one another.’ No one, however, should conclude that a person who simply pronounces the words, ‘Children, love one another’, knows the essence of Christianity and of all truth for men. Before the Apostle John was entitled to pronounce these words, he had fulfilled various preconditions. We know it was at the end of a long life, in his ninety-fifth year, that he came to this utterance; only by then, in that particular incarnation, had he earned the right to use such words, Indeed, he stands there as a witness that this saying, if it came from any chance individual, would not have the power it had from him. For he had achieved something else, also. Although the critics dispute it, he was the author of the John Gospel, the Apocalypse, and the Epistles of John. Throughout his life he had not always said, ‘Children, love one another!’ He had written a work which belongs to the most difficult productions of man, the Apocalypse, and the John Gospel, which penetrates most intimately and deeply into the human soul. He had gained the right to pronounce such a saying only through a long life and through what he had accomplished. If anyone lives a life such as his, and does what he did, and then says, as he did, ‘Children, love one another!’ there are no grounds for objecting to it. We must, however, be quite clear that although some things can be compressed into a few words, so that these few words signify very much, the same few words may also say nothing. Many a person who pronounces a word of wisdom which in its proper setting would perhaps signify something very deep, believes that by merely uttering it he has said a very great deal. The writer of the Apocalypse and of the John Gospel, in his greatest age, could speak the words ‘Children, love one another!’ out of the essence of Christianity, but the same words from the mouth of another person may be a mere phrase. We must gather matters for the understanding of Christianity from far a field, so that we may apply them to the simplest truths of daily life. Yesterday we had to approach the question, so fateful for modern thought: What are we to make of the physical body in relation to the four-fold being of man? We shall see how the points brought out yesterday in looking at the differing views of the Greeks, the ancient Hebrews and the Buddhists will lead us further towards understanding the nature of Christianity. But if we are to learn more concerning the fate of the physical body, we must first take up a question which is central to the whole Christian cosmic conception; a question which lies at the very core of Christianity: How it is with the Resurrection of Christ? Must we not assume that for the understanding of Christianity it is essential to reach an understanding of the Resurrection? To see how important this is, we need only recall a passage in the first Epistle of Paul to the Corinthians, (I Corinthians 15:14–20):
We must remember that Christianity, in so far as it has extended over the world, began with Paul. And if we are disposed to take these important words seriously, we cannot simply pass them over by saying that we must leave the question of the Resurrection unexplained. For what is it that Paul says? That the whole of Christianity has no justification, and the whole Christian Faith no meaning, if the Resurrection is not true! That is what is said by Paul, with whom Christianity as a fact of history had its starting-point. And it means that anyone who is willing to give up the Resurrection must give up Christianity as Paul understood it. And now let us pass over almost two thousand years and ask people of the present day how, according to the requirements of modern culture, they stand with regard to the question of the Resurrection. I shall not now take note of those who simply deny Jesus entirely; it is naturally quite easy for them to be clear regarding the question of the Resurrection. If Jesus never lived, one need not trouble about the Resurrection. Leaving such persons aside, we will turn to those who about the middle or in the last third of the nineteenth century had accepted the current ideas of our time—the time in which we are still living. We will ask them what they think, in conformity with the whole culture of our day, concerning the question of the Resurrection. We will take a man who has gained great influence over the way of thinking of those who consider themselves best informed—David Friedrich Strauss. In his work on Reimarus, a thinker of the eighteenth century, we read: ‘The Resurrection of Jesus is really a shibboleth, concerning which not only the various conceptions of Christianity, but the various world-philosophies and stages of spiritual evolution, are at variance.’ And in a Swiss journal almost of the same date we read: ‘As soon as I can convince myself of the reality of the Resurrection of Christ, this absolute miracle, I tear down the modern conception of the world. This breach in what I believe to be the inviolable order of Nature would make an irreparable rent in my system, in my whole thought-world.’ Let us ask how many persons of our present time who, according to the modern standpoint, must and do subscribe to these words, would say, ‘If I were obliged to recognise the Resurrection as historical fact, I would tear down my whole system of thought, philosophical or otherwise.’ Let us ask how should the Resurrection, as historical fact, fit in with a modern man's outlook on the world. Let us recall something indicated in my first public lecture on this subject, that the Gospels are to be taken first and foremost as Initiation writings. The leading events depicted in the Gospels are fundamentally Initiation events—events which had formerly taken place within the secret places of the temples of the Mysteries, when this or that person, who had been deemed worthy, was initiated by the hierophants. Such a person, after he had been prepared for a long time, went through a kind of death and a kind of resurrection. He had also to go through certain situations in life which reappear for us in the Gospels—in the story of the Temptation, the story set on the Mount of Olives, and other similar ones. That is why the accounts of ancient Initiates, which do not aim to be biographies in the usual sense, show such resemblance to the Gospel stories of Christ Jesus. And when we read the history of the greatest initiates, of Apollonius of Tyana, or indeed even of Buddha or Zarathustra, or the life of Osiris or of Orpheus, it often seems that important characteristics of their lives are the same as those narrated of Christ Jesus in the Gospels. But although we must grant that we have to seek in the Initiation ceremonies of the old Mysteries for the prototypes of important events narrated in the Gospels, on the other hand we see quite clearly that the great teachings of the life of Christ Jesus are saturated throughout with individual details which are not intended as a mere repetition of Initiation ceremonies, but make it very plain that what is described is actual fact. Must we not say that we receive a remarkably factual impression when the following is pictured for us in the Gospel of John XX:1–10: Now on the first day of the week Mary Magdalene came to the tomb early, while it was still dark, and saw that the stone had been taken away from the tomb. So she ran, and went to Simon Peter and the other disciple, the one whom Jesus loved, and said to them, ‘They have taken the Lord out of the tomb, and we do not know where they have laid him.’ Peter then came out with the other disciple, and they went towards the tomb. They both ran, but the other disciple outran Peter and reached the tomb first; and stooping to look in, he saw the linen cloths lying there, but he did not go in. Then Simon Peter came, following him, and he went into the tomb; he saw the linen cloths lying, and the napkins, which had been on his head, not lying with the linen cloths but rolled up in a place by itself. Then the other disciple, who reached the tomb first, also went in, and he saw and believed; for as yet they did not know the scripture, that he must rise from the dead. Then the disciples went back to their homes. But Mary stood weeping outside the tomb, and as she wept she stooped to look into the tomb; and she saw two angels in white, sitting where the body of Jesus had lain, one at the head and one at the feet. They said to her, ‘Woman, why are you weeping?’ She said to them, ‘Because they have taken away my Lord, and I do not know where they have laid him.’ Saying this, she turned and saw Jesus standing, but she did not know that it was Jesus. Jesus said to her, ‘Woman, why are you weeping? Whom do you seek?’ Supposing him to be the gardener, she said to him, ‘Sir, if you have carried him away, tell me where you have laid him and I will take him away.’ Jesus said to her, ‘Mary.’ She turned and said to him in Hebrew, ‘Rabboni!’ (which means Teacher). Jesus said to her, ‘Do not hold me, for I have not yet ascended to the Father; but go to my brethren and say to them, I am ascending to my Father and your Father, to my God and your God.’ Here is a situation described in such detail that if we wish to picture it in imagination there is hardly anything lacking—when, for example, it is said that the one disciple runs faster than the other, or that the napkin which had covered the head was laid aside in another place, and so on. In every detail something is described which would have no meaning if it did not refer to a fact. Attention was drawn on a former occasion to one detail, that Mary did not recognise Christ Jesus, and we asked how was it possible that after three days anyone could fail to recognise in the same form a person previously known. Hence we had to note that Christ appeared to Mary in a changed form, or these words would have no meaning. Here, therefore, a distinction must be kept in mind. First, we have to understand the Resurrection as a translation into historic fact of the awakening that took place in the holy Mysteries of all times, only with the difference that he who in the Mysteries raised up the individual pupil was the hierophant; while the Gospels indicate that He who raised up Christ is the Being whom we designate as the Father—that the Father Himself raised up the Christ. Here we are shown that what had formerly been carried out on a small scale in the depths of the Mysteries was now and once for all enacted for humanity by Divine Spirits, and that the Being who is designated as the Father acted as hierophant in the raising to life of Christ Jesus. Thus we have here, enhanced to the highest degree, something which formerly had taken place on a small scale in the Mysteries. That is the first point. The other is that, interwoven with matters which carry us back to the Mysteries, there are descriptions so detailed that even today we can reconstruct from the Gospels the situations even to their minute particulars, as we have just seen in the passage read to you. But this passage includes one detail that calls for particular attention. There must be a meaning in the words, ‘For they did not as yet know the Scripture, that He must rise from the dead. Then the disciples went back to their homes.’ Let us ask: Of what had the disciples been able so far to convince themselves? It is described as clearly as anything can be that the linen wrappings are there, but the body is not there, is no longer in the grave. The disciples had not been able to convince themselves of anything else, and they understood nothing else when they now went home. Otherwise the words have no meaning. The more deeply you enter into the text, the more you must say that the disciples who were standing by the grave were convinced that the linen wrappings were there, but that the body was no longer in the grave. They went home with the thought: ‘Where has the body gone? Who has taken it out of the grave?’ And now, from the conviction that the body is not there, the Gospels lead us slowly to the events through which the disciples were finally convinced of the Resurrection. How were they convinced? Through the fact that, as the Gospels relate, Christ appeared to them by degrees, so that they could say, ‘He is there!’, and this went so far that Thomas, called the Doubter, could lay his finger in the prints of the wounds. In short, we can see from the Gospels that the disciples became convinced of the Resurrection through Christ having come to them after it as the Risen One. The proof for the disciples was that He was there. And if these disciples, who had gradually come to the conviction that Christ was alive, although He had died, had been asked what they actually believed, they would have said: ‘We have proofs that Christ lives.’ But they certainly would not have spoken as Paul spoke later, after he had gone through his experience on the road to Damascus. Anyone who allows the Gospels and the Pauline Epistles to work upon him will notice the deep underlying difference between the fundamental tone of the Gospels as regards the understanding of the Resurrection, and the Pauline conception of it. Paul, indeed, draws a parallel between his conviction of the Resurrection and that of the Gospels, for in saying ‘Christ is risen’, he indicates that Christ, after He had been crucified, appeared as a living Being to Cephas, to the Twelve, then to five hundred brethren at one time; and last of all to himself, Paul, as to one born out of due time, Christ had appeared from out of the fiery glory of the Spiritual. Christ had appeared to the disciples also; Paul refers to that, and the events lived through with the Risen One were the same for Paul as they had been for the disciples. But what Paul immediately joins to these, as the outcome for him of the event of Damascus, is his wonderful and easily comprehensible theory of the Being of Christ. What, from the event of Damascus onwards, was the Being of Christ for Paul? The Being of Christ was for him the ‘Second Adam’; and he immediately differentiates between the first Adam and the second Adam, the Christ. He calls the first Adam the progenitor of men on Earth because he sees in him the first man, from whom all other men are descended. For Paul, it is Adam who has bequeathed to human beings the body which they carry about with them as a physical body. All men have inherited their physical body from Adam. This is the body which meets us in external Maya, and is mortal; it is the body inherited from Adam, the corruptible body, the physical body of man that decays in death. With this body men are ‘clothed’. The second Adam, Christ, is regarded by Paul as possessing, in contrast to the first, the incorruptible, the immortal body. Paul then affirms that through Christian evolution men are gradually made ready to put on the second Adam in place of the first Adam; the incorruptible body of the second Adam, Christ, in place of the corruptible body of the first Adam. What Paul seems to require of all who call themselves true Christians is something that violates all the old conceptions of the world. As the first corruptible body is descended from Adam, so must the incorruptible body originate from the second Adam, from Christ. Every Christian could say: ‘Because I am descended from Adam, I have a corruptible body as Adam had; but in that I set myself in the right relationship to Christ, I receive from Him, the second Adam, an incorruptible body.’ For Paul, this view shines out directly from the experience of Damascus. We can perhaps express what Paul wishes to say by means of a simple diagram: 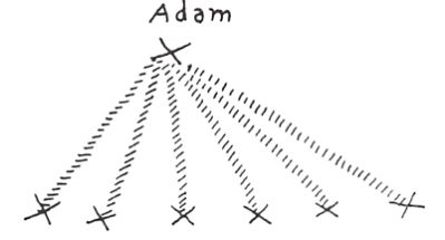 Here we have (x, x ...) a number of people at a given time. Paul would trace them all back to the first Adam, from whom they are all descended and by whom they are given the corruptible body. According to Paul's conception, however, something else is possible. Just as human beings can say, ‘We are related because we are all descended from the one progenitor, Adam,’ so they can say, ‘As without any action of ours, through the relationships of human generation lines can be traced back to Adam, so it is possible for us to cause something else to arise within us; something that could make us different beings. Just as the natural lines lead back to Adam, so it must be possible to represent lines which lead, not to the corruptible body of the fleshly Adam, but to the body that is incorruptible. Through our relationship to Christ, we can—according to the Pauline view—bear this incorruptible body within us, just as through Adam we bear the Corruptible body.’ 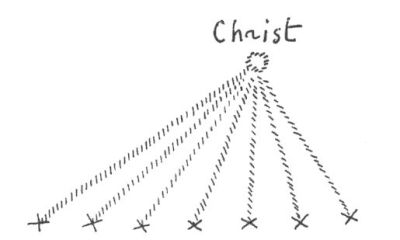 There is nothing more uncomfortable for the modern consciousness than this idea. For looking at the matter quite soberly, what does it demand from us? It demands something which, for modern thought, is really monstrous. Modern thought has long disputed whether all human beings are descended from one primeval human being, but it may be allowed that all are descended from a single human being who was the first on earth as regards physical consciousness. Paul, however, demands the following. He says: ‘If you desire to be a Christian in the true sense, you must conceive that within you something can arise which can live in you, and from which you can draw spiritual lines to a second Adam, to Christ, to that very Christ who on the third day rose from the grave, just as all men can trace lines back to the physical body of the first Adam.’ So Paul demands that all who call themselves Christians should cause something within them to arise; something leading to that entity which on the third day rose out of the grave in which the body of Christ Jesus had been laid. Anyone who does not grant this cannot come into any relationship with Paul; he cannot say he understands Paul. If man, as regards his corruptible body, is descended from the first Adam, then, by receiving the Being of Christ into his own being, he has the possibility of having a second ancestor. This ancestor, however, is He who, on the third day after His body had been laid in the earth, rose out of the grave. Let us clearly understand that Paul makes this demand, however displeasing it may be to modern thinkers. From this Pauline statement we will indeed approach the modern thinker; but one ought not to have any other opinion concerning that which meets us so clearly in the Pauline writings; one ought not to twist the meaning of something so clearly expressed by Paul. Certainly it is pleasant to interpret something allegorically and to say it was meant in such and such a way; but all these interpretations make no sense. If we wish to connect a meaning with the Pauline statement we are bound to say—even if modern consciousness regards it as superstition—that, according to Paul, Christ rose from the dead after three days. Let us go further. An assertion such as this, made by Paul after he had reached the summit of his initiation through the event of Damascus—the assertion concerning the second Adam and His rising from the grave—could be made only by someone whose whole mode of thought and outlook had been derived from Greek thought; by one whose roots were in Greece, even if he were also a Hebrew; by one who in a certain respect had brought all his Hebraism as an offering to the Greek mind. For, if we come closer to all this, what is it that Paul really declares? Looking with inner vision on that which the Greeks loved and valued, the external form of the human body, concerning which they had the tragic feeling that it comes to an end when the individual passes through the gate of death, Paul says: ‘With the Resurrection of Christ, the body has been raised in triumph from the grave.’ If we are to build a bridge between these two world-outlooks, we can best do it in the following way. The Greek hero said from his Greek feeling: ‘Better a beggar in the upper world than a king in the land of shades.’ He said this because he was convinced that the external form of the physical body, so highly cherished by the Greeks, was lost for ever in passing through the gate of death. On this same soil, out of which this tragic mood of intoxication with beauty had grown, Paul appeared, he who first proclaimed the Gospel to the Greeks. We do not deviate from his words if we translate them as follows: ‘That which you value above all, the human bodily form, will no longer be destroyed. Christ is risen as the first of those who are raised from the dead! The Form of the physical body is not lost, but is given back to humanity through the Resurrection of Christ!’ That which the Greeks valued most highly was given back to them with the Resurrection by Paul the Jew, who had been steeped in Greek culture. Only a Greek would so think and speak, but only someone who had become a Greek with all the preconceptions derived from his Jewish ancestry. Only a Jew who had become a Greek could speak in this way; no one else. But how can we approach these things from the standpoint of Spiritual Science? For we have reached the point of knowing that Paul demands something which thoroughly upsets the calculations of the modern thinker. Let us endeavour from the standpoint of Spiritual Science to get nearer to what Paul demands. Let us collect what we know from Spiritual Science, so as to bring an idea to meet Paul's statement. When we review the very simplest spiritual-scientific truths, we know that man consists of physical body, etheric body, astral body, and Ego. If now you ask someone who has studied Spiritual Science a little, but not very thoroughly, whether he knows the physical body of man, he will be sure to answer: ‘I know it quite well, for I see it when a person stands before me. The other members are supersensible, invisible, and one cannot see them, but the physical human body I know very well.’ Is it really the physical body of man that appears before our eyes when we meet a man with our ordinary vision? I ask you, who without clairvoyant vision has ever seen a physical human body? What is it that people have before them if they see only with physical eyes and physical understanding? A human body, but one consisting of physical body, etheric body, astral body, and Ego. And when a man stands before us, it is as an organised assembly of physical body, etheric body, astral body, and Ego. It would make as little sense to say that a physical body stood before us as it would if, when giving someone a glass of water, we were to say, ‘There is hydrogen in that glass.’ Water consists of hydrogen and oxygen, as man consists of physical, etheric and astral bodies, and Ego. Their assemblage is visible, just as water is, but the hydrogen and oxygen are not. Anyone who said he saw hydrogen in the water would be obviously mistaken. So is anyone who thinks he sees the physical body when he sees a man in the external world. What he normally sees is not a physical human body, but a four-membered being. He sees the physical body only in so far as it is permeated by the other members of the human being. And it is then changed in the same way that hydrogen is changed when it is permeated with oxygen in water. For hydrogen is a gas, and oxygen also; from the two gases united we get a liquid. Why should it be incomprehensible that the man who meets us in the physical world is quite unlike his single members, the physical, etheric and astral bodies and the Ego, just as water is quite unlike hydrogen? And so he is! Hence we cannot rely upon the Maya which appears to us as the physical body. We must think of the physical body in a quite different way if we want to draw nearer to its nature. The observation of the physical human body, in itself, belongs to the most difficult clairvoyant problems, the hardest of all! Suppose we allow the external world to perform on man the experiment which is similar to the disintegration of water into hydrogen and oxygen. In death this experiment is performed by the great world. We then see how man lays aside his physical body. But does he really lay aside his physical body? The question seems absurd, for what could be clearer than the apparent fact that at death man lays aside his physical body? But what is it that he lays aside? It is something no longer imbued with the physical body's most important possession during life: its Form. Directly after death the Form begins to withdraw from the dead body. We are left with decaying substances, no longer characterised by the Form. The body laid aside is composed of substances and elements which we can trace also in Nature; in the natural order of things they would not produce a human Form. Yet this Form belongs quite essentially to the physical human body. To ordinary clairvoyance it seems evident that at death a person simply discards these material substances, which are then handed over to decay or burning, and that nothing of the physical body is left. The clairvoyant then observes how after death the Ego, astral body, and etheric body remain connected during the person's review of his past life. Then he sees how the etheric body separates itself, how an extract of it remains, while the main portion dissolves in one way or another into the general cosmic ether. It does indeed seem that the person has laid aside his physical body, with its substances and forces, and then, after a few days, the etheric body. When the clairvoyant follows the person further through the Kamaloka period, he sees how an extract of the astral body goes with him during the life between death and a new birth, while the rest of the astral body is given over to the cosmic astrality. So we see that physical, etheric and astral bodies are laid aside, and that the physical body seems to drain away completely into materials and forces which, through decay or burning or some other form of dissolution, are returned to the elements. But the more clairvoyance is developed in our time, the clearer will it be that the physical forces and substances laid aside are not the whole physical body, for its complete configuration could never derive from them alone. To these substances and forces there belongs something else, best called the ‘Phantom’ of the man. This Phantom is the Form-shape which as a spiritual texture works up the physical substances and forces so that they fill out the Form which we encounter as the man on the physical plane. The sculptor can bring no statue into existence if he merely takes marble or something else, and strikes away wildly so that single pieces spring off just as the substance permits. As the sculptor must have the ‘thought’ which he impresses on the substance, so is a ‘thought’ related to the human body: not in the same way as the thought of the artist, for the material of the human body is not marble or plaster, but as a real thought, the Phantom, in the external world. Just as the thought of the plastic artist is stamped upon his material, so the Phantom of the physical body is stamped upon the substances of the earth which we see given over after death to the grave or the fire. The Phantom belongs to the physical body as its enduring part, a more important part than the external substances. The external substances are merely loaded into the network of the human Form, as one might load apples into a cart. You can see how important the Phantom is. The substances which fall asunder after death are essentially those we meet externally in nature. They are merely caught up by the human Form. If you think more deeply, can you believe that all the work of the great Divine Spirits though the Saturn, Sun, and Moon periods has merely created something which is handed over at death to the elements of the Earth? No—that which was developed during the Saturn, Sun, and Moon periods is not the physical body that is laid aside at death. It is the Phantom, the Form, of the physical body. We must be quite clear that to understand the physical body is not an easy thing. Above all, this understanding must not be sought for in the world of illusion, the world of Maya. We know that the foundation, the germ, of this Phantom of the physical body was laid down by the Thrones during the Saturn period; during the Sun period the Spirits of Wisdom worked further upon it, the Spirits of Movement during the Moon period, and the Spirits of Form during the Earth period. And it is only in this period that the physical body received the Phantom. We call these Spirits the Spirits of Form, because they really live in the Phantom of the physical body. So in order to understand the physical body, we must go back to the Phantom. If we look back to the beginning of our Earth-existence, we can say that the hosts from the ranks of the higher Hierarchies who had prepared the physical human body in its own proper Form during the Saturn, Sun and Moon periods, up to the Earth period, had from the outset placed this Phantom within the Earth evolution. In fact the Phantom, which cannot be seen with the physical eye, was what was first there of the physical body of man. It is a transparent body of force. What the physical eye sees are the physical substances which a person eats and takes into himself, and they fill out the invisible Phantom. If the physical eye looks upon a physical body, what it sees is the mineral part that fills the physical body, not the physical body itself. But how has this mineral part found its way into the Phantom of man's physical body? To answer this question, let us picture once more the genesis, the first ‘becoming’, of man on Earth. From Saturn, Sun and Moon there came over that network of forces which in its true form meets us as the invisible Phantom of the physical body. For a higher clairvoyance it appears as Phantom only when we look away from all the external substance that fills it out. This is the Phantom which stands at the starting-point of man's Earth existence, when he was invisible as a physical body. Let us suppose that to this Phantom of the physical body the etheric body is added; will the Phantom then become visible? Certainly not; for the etheric body is invisible for ordinary sight. Thus the physical body as Phantom, plus etheric body, is still invisible to external physical sense. And the astral body even more so; hence the combination of physical body as Phantom with the etheric and astral bodies is still invisible. And when the Ego is added it would certainly become perceptible inwardly, but not externally visible. Thus, as man came over out of the Saturn, Sun, and Moon periods, he was still visible only to a clairvoyant. How did he become visible? But for the occurrence described in the Bible symbolically, and factually in occult science, as the entry of the Lucifer influence, he would not have become visible. What happened through that influence? Read what is said in Occult Science. Out of that path of evolution in which his physical, etheric and astral bodies were still invisible, man was thrown down into denser matter, and was compelled under the influence of Lucifer to take this denser matter into himself. If the Lucifer force had not been introduced into our astral body and Ego, this dense materiality would not have become as visible as it has become. Hence we have to represent man as an invisible being, made visible in matter only through forces which entered into him under the influence of Lucifer. Through this influence external substances and forces are drawn into the domain of the Phantom and permeate it. As when we pour a coloured fluid into a transparent glass, so that the glass looks coloured, so we can imagine that the Lucifer influence poured forces into the human Phantom, with the result that man was adapted for taking in on Earth the requisite substances and forces which make his Form visible. Otherwise his physical body would have remained always invisible. The alchemists always insisted that the human body really consists of the same substance that constitutes the perfectly transparent, crystal-clear ‘Philosopher's Stone’. The physical body is itself entirely transparent, and it is the Lucifer forces in man which have brought him to a non-transparent state and placed him before us so that he is opaque and tangible. Hence you will understand that man has become a being who takes up external substances and forces of the Earth, which are given off again at death, only because Lucifer tempted him, and certain forces were poured into his astral body. It follows that because the Ego entered into connection with the physical, etheric and astral bodies under the influence of Lucifer, man became what he is on earth and otherwise would not have been—the bearer of a visible, earthly organism. Now let us suppose that at a certain point of time in life the Ego were to go out from a human organism, so that there stood before us physical, etheric and astral bodies, but not the Ego. This is what happened in the case of Jesus of Nazareth in the thirtieth year of His life. The human Ego then left this cohesion of physical, etheric and astral bodies. And into this cohesion the Christ-Being entered at the Baptism in Jordan. We now have the physical, etheric and astral bodies of a man, and the Christ-Being. The Christ-Being had now taken up His abode in a human organism, as otherwise the Ego would have done. What now differentiates this Christ Jesus from all other men on Earth? It is this: that all other men bear within them an Ego that once was overcome by Lucifer's temptation, but Jesus no longer bears an Ego within Him; instead, He bears the Christ-Being. So that from this time, beginning with the Baptism in Jordan, Jesus bears within Himself the residual effects that had come from Lucifer, but with no human Ego to allow any further Luciferic influences to enter his body. A physical body, an etheric body, and astral body—in which the residue of the earlier Luciferic influences was present, but into which no more Luciferic influence could enter—and the Christ-Being: thus was Christ Jesus constituted. Let us set before us exactly what the Christ is from the Baptism in Jordan until the Mystery of Golgotha: a physical body, an etheric body, and an astral body which makes this physical body together with the etheric body visible because it still contains the residue of the Luciferic influence. Because the Christ-Being had the astral body that Jesus of Nazareth had had from birth to his thirtieth year, the physical body was visible as the bearer of the Christ. Thus from the time of the Baptism in Jordan we have before us a physical body which as such would not be visible on the physical plane; an etheric body which as such would not have been perceptible; the astral body which makes the other two bodies visible and so makes the body of Jesus of Nazareth into a visible body; and, within this organism, the Christ-Being. We will inscribe firmly in our souls this four-fold nature of Christ Jesus, saying to ourselves: Every person who stands before us on the physical plane consists of physical body, etheric body, astral body, and Ego; and this Ego is such that it always works into the astral body up to the hour of death. The Christ-Jesus-Being, however, stands before us as One who had physical body, etheric body and astral body, but no human Ego, so that during the three years up to his death he was not subject to the influences that normally work upon human beings. The only influence came from the Christ-Being. |
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: The Mystery of Golgotha, Greek, Hebrew and Buddhist Thought
11 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| 131. From Jesus to Christ: The Mystery of Golgotha, Greek, Hebrew and Buddhist Thought
11 Oct 1911, Karlsruhe Translated by Harry Collison Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Yesterday we saw that in a certain respect the question of Christianity is the question of the Resurrection of Christ Jesus. In particular, we spoke of Paul, the proclaimer of Christianity, who from his knowledge of the essential nature of the Christ-Impulse recognised immediately that after and since the Event of Golgotha, Christ lives. We saw that for Paul, after his experience on the road to Damascus, a powerful, magnificent picture of human evolution opened up. From this point we went on to build up a picture of what Christ Jesus was directly after the Baptism in Jordan by John. Our next task will be to inquire into the course of events from the Baptism to the Mystery of Golgotha. But if we are to rise to an understanding of the Mystery of Golgotha, we must clear away certain hindrances. From all that has been said concerning the Gospels in the course of years, and also from what has been said already in these few lectures, you will have been able to gather that certain theosophical ideas, which in some quarters are esteemed sufficient, are really not sufficient to answer the question with which we are here concerned. Before everything else we must take quite seriously what has been said about the three streams of human thought: the stream which has its source in ancient Greece; the stream which comes down from ancient Hebraism, and lastly the stream which found expression in Gautama Buddha half a millennium before our era. We have seen that this Buddha stream, especially as it developed among his followers, is least of all adapted to an understanding of the Mystery of Golgotha. To the modern man, whose consciousness is filled with the intellectual culture of the present day, the stream of thought which finds expression in Buddhism certainly offers something very pleasant. Hardly any other form of thought suits so well the concepts of the present day, in so far as they prefer to remain silent in face of the greatest question that humanity has to grasp—the question of the Resurrection. For with this question the whole evolutionary history of mankind is connected. Now in Buddhist teaching the real being of the Ego, which in the true sense we can call the fourth member of human nature, has been lost. Certainly in these matters one can employ all kinds of interpretations, one can twist them in all sorts of ways, and plenty of people will find fault with what has been said here about Buddhist teaching, but that is not the point. For such things as I have quoted from the heart of Buddhism—for example, the conversation between King Milinda and the Buddhist sage Nagasena—testify clearly that the Ego-nature cannot be spoken of in Buddhism as we must speak of it. For a genuine follower of Buddhism it would indeed be heretical to speak of the Ego-nature as we must represent it. On this very account we must ourselves be clear regarding the Ego-nature. The human Ego, which in the case of every human being, even of the highest Adept, passes from incarnation to incarnation, is a term which (as we saw yesterday) can be applied to Jesus of Nazareth only from his birth to the Baptism in Jordan. After the baptism, we still have before us the physical body, the etheric body and the astral body of Jesus of Nazareth; but these external human sheaths are now indwelt not by a human Ego but by a Cosmic Being, the Christ-Being. Through years of endeavour we have tried by means of words to bring the Christ-Being nearer to our understanding. As soon as one comprehends the whole nature of Christ Jesus, it is obvious that for Him one must rule out any kind of physical or bodily reincarnation. The expression employed in my mystery drama, The Soul's Probation, about Christ having been present once only in a body of flesh, must be taken seriously and quite literally. Accordingly we must first concern ourselves with the being, the nature, of the ordinary human Ego. The Christ-Jesus-Being was completely independent of the human Ego from the Baptism to the Mystery of Golgotha. In earlier lectures it was shown that the evolution of the earth was preceded by a Saturn existence, a Sun existence and a Moon existence, and these three planetary embodiments were followed by the fourth, our Earth-embodiment. You know from those lectures that only during the Earth-existence, the fourth of the planetary conditions which were necessary to bring into existence our Earth with all its creatures, could the human Ego enter into connection with human nature. Just as in the Ancient Saturn period we speak of the beginning of the physical body, so in the period of the ancient Sun we speak of the first development of the etheric body, in the Moon period of the first development of the astral body, and only in the Earth period of the unfolding of the Ego. In this way the whole matter is brought cosmically and historically into view. But how is it when we look at the history of peoples? Through our former studies we know that although the seed-kernel of the Ego was laid down in human beings during the Lemurian time, the possibility of attaining to Ego-consciousness arose only towards the end of the Atlantean period, and that even then this Ego-consciousness was very dim and vague. Indeed, after the Atlantean time, through the various periods of civilisation which preceded the Mystery of Golgotha, the Ego-consciousness was still dull, dream-like, dim. But if you turn your attention to the development of the Hebrew people, it will be clear to you that here the Ego-consciousness found expression in a very unusual way. A kind of Folk-Ego lived in each single member of the ancient Hebrew people; in fact, every member of this people traced his Ego back to his ancestor in the flesh, to Abraham. The Ego of the ancient Hebrew people was still such that we can designate it as a Group-Ego, a Folk-Group-Ego. Consciousness had not yet penetrated as far as the separate individuality in each man. Why was this so? Each part of the four-membered human being we now regard as normal developed gradually in the course of the earth's evolution. It was only towards the end of the Atlantean Period that part of the etheric body, which until then had been external to the physical body, was gradually drawn into the body. This led towards the condition now recognised by clairvoyant consciousness as normal, namely that the physical body and the etheric body approximately coincide, and only then was it possible for man to develop his Ego-consciousness Let us slowly and gradually form an impression of the very peculiar way in which this Ego-consciousness meets us in man. I described yesterday how people speak of the Resurrection when they approach it with all the intellectual preconceptions of the present day. If, they say, ‘I had to assent to the real Pauline teaching about the Resurrection, I would have to tear up my whole conception of the world.’ That is what they say, these up-to-date people who have at their command all the resources of modern intellectualism. To people who speak thus, what must now be said will seem very strange. But is it not possible that such a person might reflect: ‘Yes, if I am to accept the Resurrection, I shall have to tear up all my intellectual concepts. But is that a reason for setting this question aside? Because we cannot understand the Resurrection and have to regard it as a miracle, must we assume that the only way out of this difficulty is to pass it by? Is there no other way?’ The other way is far from easy for a modern man, for he would have to admit to himself: ‘Perhaps it is not the fault of the Resurrection that I am unable to understand it. Perhaps the reason is that my intellect is unfitted to understand it.’ So little is this matter taken seriously in our day that we may say: Modern man is prevented by his pride—and just because he does not suspect that pride could come into it—from admitting that his intellect may be incompetent to fathom this question. For which is more reasonable: to say that I am setting aside something that shatters my intellectual outlook, or to admit that it may be beyond my understanding? Pride, however, forbids this admission. Of course, an anthroposophist must have trained himself to rise above this kind of pride. It should not be far from the heart of a true anthroposophist to say: ‘Perhaps my intellect is not competent to form an opinion about the Resurrection.’ But then he has to face another difficulty: he now has to answer the question why the human mind is not adapted to comprehend the greatest fact in human evolution. To answer this question we must go somewhat more closely into the real nature of human understanding. Here I should like to remind you of my Munich lectures, Wonders of the World, of which I will now give a resume as far as we need one. The elements that go to make up our soul life, our thoughts, feelings and perceptions, are not to be found in our present-day physical body; they penetrate only as far as the etheric body. In order to be clear about this, let us imagine our human nature, in so far as it consists of Ego, astral body and etheric body, enclosed in an ellipse:  We will take this diagram to represent schematically what we call our inward life and can experience in our souls; the diagram shows it coming to expression only in the streams and forces of the etheric body. If we experience a thought or perception, it has three lines of action in our soul-nature, as indicated in the following diagram.  Within our soul-nature there is nothing that is not present in this way. Now if a man's ordinary earthly consciousness were restricted to soul-experiences within the confines of the diagram, the experiences would occur, but he would not be conscious of them; they would remain unconscious. Our soul-experiences become conscious only through a process which an analogy will help us to understand. Imagine you are going in a certain direction, looking straight ahead. Your name is Smith. While you are going straight ahead you do not see Smith, yet you are he, you experience him, you are the person ‘Smith’. Imagine that someone puts a mirror in front of you. Now ‘Smith’ stands before you. What you had previously experienced you now see; it meets you in the mirror. So it is with the soul-life of man. A person has an experience, but he does not become conscious of it without a mirror. The mirror is the physical body. The perceptions, the thoughts, are thrown back by the sheath of the physical body. Thereby we become conscious of them. Hence in the diagram we can represent the physical body as the enclosing sheath. For us, as earthly men, the physical body is in truth a reflecting apparatus. If in this way you go more and more deeply into the nature of the human soul and of human consciousness, it will be impossible for you to consider as in any way dangerous or significant all those things which are brought forward again and again by materialism in opposition to the spiritual conception of the world. If through any damage to the reflecting apparatus, the soul-experience is no longer perceived by the consciousness, it is absolute nonsense to conclude that the soul-experience itself is bound up with the mirror. If someone breaks a mirror in which you see yourself, he does not break you. You merely disappear from your own field of vision. So it is when the reflecting apparatus for the soul-life, the brain, is disturbed. Perception ceases, but the soul-life itself, in so far as it goes on in the etheric body and the astral body, is not in the least disturbed. But have we not come to a point when we must consider closely the nature of the physical body? You will agree that without consciousness we could not be conscious of the Ego. In order to make Ego-consciousness our own during life on earth, our physical body, with its brain organisation, has to be a reflecting apparatus. We learn to become conscious of ourselves through our own mirrored reflection. If we had no mirror apparatus, we could not be conscious of our own selves. What is this mirror? We are shown by occult investigations, which reach back through reading the Akashic record as far as the origin of our earth existence, that in the beginning of Earth-existence this reflecting apparatus, the external physical body, came under Luciferic influence and was changed. Yesterday we saw what this physical body has become for earthly man. It has become something that falls to pieces when he passes through the gate of death. We have said that the body which falls to pieces is not the body which Divine Spirits had prepared through four planetary evolutions so that it should become the physical body on earth. What the Divine Spirits prepared, which yesterday we called the Phantom, belongs to the physical body as a form-body which permeates, and at the same time holds together, the material parts that are woven into our physical body. If no Luciferic influence had intervened, then, at the beginning of his Earth-existence, man would have received this Phantom in full strength together with his physical body. But into the human organisation, in so far as it consists of physical body, etheric body, and astral body, the Luciferic influence penetrated, and the consequence was the disorganisation of the Phantom of the physical body. As we shall see, this is symbolically expressed in the Bible as the Fall, together with the fact, related in the Old Testament, that death followed the Fall. Death was indeed the result of the disorganisation of the Phantom of the physical body. The outcome is that, when man goes through the gate of death, he has to see the dissolution of his physical body. This crumbling physical body, lacking the strength of the Phantom, is indeed borne by man from birth to death. The crumbling away goes on all the time, and the decomposition, the death of the physical body, is only the final stage of a continuous process. For if the disintegration of the body—preceded by the disorganisation of the Phantom—is not countered by processes of reconstruction, death finally ensues. If no Luciferic influence had come in, the destructive and reconstructive forces in the physical body would have remained in balance. But then everything in earthly human nature would have been different; there would, for example, have been no mind incapable of comprehending the Resurrection. For what kind of understanding is it that cannot grasp the Resurrection? It is the kind that is bound up with the decadence of the physical body, and is what it is because the individual has incurred, through the Luciferic influence, the progressive destruction of the Phantom of the physical body. In consequence the human understanding, the human intellect, has become so thin, so threadbare, that it cannot take in the great processes of cosmic evolution. It looks on them as miracles, or says it cannot comprehend them. If the Luciferic influence had not come, and the upbuilding forces in the human body had held the destructive forces in balance, then the human understanding, equipped with all that was intended for it, would have seen into the upbuilding forces, rather as one follows a laboratory experiment. But our understanding is now such that it remains on the surface of things and has no insight into the cosmic depths. Anyone, therefore, who wishes to characterise these conditions correctly must say: In the beginning of our Earth-existence, the physical body was prevented by the Luciferic influence from becoming what it should have become according to the will of the Powers who worked through Saturn, Sun and Moon. Instead, it took into itself a destructive process. Since the beginning of the Earth-existence man has lived in a physical body which is subject to destruction; a body which cannot adequately counter the destructive forces with upbuilding forces. So there is truth in something which appears to the modern man as such folly: that a hidden connection exists between what has come to pass through the working of Lucifer, and death. And now let us look at this working. What was the effect of this destruction of the real physical body? If we had the complete physical body, as was intended at the beginning of the earth-existence, our soul-powers would reflect themselves in quite another way: we should then know in truth what we are. As things are, we do not know what we are because the physical body is not given us in its completeness. We do certainly speak of the nature and being of the human Ego—but how far does man know the Ego? So problematic is the Ego that Buddhism can even deny that it goes from one incarnation to another. So problematic is it that Greece could fall into the tragic mood which found expression in those words of the Greek hero: ‘Better a beggar in the upper world than a king in the realm of shades.’ So it was that when a Greek saw the treasured physical body—the body shaped by the Phantom—given over to destruction, he felt a sadness in face of the darkening, the fading away, of the Ego, for he felt that it could exist only together with the Ego-consciousness. And when he saw the Form of the physical body falling into decadence, he shuddered at the thought that the Ego would grow dark and dim; this Ego which is reflected by the Form of the physical body. And when we follow human evolution from the beginning of the Earth to the Mystery of Golgotha, we find that the process we have just indicated shows itself in an ever-increasing degree. In earlier times, for example, no one would have preached the annihilation of the physical body in so radical a fashion as did Gautama Buddha. For such teaching to be given, it was necessary that the decadence of the physical body, its complete annulment as regards its Form, should have become more and more nearly complete, so that the human mind no longer had any idea that the entity which becomes conscious through the physical body—that is, through the Form—can pass over from one incarnation to another. The truth is that man, in the course of the Earth-evolution, lost the Form of the physical body, so that he no longer has what the Divine Beings had intended for him from the beginning of the Earth. This is something he must regain; but it had first to be imparted to him once more. And we cannot comprehend Christianity unless we understand that at the time when the Events of Palestine took place, the human race on earth had reached a stage where the decadence of the physical body was at its peak, and where, because of this, the whole evolution of humanity was threatened with the danger that the Ego-consciousness—the specific achievement of the earth-evolution—would be lost. If this process had continued unchanged, the destructive element would have penetrated ever more deeply into the human bodily organism, and men born after the time when the events of Palestine were due would have had to live with an ever-duller feeling of the Ego. Everything that depends on perfect reflection from the physical body would have become increasingly worn out. Then came the Mystery of Golgotha; it came as we have characterised it, and through it something happened which is so hard to grasp for an intellect bound up with the physical body only, a body in which the destructive forces preponderate. It came to pass that one man, who was the bearer of the Christ, had gone through such a death that after three days the specifically mortal part of the physical body had to disappear, and out of the grave there rose the body which is the force-bearer of the physical, material parts. The body that was really intended for man by the Rulers of Saturn, Sun, and Moon—the pure Phantom of the physical body with all the attributes of the physical body—this it was that rose out of the grave. So was given the possibility of that spiritual genealogy of which we have spoken. Let us think of the body of Christ that rose out of the grave. Just as from the body of Adam the bodies of earth-men are descended, in so far as these men have the body that crumbles away, even so are the spiritual bodies, the Phantoms for all men, descended from that which rose out of the grave. And it is possible to establish a relationship with Christ through which an earthly human being can bring into his otherwise decaying physical body this Phantom which rose out of the grave of Golgotha. It is possible for man to receive into his organism those forces which then rose from the grave, just as through his physical organism at the beginning of the earth evolution, as a consequence of the Luciferic forces, he received the organism of Adam. It is this that Paul wishes to say. Just as man, through his place in the stream of physical evolution, inherits the physical body in which the destruction of the Phantom, the force-bearer, is gradually taking place, so from the pure Phantom that rose out of the grave he can inherit what he has lost. He can inherit it, he can clothe himself with it, as he clothed himself with the first Adam; he can become one with it. Thereby he can go through a development by means of which he can climb upwards again, even as before the Mystery of Golgotha he had descended in evolution. In other words, that which had been taken from him through the Luciferic influence can be given back to him through its presence as the Risen Body of Christ. That is what Paul wishes to say. Now, just as it is very easy, from the standpoint of modern anatomy or physiology, to refute what has been said in this lecture—apparently to refute it—so is it very easy to raise another objection. Some such question as this might be asked: If indeed Paul really believed that a spiritual body had risen, what has this spiritual body which had risen out of the grave to do with what every man now bears in himself? This is not hard to understand: we need only consider the analogy offered by the coming into existence of a human individual. As physical human being he begins from a single cell; a physical body consists entirely of cells which are all children of the original cell; all cells which compose a human body are traceable to the original cell. Now imagine that, through what we may call a mystical Christological process, man acquires a body quite other than the one he has gradually acquired in his downward evolution. Then think of each of these new bodies as having an intimate connection with the pure Phantom that rose from the grave, somewhat as the human cells of the physical body are connected with the original cell. That is, we must think of the Phantom as multiplying itself, as does the cell which gives rise to the physical body. So, in the evolution which follows the Event of Golgotha, every man can inwardly acquire something which is spiritually descended from the Phantom which rose from the grave, just as—to echo Paul—the ordinary body which falls into dissolution is descended from Adam. Of course it is an insult to the human intellect, which thinks so arrogantly of itself at the present time, when one says that a process similar to the multiplication of the cell, which if need be can be seen, takes place in the invisible. This outcome of the Mystery of Golgotha, however, is an occult fact. To someone who contemplates evolution with occult sight it is apparent that the spiritual cell, the body which overcame death, the body of Christ Jesus, has risen from the grave and in the course of time imparts itself to anyone who enters into the corresponding relationship with the Christ. To anyone resolved to deny supersensible happenings altogether, this statement will naturally seem absurd. But to anyone who grants the supersensible, the event with which we are here concerned must be presented in the way described. The Phantom which rose from the grave communicates itself to those who make themselves fitted for it. This, then, is a fact that everyone who grants the supersensible can understand. If we can inscribe upon our souls what is in very truth the Pauline teaching, we come to regard the Mystery of Golgotha as a reality that took place and had to take place in the evolution of the earth; for it signifies literally the rescue of the human Ego. We have seen that if the process of evolution had continued along the path it had followed up to the time of the Events of Palestine, the Ego-consciousness could not have been developed; it would not only have failed to advance, but would have gone down ever further into darkness. But the path turned upwards, and will continue to ascend in proportion as men find their relation to the Christ-Being. Now we can understand Buddhism very well. About five hundred years before the Events of Palestine, a truth was proclaimed: ‘Everything that envelops a man as his physical body and makes him a being incarnated in the flesh—all this must be looked upon as worthless; it is fundamentally a left over from the past and must be cast off.’ Certainly up to that time conditions were such that humanity would have had to set its course towards this philosophy of life, if nothing else had intervened. But there came the Event of Golgotha, an Event which completely restored the lost principles of human evolution. In so far as man takes into himself the incorruptible body we spoke of yesterday, and have brought before our souls in closer detail today, if he clothes himself with this incorruptible body, he will become more and more clearly aware of his Ego-consciousness, and of that part of his nature which journeys on from one incarnation to another. That which came into the world with Christianity must therefore not be regarded merely as a new teaching—this must be specially emphasised—and not as a new theory, but as something real, something factual. Hence when people insist that everything Christ taught had been known previously, this signifies nothing for a real understanding of Christianity. The important thing is not what Christ taught, but what he gave: his Body. For the Body that rose from the grave of Golgotha had never before entered into human evolution. Never before had there been present on earth, through the death of a man, that which came to be present as the Risen Body of Christ Jesus. Previously, after men had passed through the gate of death, and had gone through the period between death and a new birth, they had brought to earth with them the defective Phantom, given over to deterioration. No one had ever caused a perfect Phantom to arise. Here we can refer to the Initiates and Adepts. They always had to receive initiation outside their physical bodies, by overcoming their physical bodies, but this overcoming never went as far as a resuscitation of the physical Phantom. No pre-Christian initiations went farther than the outermost limits of the physical body; they did not touch the forces of the physical body, except in so far as the inner organism impinges in a general way on the outer. No one, having gone through death, had ever overcome death as a human Phantom. Similar things had certainly occurred, but never this—that a man had gone through a complete human death and that the complete Phantom had then gained victory over death. Just as it is true that only this Phantom can give rise to a complete humanity in the course of human evolution, so is it true that this Phantom took its beginning from the grave of Golgotha. That is the important fact in Christian evolution. Hence the commentators are not at fault when they say again and again that the teaching of Christ Jesus has been transformed into a teaching about Christ Jesus. It had to be so. For the important thing is not what Christ Jesus taught, but what He gave to humanity. His Resurrection is the coming to birth of a new member of human nature—an incorruptible body. But for this to happen, this rescue of the human Phantom through death, two things were necessary. It was necessary, first, that the Being of Christ Jesus should be such as we have described it—constituted of physical body, etheric body, and astral body, and—instead of a human ego—the Christ-Being. Secondly, it was necessary that the Christ-Being should have resolved to descend into a human body, to incarnate in a human body of flesh. For if we are to contemplate the Christ-Being in the right light, we must seek Him in the time before the beginning of man on earth. The Christ-Being was of course existent at that time. He did not enter into the course of human evolution; He dwelt in the spiritual world. Humanity continued along its ever-decreasing path. At a point in time when the crisis of human evolution had been reached, the Christ-Being incorporated Himself in the body of a man. That is the greatest sacrifice that could have been brought to the earth-evolution by the Christ-Being. And the second thing we must learn to understand is wherein this sacrifice consisted. Yesterday we dealt with one part of the question concerning the nature of Christ, confining our study to the time after the Baptism by John in Jordan. We must now go on to ask: What is the significance of the fact that at the Baptism the Christ-Being descended into a body of flesh, and how did death come about in the Mystery of Golgotha? |

